Abstract
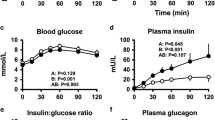
To determine whether the autonomic nervous system has a direct effect on GIP secretion, six normal subjects received a 4-hr intraduodenal perfusion of glucose (225 mg/min) and polyethylene glycol on four successive days. During the latter 2 hr, either normal saline, propranolol, phentolamine, or atropine were infused intravenously. Glucose absorption was calculated by measuring glucose and polyethylene glycol following luminal aspiration distal to the perfusion site. Basal and peak or nadir values in the saline study of plasma glucose, insulin, glucagon, and GIP were similar to the other three studies prior to autonomic blockade. During the latter 2 hr of the glucose perfusion, the plasma glucose and glucagon responses to saline did not differ from responses to the three blocking agents. Phentolamine but not atropine or propranolol resulted in a greater insulin response compared to saline (3247±762 vs 1348±388 μU/ml/120 min,P<0.01). GIP was not significantly affected by phentolamine (18,146±4574), propranolol (7585±5854), or atropine (15,797±6297) compared to saline (11,717±5204 pg/ml/120 min). Glucose absorption was unaffected by infusions of saline, phentolamine, and propranolol, but was increased following atropine infusion (5841±1120 vs 1044±808 mg/120 min,P<0.02). There appears to be no direct effect of the autonomic nervous system on glucose-induced secretion of GIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown JC, Otte SC: Gastrointestinal hormones and the control of insulin secretion. Diabetes 27:782, 1978
Creutzfeldt W: The incretin concept today. Diabetologia 16:75, 1979
Sirinek KR, O'Dorisio T, Levine BA, Cataland: Selective release of gastric inhibitory polypeptide by some actively transported structurally similar carbohydrates. Surg Forum 30:358, 1979
Sykes S, Mangan LM, English J, Marhs V: Evidence for preferential stimulation of gastric inhibitory polypeptide secretion in the rat by actively transported carbohydrates and their analogs. Endocrinology 85:201, 1980
Ross SA, Shaffer EA: The importance of triglyceride, hydrolysis for the release of gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Gastroenterology 80:108, 1981
Gayle RG, Ludewig RM: Effect of truncal, selective and highly selective vagotomy on fat-induced gastric inhibitory polypeptide release. Surg Forum 29:397, 1978
Williams RH, Beisbroeck J: Gastric inhibitory polypeptide and insulin secretion after infusion of acetylcholine, catecholamines, and gut hormones. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 163:39, 1980
Sirinek KR, Levine BA, O'Dorsio TM, Cataland S: Parasympathetic neuroendocrine regulation of GIP response to glucose. J Surg Res 30:343, 1981
Baumert JE, Cataland S, Tetirick CE, Pace WG, Mazzaferri EL: Effect of atropine on meal-stimulated gastrin and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) release. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 46:473, 1978
Sirinek KR, Cataland S, O'Dorisio TM, Mazzaferri EL, Crockett S, Pace WG: Sympathetic neuroendocrine regulation of gastric inhibitory polypeptide response to glucose. Surg Forum 28:377, 1977
Thomford NR, Sirinek KR, Crockett SE, Mazzaferri EL, Cataland S: Gastric inhibitory polypeptide response to oral glucose after vagotomy and pyloroplasty. Arch Surg 109:177, 1974
Levitt NS, Vinik AI, Child PT: Glucose-dependent insulinreleasing peptide in non-insulin-dependent maturity-onset diabetes: Effects of autonomic neuropathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 51:254, 1980
Taylor IL, Feldman M: Effect of cephalic-vagal stimulation on insulin, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, and pancreatic polypeptide release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 55:1114, 1982
Larrimer JN, Mazzaferri EL, Cataland S, Makhjian HS: Effect of atropine on glucose-stimulated gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Diabetes 27:638, 1978
Flaten O: The effect of adrenoreceptor blockade on the release of gastric inhibitory polypeptide after intraduodenal glucose in humans. Scand J Gastroenterol 16:641, 1981
Salera M, Ebert R, Giacomoni P, Pironi L, Venturi S, Miglioli M, Barbara L: Adrenergic modulation of gastric inhibitory polypeptide secretion in man. Regul Peptide, (Suppl)1: 597, 1980 (abstract)
Goyal RK: Neurology of the gut.In Gastrointestinal Disease, 2nd ed. M Sleisenger, JS Fordham (eds). Philadelphia, Saunders, 1978, p 156
Jacob H, Brandt LJ, Farkas P, Fishman W: Beta-adrenergic blockade and the gastrointestinal system. Am J Med 74:1042, 1983
McCullough AJ, Miller FJ, Service FJ, Go VLW: Effect of graded intraduodenal glucose infusions on the release and physiological action of gastric inhibitory polypeptide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 56:234, 1983
Rizza RA, Cryer P, Gerich JE: Role of glucagon, catecholamines and growth hormone in human glucose counterregulation. Effect of somatostatin and combined alpha- and beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma glucose recovery and glucose flux rates after insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest 64:62, 1979
Herbert V, Lau K-S, Gottlieb CW, Bleicher SJ: Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 25:1375, 1965
Faloona G, Unger R: Glucagon.In Methods of Hormone Radioimmunoassay. B Jaffe, H Behrman (eds). New York, Academic Press, 1974, p 317
Kuzio M, Dryburgh JR, Malloy KM, Brown JC: Radioimmunoassay for gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Gastroenterology 66:357, 1974
Brunner H, Northfield TC, Hofmann AF, Go VLW, Summetskill WHJ: Gastric emptying and secretion of bile acids, cholesterol and pancreatic enzyme during digestion. Duodenal perfusion studies in healthy subjects. Mayo Clin Proc 19:851, 1974
Beck B, Villaume C, Debry G: Clinical aspects of GIP secretion. Acta Diabetol Lat 19:1–11, 1982
Ross SA, Shaffer EA: Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) reverses the suppression of intestinal glucose absorption by somatostatin. Clin Res 30:38A, 1982
Gerich JE, Langlois M, Noacco C, Schneider V, Forsham PH: Adrenergic modulation of pancreatic glucagon secretion in man. J Clin Invest 53:1441, 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (AM 20973, AM 07198, RR 00585) and the Mayo Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, R.L., Go, V.L.W., McCullough, A.J. et al. Lack of a direct effect of the autonomic nervous system on glucose-stimulated gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) secretion in man. Digest Dis Sci 31, 929–935 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01303213
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01303213