Abstract
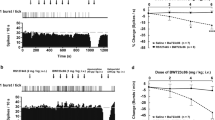
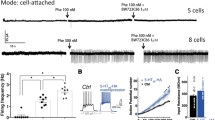
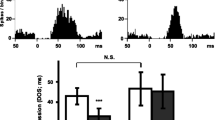
In this study we have examined the acute effects of systemic administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), citalopram, in combination with either of the two selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonists, (S)-5-fluoro-8-hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino)-tetralin [(S)-UH-301] or (+)-N-tertbutyl 3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-phenylpropionamide dihydrochloride [(+)-WAY100135], on the activity of single 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) of anesthetized rats using extracellular recording techniques. Acute administration of citalopram (0.3 mg/kg i.v.) significantly decreased the firing rate of DRN-5-HT cells most likely as a result of indirect stimulation of inhibitory somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors located on 5-HT cells in the DRN. This effect of citalopram was completely reversed by (S)-UH-301 (0.5 mg/kg i.v.) and partly by (+)WAY100135 (0.5 mg/kg i.v.). Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of citalopram on the activity of 5-HT neurons was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with (S)-UH-301 (0.25 mg/kg i.v.) or (+)-WAY100135 (0.25 mg/kg i.v.).
We have also studied the effects of (S)-UH-301 (0.03–0.50 mg/kg i.v.) on the firing rate of single DRN5-HT cells in rats chronically treated with citalopram (20 mg/kg/day i.p. × 14 days). Administration of (S)UH-301 significantly and dose-dependently increased the activity of 5-HT cells in citalopram-treated rats, but did not affect these neurons in saline-treated (1 m1/kg/day i.p. × 14 days), control rats. Our results thus suggest that 5-HT1A receptor antagonists can augment both the acute and chronic effects of citalopram on central serotonergic neurotransmission. Since the antidepressant effect of SSRIs is critically linked to the availability of 5-HT, these findings support the notion that 5-HT1A receptor antagonists may not only shorten the latency of onset of SSRIs in the treatment of depression, but also increase their efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adell A, Artigas F (1991) Differential effects of clomipramine given locally or systemically on extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in raphe nuclei and frontal cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:237–244
Aghajanian GK (1978) Tolerance of locus coeruleus neurones to morphine and suppression of withdrawal response by clonidine. Nature 278:186–188
Aghajanian GK, Wang RY, Barban J (1978) Serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons of the dorsal raphe: reciprocal changes in firing induced by peripheral nerve stimulation. Brain Res 153:169–175
Arborelius L, Chergui K, Murase S, Nomikos GG, Backlund Höök B, Chouvet G, Hacksell U and Svensson TH (1993) The 5-HT1A receptor selective ligands, (R)-8-OH-DPAT and (S)-UH-301, differentially affect the activity of midbrain dopamine neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347:353–362
Arborelius L, Backlund Höök B, Hacksell U, Svensson TH (1994) The 5-HT1A receptor antagonist (S)-UH-301 blocks the (R)-8OH-DPAT-induced inhibition of serotonergic dorsal raphe cell firing. J Neural Transm (GenSect) 96:179–186
Arnt J, Fredricson Overö K, Hyttel J, Olsen R (1984) Changes in rat dopamine- and serotonin function in vivo after prolonged administration of a specific 5-HT uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 84:457–465
Artigas F (1993) 5-HT and antidepressants: new views from microdialysis studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:262
Artigas F, Perez V, Alvarez E (1994) Pindolol induces a rapid improvement of depressed patients treated with serotonin reup-take inhibitors. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:248–251
Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK (1980) Suppression of firing activity of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 19:355–363
Beasley CM, Masica DN, Potvin JH (1992) Fluoxetine: a review of receptor and functional effects and their clinical implications. Psychopharmacology 107:1–10
Bech PA (1990) A meta-analysis of the antidepressant properties of serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Int Rev of Psychiatry 2:207–211
Bel N, Artigas F (1992) Fluvoxamine preferentially increases extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in the raphe nuclei: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 229:101–103
Bel N, Artigas F (1993) Chronic treatment with fluvoxamine increases extracellular serotonin in frontal cortex but not in raphe nuclei. Synapse 15:243–245
