Abstract
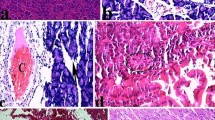
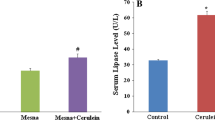
Since oxygen free radicals and lipidperoxidation have been implicated in the pathogenesis ofan early stage of acute pancreatitis, we examinedwhether melatonin, a recently discovered free-radicalscavenger, could attenuate pancreatic injury inSprague-Dawley rats with cerulein-induced pancreatitis.Acute pancreatitis was induced by four intraperitonealinjections of cerulein (50 μg/kg body wt) given at1-hr intervals. Thirty minutes after the lastcerulein injection, the rats were killed and the degreeof pancreatic edema, the level of lipid peroxidation inthe pancreas, and serum amylase activity were increased significantly. Pretreatment with melatonin (10or 50 mg/kg body wt) 30 min before each ceruleininjection resulted in a significant reduction inpancreatic edema and the levels of lipid peroxidation.Serum amylase activity, however, was notsignificantly influenced by either dose of melatonin.Moreover, we found that cerulein administration wasassociated with stomach edema as well as high levels oflipid peroxidation in the stomach and smallintestine, which were also reduced by melatonin.Melatonin's protective effects in cerulein-treated ratspresumably relate to its radical scavenging ability andto other antioxidative processes induced bymelatonin.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sanfey H, Bulkley GB, Cameron JL: The pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis: The source and role of oxyge n-derived free radicals in three different experimental models. Ann Surg 201:633-639, 1985
Guice KS, Miller DE, Oldham KT, Townsend CM, Thompson JC: Superoxide dismutase and catalase: A possible role in established pancreatitis. Am J Surg 151:163-169, 1986
Halliwell B: Reactive oxygen species in living systems: Source, biochemistry and role in human disease. Am J Med 91( suppl3C): 14-22, 1991
Sies H: Oxidative stress: From basic research to clinical application. Am J Med 91( suppl 3C):31-38, 1991
Slater TF: Free radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem J 222:1-15, 1984
McCord JM: Oxygen-derived free radical in post ischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312:159-164, 1985
Dabrowski A, Gabryelewicz A, Wereszczynska U, Chyczewski L: Oxyge n-derived free radicals in cerulein induced acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 23:1245-1249, 1988
Dabrowski A, Chwiecko M: Oxygen radicals mediate depletion of pancreatic sulfhydryl compounds in rats with cerulein induced acute pancreatitis. Digestion 47:15-19, 1990
Schoenberg MH, Buchler M, Schadlich H, Younes M, Bultmann B, Beger HG: Involvement of oxygen radicals and phospholipase A2 in acute pancreatitis of the rats. Klin Wochenschr 67:166-171, 1989
Schoenberg MH, Buchler M, Gaspar M, Stinner A, Younes M, Melzner I, Bultman B, Beger HG: Oxygen free radicals in acute pancreatitis in rats. Gut 31:1138-1143, 1990
Nonaka A, Manbe T, Kyogoku T, Tamura K, Tobe T: Changes in lipid peroxide and oxygen radical scavengers in cerulein induced acute pancreatitis. Digestion 47:130-137, 1990
Reiter RJ, Tang L, Garcia JJ, Munoz-Hoyos A: Pharmacological actions of melatonin in oxygen radical pathophysiology. Life Sci 60:2255-2271, 1997
Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Sewerynek E, Poeggeler B, Barlow-Walden LR, Chuang JI, Ortiz GG, Acuna-Castroviejo D: A review of the evidence supporting melatonin's role as an antioxidant. J Pineal Res 18:1-11, 1995
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Kim SJ, Qi W: Melatoninas a pharmacological agent against oxidative damage to lipids and DNA. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 41:229-236, 1998
Tan D-X, Chen L-D, Poeggeler B, Manchester LJ, Reiter RJ: Melatonin: A potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocrine J 1:57-60, 1993
Matsuzek Z, Reszka K, Chignell CF: Reaction of melatonin and related indoles with hydroxyl radical: EPR and spin trapping inve stigations. Free Rad Biol Med 23:367-372, 1997
Stasica P, Ulanski P, Rosiak JM: Melatonin as a hydroxyl radical scavenger. J Pineal Res 25:65-66, 1998
Pieri C, Moroni F, Marra M, Marcheselli F, Recchioni R: Melatonin as an antioxidant. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 20:159-165, 1995
Cagnoli CM, Atabay C, Kharlamov E, Manev H: Melatonin protects neurons from singlet oxygen-induced apoptosis. J Pineal Res 18:222-228, 1995
King M, Scaiano JC: The excited states of melatonin. Photochem Photobiol 65:538-542, 1997
Gilad E, Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B, Salzman AL, Szabo C: Melatonin is a scavenger of peroxynitrite. Life Sci 60:169-174, 1997
Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B, Gilad E, Hake P, Salzman AL, Szabo C: Protective effect of melatonin in carragee nan-induced models of local inflammation: Relationship to its inhibitory effect on nitric oxide production and its peroxynitrite scavenging activity. J Pineal Res 23:106-116, 1997
Antolin I, Rodriquez C, Sainz RM, Antolin F, Menendez-Pelaez A: Neurohormone melatonin prevents cell damage: effect on gene expression for antioxidant enzymes. FASEB J 10:882-890, 1996
Kotler M, Rodriquez C, Sainz RM, Antolin I, Menendez-Pelaez A: Melatonin increases gene expression for antioxidant enzymes in rat brain cortex. J Pineal Res 24:83-89, 1998
