Abstract
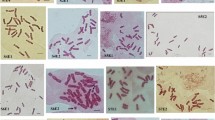
Phylogenetic relationships among eight taxa of seven species of Phaseolus and Vigna (Phaseolus angularis, P. aureus, P. calcaratus, P. coccineus, P. vulgaris, Vigna sesquipedalis and V. sinensis; 2n = 22 each) were studied by the fluorescent chromosome banding technique. Preparations of somatic metaphase chromosomes of each taxon were sequentially stained with Giemsa, GC-specific fluorochrome chromomycin A3 (CMA) and AT-specific fluorochrome 4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). On the basis of the fluorescent banding patterns of the 22 chromosomes of each taxon, P. angularis, P. coccineus (from China and Korea) and P. vulgaris were grouped into one group (“Phaseolus group”), P. aureus and two Vigna species were grouped into another (“Vigna group”) and P. calcaratus was grouped in an independent group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya S (1978) Giemsa-banding pattern of chromosomes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Cytologia 43:581–588
Hizume M, Ohgiku A, Tanaka A (1989) Chromosome banding in the genus Pinus. II. Interspecific variation of fluorescent banding patterns in P. densiflora and P. thunbergii. Bot Mag Tokyo 102:25–35
Joseph L, Bouwkamp J (1978) Karyomorphology of several species of Phaseolus and Vigna. Cytologia 43:595–600
Lackey J (1980) Chromosome numbers in the Phaseolus and their relation to taxonomy. Am J Bot 6:595–602
Lavania U, Lavania S (1982) Chromosome banding patterns in some Indian pulses. Ann Bot 49:235–239
Mok D, Mok M (1976) A modified Giemsa technique for identifying bean chromosomes. J Hered 67:187–188
Sarbhoy R (1977) Cytological studies in the Genus Phaseolus Linn. III. Evolution in the Genus Phaseolus. Cytologia 42:401–403
Schweizer D, Ambros P (1979) Analysis of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in mitotic and polytene chromosomes of Phaseolus coccineus by silver staining and Giemsa C-banding. Plant Syst Evol 132:27–51
Sen N, Bhowal J (1960) Cytotaxonomic studies on Vigna. Cytologia 25:195–207
Sen O, Bhattacharya S, Chanda S (1989) Cytomorphological studies in some taxa of Phaseolus Linn, and Vigna Savi. Cytologia 54:97–108
Sinha S, Roy H (1979) Cytological studies in the genus Phaseolus. I. Mitotic analysis in fourteen species. Cytologia 44:191–199
Takashima S, Niiuchi K, Watanabe H (eds) (1964) Vegetable crops of Japan in colour. Hoikusha Publishing Co, Osaka, pp 44–48 (in Japanese)
Verdcourt B (1970) Studies in the Leguminosae-Papilionoideae for the flora of tropical East Africa IV. Kew Bull 24:507–569
Zheng JY, Nakata M, Uchiyama H, Morikawa H, Tanaka R (1991) Giemsa C-banding patterns in several species of Phaseolus L. and Vigna Savi, Fabaceae. Cytologia 56:459–466
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by K. Tsunewaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, J.Y., Nakata, M., Irifune, K. et al. Fluorescent banding pattern analysis of eight taxa of Phaseolus and Vigna in relation to their phylogenetic relationships. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 87, 38–43 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223741
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223741