Summary
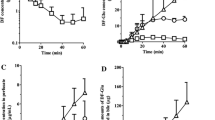
Rats treated with the hypolipidemic agent, nafenopin (SU-13, 437) exhibit a higher plasma retention and a markedly reduced biliary excretion of organic anions, such as sulfobromophthalein (BSP) and its dibromo analog (DBSP), indocyaninegreen (ICG), succinylsulfathiazole (SST) and polar metabolites of bilirubin and the carcinogens 7, 12-dimethylbenzanthracene (DMBA) and 3,4-benz-pyrene (BP), despite an increase in liver mass and a profound choleresis. However, taurocholate is not affected in this manner, which supports the idea of a transport mechanism for taurocholate that differs from that of other organic anions. A pharmacokinetic study was made for DBSP in vivo. After nafenopin treatment, primary hepatic uptake (k12) and transport from liver into bile (k23) are reduced in vivo. Infusion studies indicate that biliary transport maximum (Tm) for DBSP is also decreased although the calculated hepatic storage (S) is only moderately affected. In the isolated perfused liver, hepatic clearance and biliary excretion of BSP are reduced by two-thirds. The time course of anion tranport inhibition and the hepato-biliary disposition of 14C-nafenopin suggest a direct effect of the drug. The extra liver mass induced by nafenopin appears to be hypo- or nonfunctional with respect to hepatic transport of organic anions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-El-Makarem, M. M., Millburn, P., Smith, R. L.: Biliary excretion of 14C-succinylsulphathiazole in the rat and rabbit. Biochim. J. 105, 1295–1299 (1967)
Alpert, S., Mosher, M., Shanske, A., Arias, I. M.: Multiplicity of hepatic excretory mechanism for organic anions. J. gen. Physiol. 53, 238–247 (1969)
Avoy, D. R., Swyryd, A. E., Gould, R. G.: Effectw of α-p-chlorphenoxyisobutyryl ethyl ester (CPIB) with and without androsterone and cholesterol biosynthesis in rat liver. J. Lipid Res. 6, 369–376 (1965)
Barber-Riley, G., Goetzee, A. E., Richards, T. G., Thomson, J. Y.: The transfer of bromsulphthalein from the plasma to the bile in man. Clin. Sci. 20, 149–159 (1961)
Barnhart, J., Ritt, D., Ware, A., Combes, B.: A comparison of the effects of taurocholate and theophylline on BSP excretion in dogs: in The Liver. Quantitative Aspects of Structure and Function, ed. by G. Paumgartner and R. Preisig, pp. 315–325. Basel: S. Karger 1973
Best, M. M., Duncan, C. H.: Lipid effects of a phenolic ether (Su-13437) in the rat: comparison with CPIB. Atherosclerosis 12, 185–192 (1970)
Clarenburg, R., Kao, C.: Shared and separate pathways for biliary excretion of bilirubin and BSP in rats. Amer. J. Physiol. 225, 192–200 (1973)
Erlinger, S., Dumot, M.: Influence of canalicular bile flow on sulfobromophthalein transport maximum in bile in the dog. In: The Liver, Quantitative Aspects of structure and Function, ed. by G. Paumgartner and R. Preising, pp. 306–314. Basel: S. Karger 1973
Gibson, G. E., Forker, E. L.: Canalicular bile flow and bromosulfophthalein transport maximum: the effect of a bile salt-independent choleretic SC-2644. Gastroenterology 66, 1046–1053 (1974)
Hess, R., Maier, R., Staubli, W.: Evaluation of Phenolic Ethers as hypolipidaemic agents: Effects of CIBA 13, 437-SU. Advanc. exp. Med. Biol. 4, 483–489 (1969)
Jaross, W., Schentke, K. U.: Studies on the kinetics of Wofaverdin and Bromsulfan® on the model of a perfused rat liver. Acta biol. med. germ. 22, 287–294 (1969)
Javitt, N. B.: Phenol-3,6-dibromphthalein disulfonate, a new compound for the study of liver disease. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 177, 254–257 (1964)
Kelman-Sraer, J., Erlinger, S., Peignoux, M., Benhamou, J. P.: Influence of dehydrocholate on hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of rose bengal in the rabbit. Biomedicine 19, 415–418 (1973)
Klaassen, C. D.: Extra hepatic distribution of sulfobromophtalein. Pharmacologist 16, 283 (1974)
Klaassen, C. D., Plaa, G. L.: Determination of sulfobromophthalein storage and excretory rate in small animals. J. appl. Physiol. 22, 1151–1155 (1967)
Klaassen, C. D., Plaa, G. L.: Studies on the mechanism of phenobarbital enhanced sulfobromophthalein disappearance. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 161, 361–366 (1968)
