Abstract
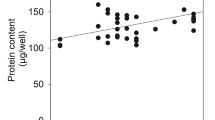
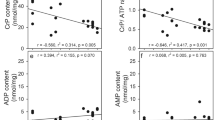
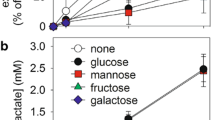
myo-Inositol uptake measured in primary astrocyte cultures was saturable in the presence of Na+ with a Km of 13–18 μM and a Vmax of 9.4 nmoles/mg protein/hour in myo-inositol-fed cells, indicating a high affinity transport system. In myo-inositol-deprived cells, Km was about 53 μM with a Vmax of 13.2 nmoles/mg protein/hour. Decreasing osmolality decreased the Vmax to about 1.9 nmoles/mg protein/hour whereas increasing osmolality increased Vmax about 5-fold, while Kms were essentially unchanged in myo-inositol fed cells. In cells deprived of myo-inositol, Vmax decreased in hypotonic medium and increased in hypertonic medium almost 10-fold, but with more than a doubling of the Km regardless of the osmolality. Glucose (25 mM) inhibited myo-inositol uptake 51% whereas the other hexoses used inhibited uptake much less. Our findings indicate that myo-inositol uptake in astrocytes occurs through an efficient carrier-mediated Na+-dependent co-transport system that is different from that of glucose and its kinetic properties are affected by myo-inositol availability and osmotic stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Berridge, M. J. 1984. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem. J. 220:345–360.
Michell, R. H. 1975. Inositol phospholipids and cell-surface receptor function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 415:81–147.
Berridge, M. J., and Irvine, R. F. 1984. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular transduction. Nature 312: 315–321.
Nishizuka, Y. 1984. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature 308:693–698.
Downes, C. P. 1989. The cellular functions of myo-inositol. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 17:259–268.
Isaacks, R. E., Bender, A. S., Kim, C. Y., Prieto, N. M., and Norenberg, M. D. 1994. Osmotic regulation of myo-inositol uptake in primary astrocyte cultures. Neurochem. Res. 19:331–338.
Strange, K., Morrison, R., Heilig, C. W., Dipietro, S., Gullans, S. R. 1991. Upregulation of inositol transport mediates inositol accumulation in hyperosmolar brain cells. Am. J. Physiol. 260: C784-C790.
Strange, K., and Morrison, R. 1992. Volume regulation during recovery from chronic hypertonicity in brain glial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C412-C419.
Strange, K., Emma, F., Paredes, A., and Morrison, R. 1994. Osmoregulatory changes in myo-inositol content and Na+/myo-inositol cotransport in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia 12:35–43.
Spector, R., and Lorenzo, A. V. 1975. The origin of myo-inositol in brain, cerebrospinal fluid and choroid plexus. J. Neurochem. 25:353–354.
Wong, Y-H. H., Kalmbach, S. J., Hartman, B. K., and Sherman, W. R. 1987. Immunohistochemical staining and enzyme activity measurements show myo-inositol-1-phospate synthase to be localized in the vasculature of brain. J. Neurochem. 48:1434–1442.
Biden, T. J., and Wollheim, C. B. 1986. Active transport of myo-inositol in rat pancreatic islets. Biochem. J. 236:889–893.
Isaacks, R. E., Lai, L. L., Kim, C. Y., Goldman, P. H., Kim, H. D. 1989. Studies on avian erythrocyte metabolism. XVII. Kinetics and transport properties of myo-inositol in chicken reticulocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 274:564–573.
Wiesinger, H. 1991. myo-Inositol transport in mouse astroglia-rich primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 56:1698–1704.
Warfield, A., Hwang, S. M., and Segal, S. 1978. On the uptake of inositol by rat brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 31:957–960.
Goresky, C. A., and Nadeau, B. E. 1974. Uptake of materials by the intact liver. The exchange of glucose across the cell membranes. J. Clin. Invest. 53:634–646.
Prpic, V., Blackman, P. F., and Exton, J. H. 1982. myo-Inositol uptake and metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 257:11315–11322.
Cotlier, E. 1970. myo-Inositol: Active transport by the crystalline lens. Invest. Ophthalmol. 9:681–691.
Gillon, K. R. W., and Hawthorne, J. N. 1983. Transport of myo-inositol into endoneurial preparations of sciatic nerve from normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Biochem. J. 210:775–781.
Greene, D. A., and Lattimer, S. A. 1982. Sodium-and energy-dependent uptake of myo-inositol by rabbit peripheral nerve. J. Clin. Invest. 70:1009–1018.
Reddy, V. N., Varma, S. D., and Chakrapani, B. 1970. Intraocular transport of myo-inositol. I. Accumulation in the rabbit ciliary body. Invest. Opthalmol. 9:785–793.
Elbrink, J., and Bihler, I. 1972. Characteristic of the membrane transport of sugars in the lens of the eye. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 282:337–351.
