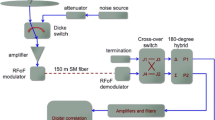
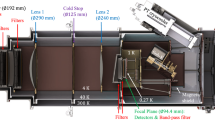
Abstract
There is a strong interest in the submillimeter astronomy community to increase the IF bandwidth of SIS receivers in order to better facilitate broad spectral linewidth and continuum observations of extragalactic sources. However, with an increase in receiver IF bandwidth there is a decrease in the mixer stability. This in turn effects the integration efficiency and quality of the measurement. In order to better understand the noise mechanisms responsible for reducing the receiver stability, we employed a technique first described by D.W. Allan and later elaborated upon by Schieder et al. In this paper we address a variety of factors that degrade the noise stability of SIS receivers. The goal of this exercise is to make recommendations aimed at maximizing SIS receiver stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Kraus, “Radio Astronomy”, 2nd Edition, pp7–8
D. W. Allan, “Statistics of Atomic Frequency Standards”, Proc. IEEE, Vol. 54,No. 2, pp 221–230, 1969
A.B Barnes, “Characterization of frequency stability”, IEEE Trans. Instrument Measurements, Vol. IM-20,No. 2, pp 105–120, 1971
R. Schieder, “Characterization and Measurement of System Stability”, SPIE, Vol. 598, Instrumentation for Submillimeter Spectroscopy (1985)
B.D. Josephson, “Possible new effects in superconductive tunneling”, Phys. Letters 1, (1962), pp 251–253
R. Bradley, NRAO, Private Communication
S. Padin, “A Cooled 1-2 GHz balanced HEMT amplifier”, IEEE, Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol 39,No. 7, pp. 1239–1243 (1991)
Infrared Laboratories, Inc. 1808 East 17th Street, Tuscon, Az 85719
B.N Ellison, “A low noise 230 GHz SIS receiver”, Int. J. Infrared and Millimeter waves, Vol. 8, pp. 609–625, June 1987
CTI-Cryogenics, Helix Technology Corporation, Nine Hampshire Street, Mansfield, MA 02048, USA.
Personal communication
G. Chattopadhyay, D. Miller, H. G. LeDuc, and J. Zmuidzinas, “A 550-GHz Dual Polarized Quasi-Optical SIS Mixer,” Proceedings of the Tenth International Symposium of Space Terahertz Technology, Charlottesville, Virginia, pp. 130–143, March 16–18, 1999.
J. W. Kooi, M. Chan, B. Bumble, and T. G. Phillips, “A low noise 345 GHz waveguide receiver employing a tuned 0.50 μm2 Nb/AlOx/Nb tunnel junction,” Int. J. IR and MM Waves, vol. 15,No. 5, May 1994.
J.W. Kooi, J. Pety, B. Bumble, C.K. Walker, H.G. LeDuc P.L. Schaffer, and T.G. Phillips, “A 850 GHz Waveguide Receiver employing a Niobium SIS Junction Fabricated on a 1um Si3N4 Membrane,” IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 46,No. 2, pp151–161, February 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kooi, J.W., Chattopadhyay, G., Thielman, M. et al. Noise Stability of SIS Receivers. International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves 21, 689–716 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026452324545
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026452324545