Abstract
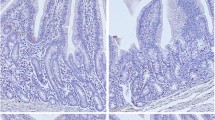
We studied the influences of cecal infusion ofNaCl, short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), and L-lactic acidat pH 5.0 or 7.0 for seven days on morphometric and cellkinetic parameters of the rat cecum. SCFA increased relative weight of the mucosa andsubmucosa, crypt size, and mitotic index in the cecum.L-Lactic acid stimulated mitosis only at pH 5.0. Cryptsize correlated positively to epithelial proliferative activity only when NaCl or L-lactic acid wasinfused. SCFA should have changed the balance betweenproduction and loss of the cecal epithelial cells. Theinfusate pH by itself had no effect, but modified the effects of SCFA and L-lactic acid indifferent ways. Crypt size correlated positively to thelogarithm of daily proton load of infusates. The aboveresults indicate that epithelial cell proliferation in the cecum is influenced by both SCFA andL-lactic acid, although differently, and by protonload.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cummings JH: Short chain fatty acid in the human colon. Gut 22:763–779, 1981
Macfarlane GT, Gibson GR: Microbiological aspects of the production of short-chain fatty acids in the large bowel. In Physiological and Clinical Aspects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. JH Cummings, JL Rombeau, T Sakata (eds). New York, Cambridge University Press, 1995, pp 87–105
von Engelhardt W: Absorption of short-chain fatty acids from the large intestine. In Physiological and Clinical Aspects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. JH Cummings, JL Rombeau, T Sakata (eds). New York, Cambridge University Press, 1995, pp 149–170
Roediger WEW: Role of anaerobic bacteria in the metabolic welfare of the colonic mucosa in man. Gut 21:793–798, 1980
Livesey G, Elia M: Short-chain fatty acids as an energy source in the colon: metabolism and clinical implications. In Physiological and Clinical Aspects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. JH Cummings, JL Rombeau, T Sakata (eds). New York, Cambridge University Press, 1995, pp 427–481
Sakata T: Stimulatory effect of short-chain fatty acids on epithelial cell proliferation in the rat intestine: a possible explanation for trophic effects of fermentable fibre, gut microbes and luminal trophic factors. Br J Nutr 58:95–103, 1987
Yajima T: Contractile effect of short-chain fatty acids on the isolated colon of the rat. J Physiol 368:667–678, 1985
Katoh K: Effects of short-chain fatty acids on exocrine and endocrine pancreatic secretion. In Physiological and Clinical Aspects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. JH Cummings, JL Rombeau, T Sakata (eds). New York, Cambridge University Press, 1995, pp 223–231
Mortensen FV, Nielsen H, Mulvany MJ, Hessov I: Short chain fatty acids dilate isolated human colonic arteries. Gut 31:1391–1394, 1990
Nordgaard-Andersen I, Clausen MR, Mortensen PB: Short-chain fatty acids, lactate, and ammonia in ileorectal and ileal pouch contents: A model of cecal fermentation. JPEN 17:324–331, 1993
Bustos D, Pons S, Pernas JC, Gonzalez H, Cardarni MI, Ogawa K, de Paula JA: Fecal lactate and short bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 39:2315–2319, 1994
Hove H, Mortensen PB: Colonic lactate metabolism and D-lactic acidosis. Dig Dis Sci 40:320–330, 1995
Vernia P, Gnaedinger A, Hauck W, Breuer RI: Organic anions and the diarrhea of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 33:1353–1358, 1988
Hoshi S: Nutritional and Physiological Effects of Indigestible Saccharides on Digestive Tract—Effect of the Fermentated Products in the Large Intestine on the Digestive Tract Size and Their Function in Rats. PhD Thesis, Tohoku University, Sendai, 1994
Umesaki Y, Yajima T, Mutai M: Effect of organic acid absorption on bicarbonate transport in rat colon. Pfluegers Arch 379:43–47, 1979
Saunders DR, Sillery J: Effect of lactate and H+ on structure and function of rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci 27:33–41, 1982
Argenzio RA, Meuten DJ: Short-chain acids induce reversible injury of porcine colon. Dig Dis Sci 36:1459–1468, 1991
Crump MH, Argenzio RA, Whipps SC: Effects of acetate on absorption of solute and water from pig colon. Am J Vet Res 41:1565–1568, 1980
