Summary
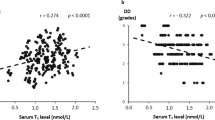
In patients with severely acute diseases, a special relationship of thyroidal hormones with decreased T3 and increased rT3 levels is known, the so-called low T3 syndrome. The aim of this study was to elucidate the involvement of the hypothalamo-pituitary thyroid axis, the pituitary-gonadal axis, the altered hepatic function, the plasma proteins in the low T3 syndrome, and the evaluation of these parameters for prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Thirty-one patients (29 male, 2 female) with AMI entered the study for the determination of hypothalamo-pituitary thyroid axis and the plasma proteins. Besides routine laboratory determinations, TRH, TSH, T4, T3, rT3, CHE, albumin, total protein, TBG, and estradiol concentrations in plasma were measured daily for 5 days after AMI using immunological and other methods. Twelve male patients with AMI entered the study for the determination of pituitary-gonadal axis; the T3, rT3, estradiol, testosterone, FSH, and LH concentrations in serum were determined using immunological methods. We found that T3 and T4 decreased significantly to a minimum on the first and the second day, respectively, after admission and increased in the course of the observation period. In contrast, rT3 was elevated significantly within the first 2 days and decreased later. TSH and TRH decreased in the first 2 days and increased in the following days. CHE, albumin, and total protein levels significantly showed a minimum on day 4 and TBG significantly showed a minimum on the second day after AMI and increased to day 4. The estradiol and testosterone levels were high on admission and decreased in the following days and increased again in the observation period. FSH decreased in the first 2 days and increased in the following course similar to estradiol and testosterone. Patients who died within 2 weaks after AMI showed a plasma hormonal pattern of hypothyroidism with low TSH levels and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism on the second day, whereas this pattern is persistent in the following days. These results show the involvement of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis in the low T3 syndrome and that characteristics for acute partial insufficiency of the anterior pituitary gland are signs of a bad prognosis. Whether Gn-RH and ACTH also decreased after AMI is unknown. The necessity for substitution is unclear and needs further investigation
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HVL:
-
Hypophysenvorderlappen
- AMI:
-
Akuter Myokardinfarkt
- T3:
-
Total-Trijodthyronin
- T4:
-
Total-Thyroxin
- rT3:
-
reverse-T3
- TRH:
-
Thyreotropin-Releasing Hormon
- Gn-RH:
-
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormon
- CRF:
-
Corticotropin-Releasing Factor
- TSH:
-
Thyreotropin
- TBG:
-
Thyroxin-bindendes Globulin
- FSH:
-
Follikelstimulierendes Hormon
- LH:
-
Luteinisierendes Hormon
- CPK:
-
Kreatin-Phospho-Kinase
- x :
-
Mittelwert
- SD:
-
Standardabweichung
Literatur
Schmidt R, Vardarlı İ, Teuber J, Hannak D, Wdowinski JM, Usadel KH (1986) Prognostische Wertigkeit der Östradiol-Serum-Spiegel bei männlichen Patienten mit Low-T3-Syndrom nach akutem Herzinfarkt. Klin Wochenschr 64 (Suppl V):10–11
Sullivan PRC, Bollinger JA, Reichlin S (1973) Selective deficiency of tissue triiodothyronine: a proposed mechanism of elevated free thyroxine in the euthyroid sick. J Clin Invest 52:83a
Vardarlı İ, Med. Dissertation. Universität Heidelberg (in preparation)
Wdowinski JM, Vardarlı İ, Schmidt R, Schwedes U, Usadel KH (1985) Plasma levels of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), T4, T3 and rT3 in acute myocardial a infarction. Isr J Clin Biochem Lab Sci 4:36
Wdowinski JM, Vardarlı İ, Bauer K, Schmidt R, Schwedes U, Usadel KH (1986) Plasmaspiegel von Thyreotropin-Releasing Hormon (TRH) und TRH degrading enzym (TDE) beim akuten Myokardinfarkt, In: Schilddrüse 1985, 7. Konferenz über die menschliche Schilddrüse, Homburg/Saar (in press)
Zouaghi H, Savu L, Guerot C, Gryman R, Coulon A, Nunez EA (1985) Total and unbound cortisol-, progesteron-, oestrone- and transcortin-binding activities in sera from patients with myocardial infarction: evidence for differential responses of good and bad prognosis cases. J Clin Invest 15:365–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Professor Dr. K. Schöffling zum 65. Geburtstag gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vardarlı, İ., Schmidt, R., Wdowinski, J.M. et al. Hypothalamo-hypophysäre Schilddrüsen-Achse, Plasmaproteinkonzentrationen und die hypophysäre Gonaden-Achse im Low-T3-Syndrom nach akutem Myokardinfarkt (AMI). Klin Wochenschr 65, 129–133 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728605
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01728605