Björk L, Cornfield LJ, Nelson DL, Hillver S-E, Andén N-E, Lewander T, Hacksell U (1991) Pharmacology of the novel 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor antagonist (S)-5-fluoro-2-(dipropylamino)tetralin: Inhibition of (R)-8-hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino)tetralin-induced effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:58–65
Blier P, de Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological investigations on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1278
Blier P, de Montigny C (1994) Current advances and trends in the treatment of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:220–226
Blier P, de Montigny C, Tardif D (1984) Effects of the two anti-depressant drugs mianserin and indalpine on the serotonergic system: single-cell studies in the rat. Psychopharmacology 84:242–249
Blier P, Steinberg S, Chaput Y, de Montigny C (1988) Electrophysiological assessment of putative antagonists of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors: a single-cell study in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus, Can J Physiol Pharmacol 67:98–105
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1986) Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 33:342–348
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1991) Presynaptic and postsynaptic modifications of the serotonin system by long-term administration of antidepressant treatments. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:219–229
Delgado PL, Charney DS, Price LH, Aghajanian GK, Landis H, Heninger GR (1990) Serotonin function and the mechanism of antidepressant action. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:411–418
Edwards JG (1992) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [editorial]. Br Med J 304:1644–1646
Ferré S, Artigas F (1993) Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated regulation of serotonin extracellular concentration in the dorsal raphe nucleus of freely moving rats. J Neurochem 61:772–775
Ferré S, Cortés R, Artigas F (1994) Dopaminergic regulation of the serotonergic raphe-striatal pathway: microdialysis studies in freely moving rats. J Neurosci 14:4839–4846
Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Bill SJ, Cliffe IA, Dover GM, Forster EA, Haskins JT, Jones D, Mansell HL, Reilly Y (1993) WAY100135: a novel, selective antagonist at presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 237:283–291
Fredricson Overö K (1982) Kinetics of citalopram in test animals; drug exposure in saftey studies. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:297–309
Gallager DW, Aghajanian GK (1975) Effects of chloripramine and lysergic acid diethylamide on efflux of precursor-formed 3H-serotonin: correlations with serotonergic impulse flow. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193:785–795
Gallager DW, Aghajanian GK (1976) Effect of antipsychotic drugs on the firing of dorsal raphe cells. 1. Role of adrenergic system. Eur J Pharmacol 39:341–355
Hillver S-E, Björk L, Li Y-L, Svensson B, Ross S, Andén N-E, Hacksell U (1990) (S)-5-fluoro-8-hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino)-tetralin: A putative 5-HT1A-receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 33:1541–1544
Hjorth S (1993) Serotonin 5-HT1A autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo: a microdialysis study. J Neurochem 60:776–779
Hjorth S, Auerbach SB (1994) Further evidence for the importance of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol 260:251–255
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram — pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:277–295
Hyttel J, Fredricson Overö K, Arnt J (1984) chemical effects and drug levels in rats after long-term treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 83:20–27
Invernizzi R, Belli S, Samanin R (1991) An increase of extracellular serotonin in the dorsal raphe masks the effect of sertraline in the frontal cortex. In: Rollema H, Westerink BHC, Drijfhout WJ (eds) Monitoring molecules in neuroscience. University Centre for Pharmacy, pp 253–255
Invernizzi R, Belli S, Samanin R (1992) Citalopram's ability to increase the extracellular concentrations of serotonin in the dorsal raphe prevents the drug's effect in the frontal cortex. Brain Res 584:322–324
Invernizzi R, Bramante M, Samanin R (1994) Chronic treatment with citalopram facilitates the effect of a challange dose on cortical serotonin output: role of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 260:243–246
Jolas T, Haj-Dahmane S, Kidd EJ, Langlois X, Lanfumey L, Fattaccini CM, Vantalon V, Laporte AM, Adrien J, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1994) Central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in rats treated chronically with a the novel antidepressant, cericlamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1432–1443
