Abstract
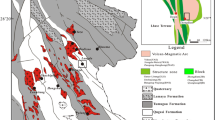
The sulfur isotope composition of 86 sulfide minerals from the Middle Proterozoic, metamorphosed, stratiform, sediment-hosted Zn-Pb-CU sulfide deposits of Dariba and Sindeswar Kalan located within the Rajpura-Dariba belt in Rajasthan, NW India, have been determined. In addition, 16 carbonaceous and 2 carbonate rock samples from the ore zone have been analyzed for their Ctot and Corg contents and carbon isotope compositions. The sulfur isotope compositions range from 9.1‰ to −6.7‰ (mean value of 1.9‰). Increasing δ34S values stratigraphically upward are observed, particularly for pyrite and pyrrhotite suggesting a syngenetic origin for the sulfur. No marked lateral isotopic variations or isotopic variation in minerals from successive laminae in banded ore samples occur. Fractionation of sulfur isotopes between coexisting sulfides suggests that the original isotopic pattern was basically preserved during the amphibolite-facies metamorphism suffered by the deposits. Corg in carbonaceous rocks ranges 0.5–9.3 wt%, with δ13C values between −21‰ and −31‰ (mean of −25.4‰) in keeping with the biogenic derivation of the carbon. Recrystallized dolostones have δ13C values close to −14.4‰
Geological evidence and isotopic features are consistant with the following genetic scheme: (a) base-metal ores along the belt formed from geothermal emanations carrying H2S, produced by the chemical reduction of seawater sulfates and leaching of mafic volcanics, in a semiclosed (with respect to SO4), shallow-water, rift-related basin with high biological activity; (b) pyrite and pyrrhotite formed diagenetically by bacterial reduction of sulfate in pore seawater in a system open to H2S, thus bringing about the gradual enrichment of 34S in these minerals stratigraphically upward; and (c) northward in the belt, at Sindeswar Kalan, the basin of ore deposition was relatively more open.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anger, G., Nielsen, H., Puchelt, H., Ricke, W.: Sulfur isotopes in the Rammelsberg ore deposit (Germany). Econ. Geol. 61:511–536 (1966)
Arnold, M., Sheppard, M.F.: East Pacific Rise at latitude 21 oN: isotopic composition and origin of the hydrothermal sulfur. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 56:148–156 (1981)
Ayres, D.E., Burns, M.S., Smith, J.W.: Sulfur isotope study of the massive sulfide orebody at Woodlawn, New South Wales. J. Geol. Soc. Australia 26:197–201 (1979)
Bachinski, D.J.: Bond strength and isotopic fractionation in coexisting sulfides. Econ. Geol. 64:56–65 (1969)
Barker, F., Friedman, I.: Carbon isotopes in the pelites of the Precambrian Uncompahgre Formation, Needle Mountains, Colorado. Bull. Geol. Soc. America 80:1403–1408 (1969)
Berner, R.A.: Sedimentary pyrite formation. Am J. Sci. 268:1–23 (1970)
Campbell, F.A., Ethier, V.G., Krouse, H.R., Both, R.A.: Isotopic composition of sulfur in the Sullivan orebody, British Columbia. Econ. Geol. 73:246–268 (1978)
Chauhan, D.S.: The Dariba main lode of Rajpura-Dariba zinclead-copper belt, Udaipur district, Rajasthan. J. Geol. Soc. India 18:611–616 (1977)
Claypool, G.E., Holser, W.T., Kaplan, I.R., Zak, I.: The age curve of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem. Geol. 28:199–260 (1980)
Deb, M., Banerjee, D.M., Bhattacharya, A.K.: Precambrian stromatolite and other structures in the Rajpura-Dariba polymetallic ore deposit, Rajasthan, India. Mineraliam Deposita 13:1–9 (1978)
Deb, M., Bhattacharya, A.K.: Geological setting and conditions of metamorphism of Rajpura-Dariba polymetallic ore deposit, Rajasthan, India. Proc. V IAGOD symposium, Snowbird, U.S.A., pp 679–697. Stuttgart: Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuch-handlung 1980
Deb, M.: Crustal evolution and Precambrian metallogenesis in western India. Rev. Bras. de Geol. 12:94–104 (1982a)
Deb, M.: Rare minerals in Rajpura-Dariba ores — some further comments. J. Geol. Soc. India 23:253–260 (1982b)
Deb, M., Kumar, R.: The volcano-sedimentary environment of Rajpura-Dariba polymetallic ore deposit, Udaipur district, Rajasthan. Proc. symp. Metallogeny of the Precambrian, Bangalore, India, pp 1–17. Geol. Surv. India, 1982
Deb, M., Thorpe, R.I., Cumming, G.L.: Lead isotope study of conformable sediment-hosted base metal deposits in the Proterozoic Aravalli-Delhi Belt, NW India (under preparation)
Galimov, E.M.: C13/C12 in Kerogen. In Kerogen (B. Burand, ed.) pp 271–300. Editions Technip. 1980
Gehrisch, W., Maucher, A., Nielsen, H.: Sulfur isotope and trace element analyses from the Sulitjelma orebodies, northern Norway. Mineralium Deposita 10:57–69 (1975)
Hekinian, R., Revrier, M., Bischoff, J.L., Picot, P., Shanks, W.C.: Sulfide deposits from the East Pacific Rise near 21 oN. Science 207:1433–1444 (1980)
