Abstract
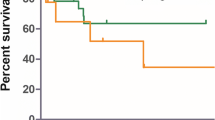
Cerebral fungal infection is becoming an increasingly recognized entity in immunocompromised patients on post-mortem examination. In order to determine the frequency of clinically significant cerebral fungal infection and define its clinical characteristics in a cohort of immunocompromised patients at high risk of fungal infection, the records of 118 patients with acute leukemia were examined for 57 clinical and laboratory features. The characteristics of 26 patients with systemic aspergillosis and acute leukemia were compared to 92 patients with acute leukemia in a control group. Eight of 118 patients (7%) had cerebral infection (seven Aspergillus, on Candida). Patients with systemic aspergillosis were more likely than patients in the control group to have focal neurologic findings (p = 0.02), confusion (p = 0.04), and abnormal computerized tomography (CT) of the brain characterized by single or multiple, enhancing or non-enhancing hypodense lesions (p = 0.02). Patients with systemic aspergillosis were more likely to die in complete remission than patients in the control group (p = 0.003); three of six patients with aspergillosis who died in remission expired as a consequence of cerebral infection. Cerebral infection complicated systemic Aspergillus infection in seven of 26 patients (27%), versus one of 16 patients with systemic Candida infection (6%) (p = NS). The authors conclude, therefore, that systemic aspergillosis complicating acute leukemia is more likely to be associated with confusion, focal neurologic findings, and and abnormal CT scan of the brain, and that these findings suggest the presence of cerebral infection. In addition, cerebral infection commonly complicates the course of systemic aspergillosis, and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with acute leukemia. A high index of suspicion is needed to insure early diagnosis and appropriate therapy, particularly in those who achieve remission of their leukemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gold J: Opportunistic fungal infections in patients with neoplastic disease. Am J Med 76: 458–463, 1984
Graus P, Rogers LR, Posner JB: Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Medicine 64: 16–35, 1985
Young RC, Bennett JE, Vogl CL, Carbone PP, DeVita VT: Aspergillosis: the spectrum of disease in 98 patients. Medicine 49: 147–173, 1970
Parker JC, McCloskey JJ, Lee RS: The emergence of candidosis: the dominant postmortem cerebral mycosis. Am J Clin Path 70: 31–36, 1978
Salaki JS, Louria DB, Chmel H: Fungal and yeast infections of the central nervous system. A clinical review. Medicine 63: 108–132, 1984
Anaissie E, Harris M, Karl C, Khan A, Bodey GP: Central nervous system fungal infection in cancer patients. Proc of the 28th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 28: 665, 1988
Lyons RW, Andriole VT. Fungal infections of the central nervous system. Neurol Clinic 4: 159–170, 1986
Walsh TJ, Hier DB, Caplan LR: Fungal infections of the central nervous system: comparative analysis of risk factors and clinical signs in 57 patients. Neurology 35: 1654–1657, 1985
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. N Eng J Med 318: 427–440, 1988
Beal MF, O'Carroll CP, Kleinman GM, Grossman RI: Aspergillosis of the nervous system. Neurology 32: 473–479, 1982
Esterhay FR, Wiernik PH, Grove WR, Markus SD, Wesley MN: Moderate dose methotrexate, vincristine, asparaginase and dexamethasone for treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 59: 334–345, 1982
Gerson SL, Talbot GH, Hurwitz S, Strom BL, Lusk EL, Cassileth PA: Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med 100: 345–351, 1984
Gucalp R, Weinberg V, Carlisle P, Sparano J, Ciobanu N, Wiernik PH: Sixth International Symposium on Infections in the Immunocompromised Host. 6: 77, 1986
Landefeld CS, Chren MM, Myers A, Geller R, Robbins S, Goldman L: Diagnostic yield of the autopsy in a university hospital and a community hospital. N Eng J Med 318: 1249–1254, 1988
Zee CS, Han JS, Segall HD: Infectious processes of the brain. In: Haaga JR, Alfidi RJ (eds) Computerized Tomography of the Whole Brain, 2nd ed. St. Louis, Washington, D.C., Toronto, C.V. Mosby 118–135, 1988
Danzinger A, Price H: Computerized axial tomography in intracranial aspergillosis — a report of two cases. South Afr Med J 54: 706–708, 1978
Grossman RI, Davis KR, Taveras JM, Beal MR, O'Carroll CP: Computed tomography of intracranial aspergillosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 5: 646–650, 1981
Enzmann DR, Brant-Zawadzki M, Britt RH: CT of central nervous system infections in immunocompromised patients. AJNR 1: 239–243, 1980
Kent DL, Larson EB: Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine. Is clinical efficacy established after the first decade? Ann Int Med 108: 402–424, 1988
Thaler M, Pastakia B, Shawker TH, O'Leary T, Pizzo P: Hepatic candidiasis in cancer patients: the evolving clinical picture. Ann Intern Med 108: 88–100, 1988
Mikhael MA, Rushivick AM, Ciric I: Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral aspergillosis. Comput Radiol 9: 85–89, 1985
Burch PA, Karp JE, Merz WG, Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK: Favorable outcome of invasive aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol 5: 1985–1993, 1987
Venugopal PV, Venugopal TV, Thiruneelakantan D, et al.: Cerebral aspergillosis. Report of two cases. Sabouraudia 15:225, 1977
Henze KG, Aldenhoff P, Stephani U, et al.: Successful treatment of pulmonary and cerebral aspergillosis in an immunocompromised child. Eur J Pediatr 138: 263, 1982
McCullough J: Granulocyte transfusion: In: Wiernik PH, Canellos GP, Kyle RA, Schiffer CA, (eds) Neoplastie Diseases of the Blood, New York, Edinburgh, London, and Melbourne, Churchill Livingstone 1061–1079, 1985
Fromtling RA: Overview of medically important antifungal azole derivatives. Clin Microbiol Rev 1: 187–217, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Parts of this paper have been presented at the Sixth International Symposium on Infections in the Immunocompromised Host, June 3–6, 1990, Peebles, Scotland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sparano, J.A., Gucalp, R., Llena, J.F. et al. Cerebral infection complicating systemic aspergillosis in acute leukemia: clinical and radiographic presentation. J Neuro-Oncol 13, 91–100 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172950
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172950