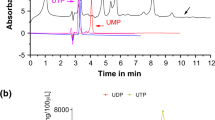
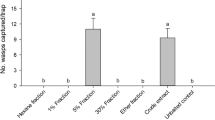
Abstract
In their natural ecosystems, the sexes of Asian elephants,Elephas maximus, live separately. For several weeks prior to ovulation, the urine and cervical mucus of female Asian elephants contain extractable chemical agents of low volatility that elicit a high frequency of flehmen responses from bull elephants as an integral part of mating. Subsequent to flehmen responses, male sexual arousal occurs and, if the female is available, mating results. During the course of our project to determine the agent(s) and describe the responses associated with female to male sexual communication, we have identified an unusual compound. This compound, apparently the sole component of the active fraction, was identified by mass, proton nuclear magnetic resonance, ultraviolet/visible, and infrared spectrometries as indolo-[2,1-b] quinazoline-6,12-dione (tryptanthrine). Exhaustive and repetitive bioassays established that pure authentic (synthetic) tryptanthrine was not the compound responsible for the bioresponse. Rather a coeluting minor component, also of low volatility, elicited the male bioresponse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann, J. 1974. Observational study of behavior: sampling methods.Behavior 49:227–265
Bergman, J., Egestad, B., andLindstrom, J. 1977. The structure of some indolic constituents inCouroupita guaianensis Aubl.Tetrahedron Lett. 30:2625–2626
Bird, C.W. 1963. The structure of methylisatoid.Tetrahedron 19:901–904
Friedlander, P., andRoschestwensky, N. 1915. An oxidation product of indigo blue.Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 48:1841–1861
Hess, D.L., Schmidt, A.M., andSchmidt, M.J. 1983. Reproductive cycle of the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) in captivity.Biol. Reprod. 28:767–773
Nelson, E.K., andWheeler, D.H. 1937. Some constituents of the cannonball fruit (Couroupita guaianensis Aubl).J. Am. Chem. Soc. 10:175–202
Rasmussen, L.E.L., andLee, T.D. 1991. Purification and initial characterization of preovulatory urinary pheromone from female Asian elephants (Elephas maximus). Association for Chemoreception Sciences, Abstract 8.Chem. Senses 16:569
Rasmussen, L.E.L., andMunger, B. 1990. Micro-anatomy of the trunk tip ofElephas maximus. Association for Chemoreception Sciences. Abstract 188.Chem. Senses 15:629
Rasmussen, L.E., Schmidt, M.J., Henneous, R., Groves, D., andDaves, G.D. Jr. 1982. Asian bull elephants: Flehmen-like responses to extractable components in female elephant estrous urine. Science 217:159–162
Rasmussen, L.E., Schmidt, M.J., andDaves, G.D., Jr. 1986. Chemical communication among Asian elephants, pp. 627–671,in D. Duvall, M. Silverstein, and D. Müller-Schwarze (eds.. Chemical Signals in Vertebrates: Evolutionary, Ecological, and Comparative Aspects, Volume 4. Plenum Press, New York.
Rasmussen, L.E.L., andHultgren, B. 1990. Gross and microscopic anatomy of the vomeronasal organ in the Asian elephant,Elephas maximus, pp. 154–161,in D. McDonald, D. Müller-Schwarze, and S.E. Natynczuk (eds.. Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 5, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Still, W., Kahn, M., andMitra, A. 1978. Rapid chromatographic technique for preparative separation with moderate resolution.J. Org. Chem. 43:2923–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmussen, L.E.L., Lee, T.D., Daves, G.D. et al. Female-to-male sex pheromones of low volatility in the Asian elephant,Elephas maximus . J Chem Ecol 19, 2115–2128 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00979651
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00979651