Hoefs, J., Frey, M.: The isotopic composition of carbonaceous matter in a metamorphic profile from the Swiss Alps. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 40:945–951 (1976)
Hubberton, H.W.: Sulfur content and sulfur isotopes of basalts from the Costa Rica rift (Hole 504 B, Deep Sea Drilling project Legs 69 and 70). Init. Repts. DSDP 69:629–635 (1983)
Kajiwara, Y., Krouse, H.R., Sasaki, A.: Experimental study of sulfur isotope fractionation between co-existing sulfide minerals. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett 7:271–277 (1969)
Marowsky, G.: Schwefel-, Kohlenstoff- und Sauerstoff-Isotopen-untersuchungen am Kupferschiefer als Beitrag zur genetischen Deutung. Contrb. Mineral. Petrol. 22:290–334 (1969)
Mauger, R.L.: A sulfur isotope study of the Ducktown, Tennessee district, U.S.A. Econ. Geol. 67:497–510 (1972)
McDuff, R.E., Edmond, J.M.: On the fate of sulfide during hydrothermal circulation of mid-oceanic ridges. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 57:117–132 (1982)
Nair, N.G.K., Agarwal, N.K.: Primary and secondary structures in the polymetallic ores of Rajpura-Dariba, Rajasthan, India. Mineralium Deposita 11:352–356 (1976)
Nielsen, H.: Sulfur isotopes. In: Lectures in isotope geology (Jäger, E., Hunzicker, J.C., ed.) pp 283–312. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1979
Oehler, D.Z., Schopf, J.W., Kvenvolden, K.A.: Carbon isotopic studies of organic matter in Precambrian rocks. Science 175:1246–1248 (1972)
Ohmoto, H., Rye, R.O.: Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In: Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits (Barnes, H.L. ed.), 2nd ed. pp 509–567. Wiley 1979
Poddar, B.C.: Evolution of sedimentary sulphide rhythmites into metamorphic tectonites in base metal deposits of Rajpura-Dariba, Rajasthan. Quart. J. Geol. Min. Med. Soc. India (Golden Job. vol.) 46:207–221 (1974)
RajaRao, C.S., Poddar, B.C., Chatterjee, A.K.: Dariba-Rajpura-Bethumni belt of zinc-lead-copper mineralization, Udaipur district, Rajasthan. Geol. Surv. India Misc. Publ. 16 (2): 617–626 (1972)
Ricke, W.: Präparation von Schwefeldioxid zur massenspektrometrischen Bestimmung des S-Isotopenverhältnisses in natürlichen S-Verbindungen. Z. Anal. Chem. 199:401 (1964)
Rye, R.O., Ohmoto, H.: Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: a review. Econ. Geol. 69:826–842 (1974)
Rye, D.M., Rye, R.O.: Homestake gold mine, South Dakota: I Stable isotope studies. Econ. Geol. 69:293–307 (1974)
Sangster, D.F.: Sulfur and lead isotopes in strata-bound deposits. In: Handbook of strata-bound and stratiform ore deposits (Wolf, K.H. ed.) pp 219–266. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1976
Schwarcz, H.P., Burnie, S.W.: Influence of sedimentary environments on sulfur isotope ratios in clastic rocks: a review. Mineralium Deposita 8:264–277 (1973)
Shanks, W.C. III, Bischoff, J.L.: Geochemistry, sulfur isotope composition, and accumulation rates of Red Sea geothermal deposits. Econ. Geol. 75:445–459 (1980)
Shanks, W.C. III, Bischoff, J.L., Rosenbaur, R.J.: Seawater sulfate reduction and sulfur isotope fractionation in basaltic systems: interaction of sea water with fayalite and magnetite at 200–350°C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 45:1977–1995 (1981)
Styrt, M., Brackmann, A., Holland, H.D., Clark, B., Pisutha-Arnold, V., Eldridge, C., Ohmoto, H.: The mineralogy and isotopic composition of sulfur in hydrothermal sulfide/sulfate deposits on the East Pacific Rise, 21 °N latitude. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 53:382–390 (1981)
Sugden, T.J., Deb, M., Windley, B.F.: The tectonic setting of mineralisation in the Proterozoic Arvalli-Delhi orogenic belt, N. W. India (under preparation)
Trudinger, P.A., Lambert, I.B., Skyring, G.W.: Biogenic sulfide ores: a feasibility study. Econ. Geol. 67:1114–1127 (1972)
Veizer, J., Hoefs, J.: The nature of O18/O16 and C13/C12 secular trends in sedimentary carbonate rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 40:1387–1395 (1976)
Wedepohl, K.H.: The geochemistry of the Kupferschiefer bed in central Europe. In: European copper deposits (Jankovic, S., Sillitoe, R.H. ed.) pp 129–135. Belgrade 1980
Williams, N., Rye, D.M.: Alternative interpretation of sulfur isotope ratios in the McArthur lead-zinc-silver deposit. Nature 247:535–537 (1974)
Zierenberg, R.A., Shanks, W.C. III, Bischoff, J.L.: Massive sulfide deposit at 21 °N, East Pacific Rise: chemical composition, stable isotopes, and phase equilibria. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 95:922–929 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deb, M. Sulfur and carbon isotope compositions in the stratiform Zn-Pb-Cu sulfide deposits of the Rajpura-Dariba belt, Rajasthan, NW India: A model of ore genesis. Mineral. Deposita 21, 313–321 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204350
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204350