Summary
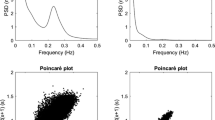
Spectral analysis of heart rate variability (HRV) was used to assess the autonomic nervous control of cardiac function during orthostatic load in insulin-dependent diabetic patients and healthy subjects. The diabetic patients were divided into three groups: diabetics without neuropathy (group 1), diabetics with peripheral neuropathy (group 2), and diabetics with peripheral and autonomic neuropathy (group 3). Resting mid-frequency (MF, 0.05–0.15 Hz) and respiration-related (RF, power around respiration rate) HRV were significantly lower in group 2 and 3 diabetics than in controls, indicating a reduced parasympathetic nervous system influence on the heart. Standing MF and RF spectral power data were significantly lower in all diabetic groups than in controls, suggesting marked alterations in the autonomic cardiovascular control during a mild physical load not only in symptomatic diabetics but also in patients with no signs and symptoms of neuropathy. The difference between supine and standing MF power, an estimate ofβ-adrenergic influence on the heart, was significantly lower in all diabetic subject groups studied than in controls. This suggests a reduced sympathetic nervous system influence on the heart in diabetic patients. Our data suggest that computerized spectral analysis of HRV during orthostatic load seems to be a very sensitive method of evaluating of the autonomie nervous systems influence on the heart in patients suffering from diabetes niellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dB:
-
decibel
- HRV:
-
heart rate variability
- LF:
-
low-frequency component
- MF:
-
mid-frequency component
- RF:
-
respiration related frequency component
References
Abenavoli T, Rubler S, Fisher VJ, Axelrod HI, Zuckerman KP (1981) Exercise testing with myocardial scintigraphy in asymptomatic diabetic males. Circulation 63:54–64
Akselrod SD, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Barger AC, Cohen RL (1981) Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuations: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science 213:220–222
Clarke BF, Ewing DJ, Campbell IW (1979) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetologia 17:195–212
Gotzsche O (1983) The adrenergicβ-receptor adenylate cyclase system in heart and lymphocytes from streptozotocicdiabetic rats. In vivo and in vitro evidence for a desensitized myocardial β-receptor. Diabetes 32:1110–1116
Hellman JB, Stacy RW (1976) Variations of respiratory sinus arrhythmia with age. J Appl Physiol 41:734–738
Hyndman BW, Gregory JR (1975) Spectral analysis of sinus arrhythmia during mental loading. Ergonomics 18:255–270
Kitney RI (1975) An analysis of the nonlinear behaviour of the human thermal vasomotor control system. J Theor Biol 52:231–248
Koepchen HP (1982) Zentralnervöse und reflektorische Steuerung der Herzfrequenz. In: Brisse B, Bender F (Hrsg) Autonome Innervation des Herzens. Steinkopff, Darmstadt, 1. Aufl., S. 66–85
Latifpour J, Jackson CV, McNeill KH (1983) Alterations in cardiac autonomic receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat. Fed Proc 42:6245
Pagani M, Lombardi F, Guzetti S, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pizzinelli P, Sandrone G, Malfatto G, Dell 'Orto S, Piccaluga E, Turiel M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Malliani A (1986) Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog. Circulat Res 59:178–193
Pomeranz B, Macaulay RJB, Candill MA, Kutz I, Adam D, Gordon D, Killborn KM, Barger AC, Shannon DC, Cohen RJ, Benson H (1985) Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am J Physiol248:H151-H153
Robinson BF, Epstein SE, Beiser GD, Braunwald E (1966) Control of heart rate by the autonomic nervous system — studies in man of the interrelation betwen baroreceptor mechanisms and exercise. Circ Res 19:400–411
Sayers BMcA (1973) Analysis of heart rate variability. Ergonomics 16:17–32
Weise F, Heydenreich F, Runge U (1987) Contributions of sympathetic and vagal mechanisms to the genesis of heart rate fluctuations during orthostatic load: a spectral analysis. J Auton Nerv Syst 21:127–134
Williams RS, Schaible TF, Scheuer J, Kennedy R (1983) Effect of experimental diabetes on adrenergic and cholinergic receptors of rat myocardium. Diabetes 32:881–886
Zola B, Kahn JK, Juni JE, Vinik AI (1986) Abnormal cardiac function in diabetic patients with autonomic neuropathy in the absence of ischemic heart disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 63:208–214
Zwiener U (1985) Pathophysiologie und Funktionsdiagnostik der nervösen Herzkreislaufregulation. Erg exp Med 46:90–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weise, F., Heydenreich, F., Gehrig, W. et al. Heart rate variability in diabetic patients during orthostatic load — A spectral analytic approach. Klin Wochenschr 68, 26–32 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01648886
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01648886