Barlow-Walden LR, Reiter RJ, Abe M, Pablos MI, Menendez-Pelaez A, Chen LD, Poeggeler B: Melatonin stimulates brain glutathione peroxidase activity. Neurochem Int 26:497-502, 1995
Sewerynek E, Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Ortiz GG, Lewinski A: Oxidative damage in liver induced by ischemia-reperfusion: Protection by melatonin. Hepato-Gastroenterol 43:898-905, 1996
Pablos MI, Reiter RJ, Ortiz GG, Guerrero JM, Agapito MT, Chuang JI, Sewerynek E: Rhythms of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase in brain of chick and their inhibition by light. Neurochem Int 5(suppl):61-66, 1998
Costa EJX, Lopes RH, Lamy-Freund MT: Permeability of pure lipid bilayers to melatonin. J Pineal Res 16:123-124, 1994
Shida CS, Castrucci AML, Lamy-Freund MT: High melatonin solubility in aqueous medium. J Pineal Res 16:198-201, 1994
Holson RR: Euthanasia by decapitation: Evidence that this technique produces prompt, painless unconsciousness in laboratory rodents. Neurotoxicol Teratol 14:253-257, 1992
Rauscher E, Bulow S, Hagele ED, Neumann U, Schaich E: Ethylidene protects substrate for the assay of human a-amylase. Fresenius Z Anal Chem 324:304, 1986
Bradford M: Rapid and sensitive method for quantification of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248-254, 1976
Aho HJ, Nevalainen TJ, Havia VT, Heinonen RJ: Human acute pancreatitis. Microbiol Immunol Scand (A) 90:367-373, 1982
Slater TF: Free radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem J 222:1-15, 1984
Del Maestro RF, Bjork J, Arfors KE: Increase in microvascular permeability induced by enzymatically generated free radicals. Microvasc Res 22:255-270, 1982
Perone WF, English DK, Wong K, Mccord JM: Free radicals and inflammation: Superoxide dependent activation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1159-1163, 1980
Bjork J, Arfors KE: Oxygen radicals and leucotrienes B4 induced increase in vascular leakage by PMN-leukocyte s. Agents Actions 11:63-73, 1984
Babior BM: Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes. N Engl J Med 298:659-668, 1978
Schoenberg MH, Birk D, Beger HG: Oxidative stress in acute and chronic pancre atitis. Am J Clin Nutr 62:1306-1314, 1995
Wisner J, Green D, Ferrell L, Renner I: Evidence for a role of oxygen derived free radicals in the pathogenesis of cerulein induced acute pancreatitis. Gut 29:1516-1523, 1988
Steer ML, Rutledge PL, Powers RE, Saluja AK: The role of oxygen-derived free radicals in two models of experimental acute pancreatitis: effects of catalase, superoxide dismutase, dime thylsulfoxide and allopurinol. Klin Wochenschr 69:1012-1017, 1991
Niederau C, Niederau M, Borchard F, Borchard F, Ude K, Luthen R, Strohmeyer G, Fe rrell LD, Grendell JH: Effect of antioxidants and free radical scavengers in three different models of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 7:486-496, 1992
Nonaka A, Manabe T, Kyogoku T, Tamura K, Tobe T: Evidence for a role of free radicals by synthe sized scavenger,2-octode cylascorbic acid, in caerulein induced mouse acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 37:274-279, 1992
Nonaka A, Manabe T, Tobe T: Effect of a new synthetic ascorbic acid derivative as a free radical scavenger on the development of acute pancreatitis in mice. Gut 32:528-532, 1991
Wisner JR, Renner IG: Allopurinol attenuates cerulein induced acute pancreatitis in the rat. Gut 29:926-929, 1988
Sanfey H, Bulkley GB, Cameron JL: The role of oxygenderived free radicals in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg 200:405-413, 1984
Reiter RJ: Melatonin, active oxygen species and neurological damage. Drug News Perspect 11:291-296, 1998
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Qi W: A brief survey of observations and me chanisms related to suppression of oxygen toxicity by melatonin. Acta Pharmacol Sin 19:575-581, 1998
Bettahi I, Guerrero JM, Reiter RJ, Osuna C: Physiological concentrations of me latonin inhibit the norepinephrine-induced activation of prostaglandin E2 and cyclic AMP production in rat hypothalamus: A mechanism involving inhibition of nitric oxide. J Pineal Res 25:34-40, 1998
Garcia JJ, Reiter RJ, Guerrero JM, Escames G, Yu BP, Oh CS, Munoz-Hoyos A: Melatonin prevents changes in microsomal membrane fluidity during induced lipid peroxidation. FEBS Lett 408:297-300, 1997
Garcia JJ, Reiter RJ, Ortiz GG, Oh CS, Tang L, Yu BP, Escames G: Melatonin enhances tamoxifen's ability to prevent the reduction in microsomal membrane fluidity induced by lipid peroxidation. J Membr Biol 162:59-65, 1998
de la Lastra CA, Motilva V, Martin MJ, Nieto A, Barranco MD, Cabeza J, Herrerias JM: Protective effect of melatonin on indomethacin-induced gastric injury in rats. J Pineal Res 26:101-107, 1999
Cuzzocrea S, Zingarelli B, Costantino G, Caputi AP: Protective effect of melatonin in a non-septic shock model induced by zymosan in the rat. J Pineal Res 25:24-33, 1998
de la Lastra CA, Cabeza J, Motilva V, Martin MJ: Melatonin protects against gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Pineal Res 23:47-52, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, W., Tan, DX., Reiter, R.J. et al. Melatonin Reduces Lipid Peroxidation and Tissue Edema in Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 44, 2257–2262 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026656720868
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026656720868