Herschel DA, Argenzio RA, Southworth M, Stevens CE: Absorption of volatile fatty acid, Na, and H2O by the colon of the dog. Am J Vet Res 42:1118–1124, 1981
Sellin JH, Desoignie R, Burlingame S: Segmental differences in short-chain fatty acid transport in rabbit colon: Effect of pH and Na. J Membr Biol 136:147–158, 1993
Squires PE, Rumsey RDE, Edwards CA, Read NW: Effect of short-chain fatty acids on contractile activity and fluid flow in rat colon in vitro. Am J Physiol 262:G813–G817, 1992
Thornton JR: High colonic pH promotes colorectal cancer. Lancet 1:1081–1082, 1981
Pietroiusti A, Caprilli R, Giuliano M, Serrano S, Vita S: Faecal pH in colorectal cancer. Ital J Gastroenterol 17:88–91, 1985
Samelson SL, Nelson RL, Nyhus LM: Protective role of faecal pH in experimental colon carcinogenesis. J R Soc Med 78:230–233, 1985
Lupton JR, Coder DM, Jacobs LR: Influence of luminal pH on rat large bowel epithelial cell cycle. Am J Physiol 249:G382–G388, 1985
Narisawa T, Magadia NE, Weisburger JH, Wynder EL: Promoting effect of bile acid on colon carcinogenesis after intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst 53:1093–1097, 1974
Deschner EE, Cohen BI, Raicht RF: Acute and chronic effect of dietary cholic acid on colonic epithelial cell proliferation. Digestion 21:290–296, 1981
Visek WJ: Diet and cell growth modulation by ammonia. Am J Clin Nutr 31:S216–S220, 1978
Clinton SK, Bostwick DG, Olson LM, Mangian HJ, Visek WJ: Effects of ammonium acetate and sodium cholate on N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced colon carcinogenesis of rats. Cancer Res 48:3035–3039, 1988
Nishihira T, Komatsu T, Endo Y, Shineha R, Sagawa J, Nakano T, Hoshino A, Yoshida K, Mori S: New technology for continuous intravenous infusion via the central and portal veins in the rat. Tohoku J Exp Med 173:275–282, 1994
Hoshi S, Sakata T, Mikuni K, Hashimoto H, Kimura S: Galactosylsucrose and xylosylfructoside alter digestive tract size and concentrations of cecal organic acids in rats fed diets containing cholesterol and cholic acid. J Nutr 124:52–60, 1994
Hayashi M: Determination of organic acids in foods by HPLC with post-column pH buffered electroconductivity detection. Shimazu Hyoron 49:59–64, 1992
Remesy C, Demigne C: Change in availability of glucogenic and ketogenic substrates and liver metabolism in fed or starved rat. Ann Nutr Metab 27:57–70, 1983
Sakata T: Effects of indigestible dietary bulk and short chain fatty acids on the tissue weight and epitherial cell proliferation rate of the digestive tract in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 32:355–362, 1986
Kissmeyer-Nielsen P, Mortensen FV, Laurberg S, Hessov I: Transmural tropic effect of short chain fatty acid infusions on atrophic, defunctioned rat colon. Dis Colon Rectum 38:946–951, 1995
Kripke SA, Fox AD, Berman JM, Settle RG, Rombeau JL: Stimulation of intestinal mucosal growth with intracolonic infusion of short-chain fatty acids. JPEN 13:109–116, 1989
Lupton JR, Kurtz PP: Relationship of colonic luminal short-chain fatty acids and pH to in vivo cell proliferation in rats. J Nutr 123:1522–1530, 1993
Zhang J, Lupton JR: Dietary fibers stimulate colonic cell proliferation by different mechanisms at different sites. Nutr Cancer 22:267–276, 1994
Bartram HP, Scheppach W, Schmid H, Hofmann A, Dusel G, Richter F, Richter A, Kasper H: Proliferation of human colonic mucosa as an intermediate biomarker of carcinogenesis: effects of butyrate, deoxycholate, calcium, ammonia, and pH. Cancer Res 53:3283–3288, 1993
Kashtan H, Gregoire RC, Bruce WR, Hay K, Stern HS: Effects of sodium sulfate on fecal pH and proliferation of colonic mucosa in patients at high risk for colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:950–952, 1990
Fleming SE, Fitch MD, de Vries S: The influence of dietary fiber on proliferation of intestinal mucosal cells in miniature swine may not be mediated primarily by fermentation. J Nutr 122:906–916, 1992
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichikawa, H., Sakata, T. Effect of L-Lactic Acid, Short-Chain Fatty Acids, and pH in Cecal Infusate on Morphometric and Cell Kinetic Parameters of Rat Cecum. Dig Dis Sci 42, 1598–1610 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018884625737
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018884625737