Abstract
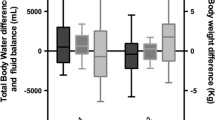
Findings in 76 subjects without cardiac failure were analyzed to detect relationships between observed changes in transthoracic electrical impedance (TEI) and total body extracellular fluid volume (ECFV) during various manoeuvres and between absolute TEI and ECFV values. TEI was normalized to electrode distance (Z0/gDel) and ECFV to lean body mass (ECFV/LBM). A distircet relation was found between percent changes of TEI and ECFV (r=-0.76, p<0.0001) and between absolute Z0/Δel and ECFV/LBM values (r=-0.66, p<0.0001 for men; r=-0.61, p<0.0001 for women). It is concluded that in the same subject a change in TEI is possibly a sensitive index for a change in ECFV and that a single measurement of TEI, normalized to electrode distance, gives information about the state of hydration (ECFV) of patients without cardiac failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer P, Roos JC, Geyskes GG, Dorhout Mees EJ (1979) Measurement of cardiac output by impedance cardiography under various conditions. Am J Physiol 237:H491
Hume R, Weyers E (1971) Relationship between total body water and surface area in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Pathol 24:234
Keller G, Blumberg A (1977) Monitoring of pulmonary fluid volume and stroke volume by impedance cardiography in patients on hemodialysis. Chest 72:56
Kubicek WG, Karnegis JN, Patterson RP, Witsoe DA, Mattson RH (1966) Development and evaluation of an impedance cardiac output system. Aerospace Med 37:1208
Luepker RV, Michael JR, Warbasse JR (1973) Transthoracic electrical impedance: quantitative evaluation of a non-invasive measure thoracic fluid volume. Am Heart J 85:83
Planque BA de, Geyskes GG, Dongen R van, Dorhout Mees EJ (1965) Simultaneous determination of extracellular volume and blood volume with the volumetron. Clin Chim Acta 11:270
Pomerantz M, Delgado F, Eiseman B (1970) Clinical evaluation of transthoracic electrical impedance as a guide to intrathoracic fluid volumes. Ann Surg 171:686
Rathbun EN, Pace N (1945) Studies on body composition. I. The determination of total body fat by means of the body specific gravity. J Biol Chem 158:667
Water JM van de, Mount BE, Barela JR, Schuster R, Leacock B (1973) Monitoring the chest with impedance. Chest 64:597
Womersley J, Boddy K, King PC, Durnin JVGA (1972) A comparison of the fat-free mass of young adults estimated by anthropometry, body density and total body potassium content. Clin Sci 43:469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roos, J.C., Koomans, H.A., Boer, P. et al. Transthoracic electrical impedance as an index of extracellular fluid volume in man. Intensive Care Med 11, 39–42 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256064
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256064