Greene, D. A., Winegrad, A. I., Carpentier, J. L., Brown, M. J., Fukuma, M., and Orci, L. 1979. Rabbit sciatic nerve fascile and endoneurial preparations for in vitro studies of peripheral nerve glucose metabolism. J. Neurochem. 33:1007–1018.
Booher, J., and Sensenbrenner, M. 1972. Growth and cultivation of dissociated neurons and glial cells from embryonic chick, rat, and human brain in flask cultures. Neurobiology 2:97–105.
Gregorios, J. B., Mozes, L. W., Norenberg, L. O. B., and Norenberg, M. D. 1985. Morphological effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. I. Light microscopic studies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44:397–403.
Stahl, B., Wiesinger, H., and Hamprecht, B. 1989. Characteristics of sorbitol uptake in rat glial primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 53:665–671.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Haneda, M., Kikkawa, R., Arimura, T., Ebata, K., Togawa, M., Maeda, S., Sawada, T., Horide, N., and Shigeta, Y. 1990. Glucose inhibits myo-inositol uptake and reduces myo-inositol content in cultured rat mesangial cells. Metabolism 39:40–45.
Batty, I. H., Michie, A., Fennel, M., and Downes, C. P. 1993. The characteristics, capacity and receptor regulation of inositol uptake in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Biochem. J. 294:49–55.
Guzman, N. J., and Crews, F. T. 1992. Regulation of inositol transport by glucose and protein kinase C in mesangial cells. Kidney Internat. 42:33–40.
Veis, J. H., Molitoris, B. A., Teitelbaum, I., Mansour, J. A., and Berl, T. 1991. myo-Inositol uptake by rat cultured inner medullary collecting tubule cells: effect of osmolality. Am. J. Physiol. 260:F619-F625.
Paredes, A., McManus, M., Kwon, H. M., and Strange, K. 1992. Osmoregulation of Na+-inositol cotransporter activity and mRNA levels in brain glial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 263:(Cell Physiol. 32) C1282-C1288.
Nakanishi, T., Turner, R. J., and Burg, M. B. 1989. Osmoregulatory changes in myo-inositol transport by renal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci (USA) 86:6002–6006.
Rubin, L. J., and Hale, C. C. 1993. Characterization of a Mgdependent, Na-inositol co-transport process in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 25:721–731.
Kwon, H. M., Yamuchi, A., Uchida, S., Robey, R. B., Garcia-Perez, A., Burg, M. B., and Handler, J. S. 1991. Renal Na-myo-inositol cotransporter mRNA expression in Xenopus oocytes: regulation by hypertonicity. Am. J. Physiol. 260:(Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol. 29) F258-F263.
Fruen, B. R., and Lester, B. R. 1990. Down's syndrome fibroblasts exhibit enhanced inositol uptake. Biochem. J. 270:119–123.
Whitesell, R. R., and Abumrad, N. A. 1985. Increased affinity predominates in insulin stimulation of glucose transport in the adipocyte. J. Biol. Chem. 260:2894–2899.
Martz, A., Mookerjee, B. K., and Jung, C. Y. 1986. Insulin and phorbol esters affect the maximum velocity rather than the half-saturation constant of 3-O-methylglucose transport in rat adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 261:13606–13609.
Suzuki, K. 1988. Reassessment of the translocation hypothesis by kinetic studies on hexose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 263:12247–12252.
Tildon, J. T., McKenna, M. C., Stevenson, J., and Couto, R. 1993. Transport of L-lactate by cultured rat brain astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 18:177–184.
Tildon, J. T., McKenna, M. C., and Stevenson, J. H., Jr. 1994. Transport of 3-hydroxybutyrate by cultured rat brain astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 19:1237–1242.
Palmano, K. P., Whiting, P. H., and Hawthorne, J. N. 1977. Free and lipid myo-inositol in tissues from rat with acute and less severe streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Biochem. J. 167:229–235.
Krupka, R. M., and Deves, R. 1981. An experimental test for cyclic versus linear transport models. The mechanisms of glucose and choline transport in erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 256: 5410–5416.
Griffin, J. F., Rampal, A. L., and Jung, C. Y. 1982. Inhibition of glucose transport in human erythrocytes by cytochalasins: A model based on diffraction studies. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci USA 79:3759–3763.
Khatami, M., and Rockey, J. H. 1988. Regulation of uptake of inositol by glucose in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 66:951–957.
Finegold, D., Lattimer, S. A., Nolle, S., Bernstein, M., and Greene, D. A. 1983. Polyol pathway activity and myo-inositol metabolism. A suggested relationship in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 32:988–992.
Kreis, R., Ross, B. D., Farrow, N. A., and Ackerman, Z. 1992. Metabolic disorders of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy detected with H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 182:19–27.
Miller, B. L., Moats, R. A., Shonk, T., Ernst, T., Woolley, S., and Ross, B. D. 1993. Alzeheimer disease: depiction of cerebral myo-inositol with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 187: 433–437.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isaacks, R.E., Bender, A.S., Kim, C.Y. et al. Effect of Osmolality and myo-Inositol Deprivation on the Transport Properties of myo-Inositol in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Neurochem Res 22, 1461–1469 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021950311308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021950311308