Levine, W. G.: The role of microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes in the biliary excretion of 3,4-benzpyrene in the rat. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 175, 301–310 (1970)
Levine, W. G.: Hepatic uptake, metabolism and biliary excretion of 7,12-dimethyl benzanthracene in the rat. Drug Metab. Disp. 2, 169–177 (1974a)
Levine, W. G.: Effect of the hypolipidemic drug nafenopin (2-methyl-2-{p-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthyl) phenoxyl} propionic acid; TPIA; SU-13,437) on the hepatic disposition of foreign compounds in the rat. Drug. Metab. Disp. 2, 178–186 (1974b)
Levine, W. G., Braunstein, I. R., Meijer, D. K. F.: Effect of nafenopin (SU-13,437) on liver function. Mechanism of choleretic effect. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 290, 221–234 (1975)
Macarol, V., Morris, T. Q., Baker, K. J., Bradley, S. E.: Hydrocortisone choleresis in the dog. J. clin. Invest. 49, 1714–1723 (1970)
Mc Intyre, N., Mulligan, R., Carson, E.: BSP Tm and S. A critical re-evaluation. In: The liver. Quantitative Aspects of Structure and Function, ed. by G. Paumgartner and R. Preisig, pp. 417–427. Basel: S. Karger 1973
Meijer, D. K. F., Bognacki, J., Levine, W. G.: Effect of nafenopin (SU-13,437) on liver function. Hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of ouabain. Drug Metab. Disp. 3, 220–225 (1975)
Meijer, D. K. F., Bos, E. S., Van der Laan, K. J.: Hepatic transport of mono and bisquaternary ammonium compounds. Europ. J. Pharmacol., 11, 371–377 (1970)
Ohnhaus, E. E., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Davies, D. S., Breckenridge, A.: Changes in liver blood flow during enzyme induction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20, 2561–2570 (1971)
O'Maille, E. R. L., Richards, T. G., Short, A. H.: Factors determining the maximal rate of organic anion secretion by the liver and further evidence on the hepatic site of action of the hormone secretin. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 186, 424–438 (1966)
Peterson, R. E., Fujimoto, J. M.: Biliary excretion of morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-3-etheral sulfate by different pathways in the rat. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 184, 409–418 (1973)
Plaa, G. L., Hine, C. H.: The effect of carbon tetrachloride on isolated perfused rat liver function. Arch industr. Hlth 21, 114–123 (1960)
Quarfordt, S. H., Hilderman, H. L., Valle, D., Waddell, E.: Compartmental analysis of sulfobromophthalein transport in normal patients and patients with hepatic dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 60, 246–255 (1971)
Reyes, H., Levi, A. J., Gatmaitan, Z., Arias, I. M.: Organic anion-binding protein in rat liver: drug induction and its physiological consequence. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 64, 168–170 (1969)
Richards, T. G., Tindall, V. R., Young, A.: A modification of the bromsulphthalein liver function test to predict the dye content of the liver and bile. Clin. Sci. 18, 499–511 (1959)
Schanker, K. S.: Handbook of Physiology, Section 6: Alimentary Canal, Vol. 5, Chapter 114, pp. 2433–2449. Washington, D. C.: American Physiological Society 1968
Smith, R. L.: The excretory function of bile. The Elimination of drugs and toxic substances in the bile. London: Chapman and Hall 1973
Vonk, R. J., v.d. Veen, H., Prop, G., Meijer, D. K. F.: The influence of taurocholate and dehydrocholate choleresis on plasma disappearance and biliary excretion of indocyanine green in the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 282, 401–410 (1974)
Wheeler, H. O., Meltzer, J. T., Bradley, S. E.: Biliary transport and hepatic storage of sulfobromophthalein sodium in the anesthetized dog, in normal man and in patients with hepatic desease. J. clin. Invest. 39, 13–114 (1960)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by U.S. Public Health Service Grant CA 14231 from the National Cancer Institute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meijer, D.K.F., Bognacki, J. & Levine, W.G. Effect of nafenopin (SU-13, 437) on liver function. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 290, 235–250 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510553
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00510553