Kreiss DS, Lucki I (1993) Repeated administration of the antidepressant fluoxetine, but not desipramine or mianserin, produces desesitization of 5-HT1A autoreceptors. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19:1867
Lanfumey L, Haj-Dahmane S, Hamon M (1993) Further assessment of the antagonist properties of the novel and selective 5-HT1A receptor ligands (+)-WAY100135 and SDZ216–525. Eur J Pharmacol 249:25–35
Lejeune F, Rivet J-M, Gobert A, Canton H, Millan M (1993) WAY100,135 and (−)-tertatolol act as antagonists at both 5-HT1A autoreceptors and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 240:307–310
Lesch K-P, Poten B, Söhnle K, Schulte HM (1990) Pharmacology of the hypothermic response to 5-HT1A receptor activation in humans. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39:17–19
Maj J (1986) Repeated treatment with antidepressant drugs: responses mediated by brain dopamine receptors. In: Hippius H, Klerman GL, Matussek N (eds) New results in depression research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 90–98
Martin-Iverson M, Leclere J-F, Fibiger HC (1983) Cholinergicdopaminergic interactions and the mechanism of action of anti-depressants. Eur J Pharmacol 94:193–201
Nomikos GG, Arborelius L, Svensson TH (1992) The novel 5-HT1A receptor antagonist (S)-UH-301 prevents (R)-8-OH-DPAT-induced decrease in interstitial concentrations of serotonin in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 216:373–378
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1980) Long-term antidepressant treatment decreases spiroperidol-labeled serotonin receptor binding. Science 210:88–90
Rasmussen K, Beitner-Johnson DB, Krystal JH, Aghajanian GK, Nestler EJ (1990) Opiate withdrawal and the rat locus coeruleus: behavioral, electrophysiological, and biochemical correlates. J Neurosci 10:2308–2317
Rigdon GC, Wang CM (1991) Serotonin uptake blockers inhibit the firing of presumed serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. Drug Dev Res 22:135–140
Routledge C, Gurling J, Wright IK, Dourish CT (1993) Neurochemical profile of the selective and silent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY100135: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 239:195–202
Rutter JJ, Gundlah C, Auerbach SB (1994) Increase in extracellular serotonin produced by uptake inhibitors is enhanced after chronic treatment with fluoxetine. Neurosci Lett 171:183–186
Sotelo C, Cholley B, El Mestikawy S, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1990). Direct immunohistochemical evidence of the existence of 5-HT1A autoreceptors on serotonergic neurons in midbrain raphe nuclei. Eur J Neurosci 2:1144–1154
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonist. Synapse 1:3–9
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1988) Responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to putative serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists: a comparative study with dorsal raphe neurons. Neuropharmacology 27:707–715
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC (1981) Behavioural evidence for supersensitivity of postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic system after chronic administration of desipramine. Eur J Pharmacol 74:195–206
Svensson TH (1978) Attenuated feed-back inhibition of brain serotonin synthesis following chronic administration of imipramine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 302:115–118
Svensson TH, Bunny BS, Aghajanian GK (1975) Inhibition of both noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in brain by the α-adrenergic agonist clonidine. Brain Res 92:291–306
Szabo B, Karsch V, Starke K (1992) Effects of inhibitors of neuronal uptake of 5-HT on sympathetic cardiovascular regulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 20:99–107
Vandermaelen CP, Aghajanian GK (1983) Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res 289:109–119
Yen TT, Wong DT, Bemis KG (1987) Reduction of food consumption and body weight of normal and obese mice by chronic treatment with fluoxetine: a serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Drug Dev Res 10:37–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arborelius, L., Nomikos, G.G., Grillner, P. et al. 5-HT1A receptor antagonists increase the activity of serotonergic cells in the dorsal raphe nucleus in rats treated acutely or chronically with citalopram. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 352, 157–165 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176769
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176769