Summary
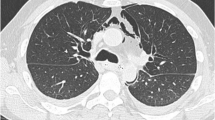
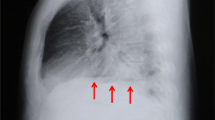
Among the different types of esophageal wall injuries Boerhaave's syndrome is associated with the highest morbidity and mortality. The classical history of retching or vomiting and retrosternal splitting pain is indicative. Roentgenograms of the chest and esophagogram with a water soluble contrast medium are able to reveal the perforation in most cases. Esophagoscopy has been recommended for diagnosis, but its use is unnecessary and frequently contraindicated. Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus should be treated by prompt surgical intervention: left side thoracotomy, direct closure of the perforation by monolayer suture, and adequate mediastinal and pleural drainage. The treatment of esophageal perforation after late diagnosis is considerably more complicated and may consist in a drainage only.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barrett NR (1947) Report of a case of spontaneous perforation of the esophagus successfully treated by operation. Br J Surg 35:216–218
Beersiek F, Schneiders H, Mehizadeh A, Jacobs G, Eigler FW (1976) Die spontane Ruptur des Ösophagus. DMW 47:1719–1723
Boerhaave H (1724) Atrocis, nec descripti prius, morbi historia. Secundum medicae artis leges conscripta. Lugduni Batavorum Boutesteniana Leyden
Derbes VJ, Mitchell RG (1956) Rupture of the esophagus. Surgery 39:865–868
Hirner A, Häring R (1982) Pathophysiologie und Klinik der spontanen Ösophagusruptur (Boerhaave-Syndrom). In: Häring R (Hrsg) Ösophaguschirurgie, Edition Medizin, Weinheim
Ivey TD, Simonowitz DA, Dillard DH, Miller DW (1981) Boerhaave syndrome. Successful conservative management in three patients with late presentation. Am J Surg 141:531–534
Kühl R, Beger HG (1987) Die chirurgische Therapie des Boerhaave-Syndroms — Erfahrungen mit der postoperativen Lavage der Thoraxhöhle. Akt Chir 22:139–142
Skajaa T (1959) Ösophagusruptur. Nord Med 61:673–681
Zimmermann F, Gehl H, von Buch K-G (1977) Die atraumatische komplette Ösophagusruptur (Boerhaave-Syndrom) MMW 119:1333–1336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thaler, W., Riedler, L. Zum Boerhaave-Syndrom. Klin Wochenschr 66, 1214–1217 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01727427
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01727427