Abstract
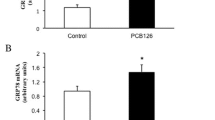
One i.p. injection of PCB induces a high stimulation of rat liver microsomal drug oxidizing enzymes; equimolar doses of tetrachlorobiphenyls are distinctly more effective then dichlorobiphenyls. The effect can still be demonstrated distinctly four weeks after application. During this time the liver concentration of tetrachlorobiphenyls decreased to 7μg/g tissue whereas the concentration of adipose tissue rose to 252 μg/g. By stress tetrachlorobiphenyls are mobilized along with fat, causing an increase of liver concentration to 32μg/g. Simultaneously, a new stimulation of microsomal activity can be seen, nearly equal to the maximum stimulation 4 days after i.p. application of 500 mg/kg b.w. Parallel to microsomal stimulation there is an increase of relative liver weight.
Stress induced activation of microsomal activity caused by PCB redistribution is important for the evaluation of PCB in environmental toxicology, in view of rising PCB concentrations in human adipose tissue.
Zusammenfassung
An Ratten wird durch einmalige intraperitoneale Gabe von PCB eine starke mikrosomale Aktivitätssteigerung ausgelöst; dabei sind äquimolare Dosen von Tetrachlordiphenyl deutlich stärker wirksam als Dichlordiphenyl. Auch 4 Wochen nach Applikation ist der Induktionseffekt noch deutlich nachweisbar, der Tetrachlordiphenylgehalt der Leber ist während dieser Zeit auf ca. 7 μg/g abgesunken, weil eine Umlagerung ins Fettgewebe erfolgt mit einer Tetrachlordiphenylkonzentration von 252 ⧎g/g. Unter Stressbedingungen wird dieses Tetrachlordiphenyl mit dem Fett mobilisiert und erhöht die Tetrachlordiphenylkonzentration in der Leber auf 32 μg/g. Gleichzeitig setzt eine erneute mikrosomale Stimulation ein, die das Maximum der Anfangsstimulation nach 500 mg/kg Tetrachlordiphenyl i.p. fast erreicht.
Parallel mit zunehmender mikrosomaler Aktivitätssteigerung läuft eine Zunahme des relativen Lebergewichts.
Der Nachweis der durch Stress ausgelösten mikrosomalen Aktivitätssteigerung ist angesichts der steigenden PCB-Konzentration im menschlichen Fettgewebe für die Bewertung des PCB's in der Umwelttoxikologie von Bedeutung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bagley, G. E., Reichel, W. L., Cromartie, F.: Identification of polychlorinated biphenyls in two bald eagles by combined gas-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Ass. Offic. Anal. Chem. 53, 251 (1970).
Benthe, H. F., Knop, J., Schmoldt, A.: Aufnahme und Verteilung nach Inhalation polychlorierter Biphenyle (PCB). Arch. Toxikol. 29, 85–95 (1972).
Biros, E. J., Walker, A. C., Medbary, A.: PCB's in human adipose tissue. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 5, 371 (1970).
Brown, J. R.: The effect of environment and dietary stress on the concentration of DDT in rats. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 17, 504 (1970).
Dale, W. E., Gaines, T. B., Hayes, W. J.: Storage and excretion of DDT in starved rats. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 4, 89 (1962).
Duke, T. W., Lowe, J. J., Wilson, A. J., Jr.: A polychlorinated Biphenyl (Arochlor 1254) in the water, sediment and biota of Escambia Bay, Florida. Bull. Environ. Contain. Toxicol. 5, 171 (1971).
Findlay, G. M., Freitag, A. S. W. de.: DDT movement from adipocyte to muscle cell during lipid utilization. Nature (Lond.) 229, 63 (1971).
Ghazal, A., Koransky, W., Portig, J., Klempau, J.: Beschleunigung von Entgiftungsreaktionen durch verschiedene Insektizide. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 249, 1 (1964).
Gram, T. E., Guarino, A. M., Schroeder, D. H., Davis, D. C., Reagan, R. L., Gilette, J. R.: The effect of starvation on the kinetics of drug oxidation by hepatic microsomal enzymes from male and female rats. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 175, 12 (1970).
Grant, D. L., Phillips, W. E., Villeneuve, D. C.: Metabolism of a polychlorinated Biphenyl (Arochlor 1254) mixture in the rat. Bull environ. Contam. Toxicol. 6, 102 (1971).
Holmes, D. C., Simmons, J. H., Tatton, O. G.: Chlorinated hydrocarbons in British wildlife. Nature (Lond.) 216, 227 (1967).
Kato, R.: Effects of starvation and refeeding on the oxidation of drugs by liver microsomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 16, 871 (1967).
Koeman, J. H., Noever, de Brauw, M. C. ten, Vos, R. H. de: Chlorinated Biphenyls in fish, mussels and birds from river Rhine and the Netherlands coastal area. Nature (Lond.) 221, 1126 (1969).
Orrenius, S., Ernster, L.: Phenobarbital induced synthesis of the oxidative demethylating enzymes of rat liver microsomes. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 16, 60 (1964).
Netter, K. J.: Untersuchungen über die Hemmung des oxidativen und hydrolytischen Arzneimittelstoffwechsels. Habilitation, Hamburg 1963.
Nissen, K.: Der Einfluß chlorierter Diphenyle auf die Leberfunktion von Ratten. Dissertation, Hamburg 1970.
Peakall, D. B., Lincer, J. C.: Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Another long life wide spread chemical in the environment. Biol. Sci. 20, 958 (1970).
Quentin, K. E.: Pestizide im Wasser — Bestimmung, Entfernung und Grenzwert. Vortrag, Hamburg 1972.
Risebrough, R. W., Rieche, P., Peakall, D. B., Hermann, S. G., Kirven, M. N.: PCB in the global Ecosystems. Nature (Lond.) 220, 1098 (1968).
Villeneuve, D. C., Grant, D. L., Phillips, E. J., Clark, M. L., Clegg, O. J.: Effects of PCB administration on microsomal enzyme activity in pregnant rabbits. Bull. Environ, Contam. Toxicol. 6, 120 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit dankenswerter Unterstützung durch das Bundesministerium für Jugend, Familie und Gesundheit.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benthe, H.F., Schmoldt, A. & Schmidt, H. Induktion mikrosomaler Leberenzyme nach einmaliger Gabe von polychlorierten Biphenylen (PCB) und anschließender Stress-Situation. Arch. Toxikol. 29, 97–106 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310974
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310974