Summary
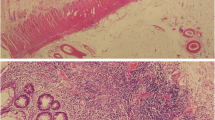
A patient is described who developed severe diarrhea with sigmoidoscopic, histologic, and radiologic evidence of pseudomembranous colitis. No pathogenic organisms were found in the feces and there was a dramatic response when she was treated by withdrawal of antibiotics and institution of corticosteroid therapy. Cases have been collected from the literature to show that pseudomembranous enterocolitis following antibiotic therapy can occur in the absence of superimposed infection. This evidence and the rapid cure of our patient with corticosteroids suggests that the disorder may be due in certain instances to a direct deleterious effect of antibiotics on intestinal mucosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Truelove, S. C. Treatment of ulcerative colitis with local hydrocortisone hemisuccinate sodium.Brit. M. J. 1:1437, 1957.
Penner, A., andBernheim, A. I. Acute postoperative enterocolitis: A study of the pathological nature of shock.Arch. Path. 27:966, 1939.
Penner, A., andDruckerman, L. J. Enterocolitis as a postoperative complication and its significance.Gastroenterology 11:479, 1948.
Bernhart, G. Todesfälle infolge superinfektionen bei der Antibioticatherapie.Schweiz. med. Wchschr. 82:1335, 1952.
Williams, M. R., andPullan, J. M. Necrotizing enteritis following gastric surgery.Lancet 2:1013, 1953.
Dawson-Edwards, P., andMorrissey, D. M. Acute enterocolitis following partial gastrectomy.Brit J. Surg. 42:643, 1954.
Pettit, J. D., Baggenstross, A. H., Dearing, W. H., andJudd, E. S. Postoperative pseudomembranous enterocolitis.Surg. Gynec. & Obstet. 98:546, 1954.
Dixon, C. F., andWeismann, R. E. Acute pseudomembranous enteritis or enterocolitis: A complication following intestinal surgery.S. Clin. North America 28:999. 1948.
Kleckner, M. S., Bargen, J. A., andBaggenstross, A. H. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis: Clinicopathological study of 14 cases in which the disease was not preceded by operation.Gastroenterology 21:212, 1952.
Markley, J. C., Carson, R. P., andHolzer, C. E. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis: A clinicopathological study of 14 cases with a common etiological factor.A.M.A. Arch. Surg. 77:452, 1958.
Dearing, W. H., andHielman, F. R. Micrococcic (staphylococcic) enteritis as a complication of antibiotic therapy: Its response to erythromycin.Proc. Staff Meet. Mayo Clin. 28:121, 1953.
Wakefield, R. D., andSommers, C. Fatal membranous staphylococcal enteritis in surgical patients.Ann. Surg. 138:249, 1953.
Speare, G. S. Staphylococcus pseudomembranous enterocolitis, a complication of antibiotic therapy.Am. J. Surg. 88:523, 1954.
Terplan, K., Paine, J. R., Sheffer, J., Egan, R., andLansky, H. Fulminating gastroenterocolitis caused by staphylococci.Gastroenterology 24:476, 1953.
Cook, J., Elliott, C., Elliot-Smith, A., Frisby, B. R., andGardner, A. M. N. Staphylococcal diarrhea with an account of 2 outbreaks in the same hospital.Brit. M. J. 1:542, 1957.
Brumfitt, W., andWright, E. A. Pseudomembranous enterocolitis with jejunal perforation associated withCl. welchii infection.Postgrad. M. J. 33:408, 1957.
Howie, J. W., Duncan, I. B. R., andMackie, L. M. Growth ofClostridium welchii in the stomach after partial gastrectomy.Lancet 2:1018, 1953.
Cregan, J., andHayward, N. J. The bacterial content of the human small intestine.Brit. M. J. 1:1356, 1953.
Reiner, L., Schlesinger, M. J., andMiller, G. M. Pseudomembranous colitis following Aureomycin and chloramphenicol.Arch. path. 54:39, 1953.
Dearing, W. H., Baggenstross, A. H., andWeed, L. A. Studies on the relationship ofStaphylococcus aureus to pseudomembranous enteritis and to post-antibiotic enteritis.Gastroenterology 38:441, 1960
Jacobson, E. D., Chodos, R. B., Prior, J. T., andFalcon, W. W. An experimental malabsorption syndrome produced by neomycin: Absorptive and histological studies.Clin. Research 7:33 and 260, 1959.
Truelove, S. C. Treatment of ulcerative colitis with local hydrocortisone hemisuccinate sodium.Brit. M. J. 2:1072, 1958.
Jufl-Jensen, B. E. Sensitivity to phenindione. A report of a case of severe diarrhea.Brit. M. J. 2:173, 1959.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valberg, L.S., Truelove, S.C. Noninfective pseudomembranous colitis following antibiotic therapy. Digest Dis Sci 5, 728–738 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231114
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231114