Summary
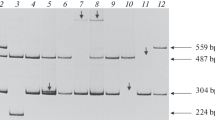
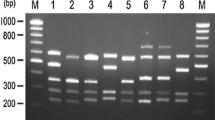
A second prenatal diagnosis of severe haemophilia B was carried out in a family with no prior history of the disease. The first prenatal diagnosis was based on linkage analysis and showed the male fetus not to be affected because he had inherited the same X-chromosome as his healthy brother. Carrier status in the female at risk could not be assessed by restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). She was found to have inherited the same marker constellation as her affected brother. However, due to the fact that a pedigree with no prior history of haemophilia B has been examined diagnosis was impossible. In addition factor IX coagulant and antigen values gave no definitive clue to a haemophilia B carriership. The problems with RFLP analysis in this pedigree were circumvented by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based direct sequencing of the factor IX gene. A previously unknown mutation could be detected in patient haemophilia B (Kleve) and the carrier status in the female at risk could be confirmed. The second prenatal diagnosis showed that the male fetus had inherited the mutation and will therefore be afflicted with haemophilia B.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bp:
-
basepairs
- FIX:Ag:
-
factor IX antigen
- FIX:C:
-
factor IX activity
- kb:
-
kilobasepairs
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RFLP:
-
restriction fragment length polymorphism
References
Barrai J, Cann HM, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Barbujani G, de Nicola P (1985) Segregation analysis of hemophilia A and B. Am J Hum Genet 37:680–699
Cooke RM, Wilkinson AJ, Baron M, Pastore A, Tappin MJ, Campbell ID, Gregory H, Sheard B (1987) The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. Nature 327:339–341
Giannelli F, Green PM, High KA, Lozier JN, Lillicrap DP, Ludwig M, Olek K, Reitsma PH, Goossens M, Yoshioka A, Sommer S, Brownlee GG (1990) Haemophilia B: — database of point mutations and short additions and deletions. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4053–4059
Green PM, Bentley DR, Mibashan RS, Nilsson IM, Giannelli F (1989) Molecular pathology of haemophilia B. EMBO J 8:1067–1072
Haldane JBS (1947) The mutation rate of the gene for haemophilia and its segregation ratio in males and females. Ann Eugen 9:232–237
Handford PA, Baron M, Mayhew M, Willis A, Beesley T, Brownlee GG, Campbell ID (1990) The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high-affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J 9:475–480
Higuchi M, Kochhan L, Schwaab R, Egli H, Brackmann HH, Horst J, Olek K (1989) Identification and characterization of mutations in the factor VIII gene and family analysis. Blood 74:1045–1051
Ikkala E (1960) Haemophilia. A study of its laboratory, clinical, genetic and social aspects based on known haemophiliacs in Finland. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 12 (Suppl 46): 1–144
Jackson CM, Nemerson Y (1980) Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem 49:765–811
Koeberl DD, Bottema CDK, Buerstedde JM, Sommer SS (1989) Functionally important regions of the factor IX gene have a low rate of polymorphism and a high rate of mutation in the dinucleotide CpG. Am J Hum Genet 45:448–457
Lubahn DB, Lord ST, Bosco J, Kirshtein J, Jeffries OJ, Parker N, Levtzow C, Silverman LM, Graham JB (1987) Population genetics of coagulant factor IX: frequencies of two DNA polymorphisms in five ethnic groups. Am J Hum Genet 40:527–536
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi RG, Horn TT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Scott CR, Chen SH, Schoof J, Kurachi K (1987) Hemophilia B: population differences in RFLP frequencies useful for carrier detection. Am J Hum Genet 41 (suppl.):A262 (abstr.)
Summers KM (1987) DNA polymorphisms in human populations: a review. Ann Hum Biol 14:203–217
Vogel F, Motulsky AG (1986) Human genetics — problems and approaches. 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Winship PR, Brownlee GG (1986) Diagnosis of haemophilia B carriers using intragenic oligonucleotide probes. Lancet II:218–219
Winship PR, Rees DJG, Alkan M (1989) Detection of polymorphisms at cytosine phosphoguanadine dinucleotides and diagnosis of haemophilia B carriers. Lancet I:631–634
Winter RM, Tuddenham EGD, Goldman E, Matthews KB (1983) A maximum likelihood of the sex mutation rates in haemophilia A. Hum Genet 64:156–159
Wong C, Dowling CE, Saiki RK, Higuchi RG, Erlich HA, Kazazian HH Jr. (1987) Characterization ofβ-thalassemia mutations using direct sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. Nature 330:384–386
Yoshitake S, Schach BG, Foster DC, Davie EW, Kurachi K (1985) Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry 24: 3736–3750
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, M., Brackmann, H.H. & Olek, K. Prenatal diagnosis of haemophilia B by the use of polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing. Klin Wochenschr 69, 196–200 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01646940
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01646940