Summary
The effects of locally administered apomorphine and pergolide were studied in the isolated autoperfused hindquarters of the rat, in an attempt to assess the possible role of presynaptic dopamine receptors at the level in the hypotensive effect of these dopamine agonists.
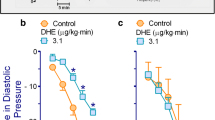
Local infusion of apomorphine (1μg·kg−1·min−1 for 5 min) or pergolide (1μg·kg−1·min−1 for 5 min) [into the hindquarters] did not alter perfusion pressure per se, but reduced the pressor response to electrical stimulation of the lumbar sympathetic chains for the whole frequency range used during a cumulative frequency-response curve (0.25–16 Hz, 1 ms, supramaximal voltage). Apomorphine and pergolide reduced the pressor response elicited by 4 Hz electrical stimulation (applied until maximum response was reached) to 54.8±7.1% and 53.9±1.7% respectively, but they did not modify similar increases of perfusion pressure produced by locally administered noradrenaline.
The inhibition by apomorphine and pergolide of the 4 Hz stimulation-evoked pressor response was completely antagonized by local administration of the dopamine antagonist haloperidol (1μg·kg−1), but was not influenced by the α2-antagonist rauwolscine (100μg·kg−1). This dose of rauwolscine antagonized the inhibitory effect of the α2-agonist UK-14,304, which was not influenced by haloperidol.
Local administration of rauwolscine increased the pressor response to stimulation at 4 Hz by 37.4–46.2%. In contrast, local administration of haloperidol did not influence the 4 Hz stimulation-evoked pressor response.
These results indicate that dopamine receptors are pressent on the sympathetic innervation of the vascular bed in the rat hindquarters but do not provide evidence for a physiological role of these receptors in modulating peripheral sympathetic neurotransmission. Stimulation of these receptors, leading to a decrease of noradrenaline release and thus of vasomotor tone, might—at least in part—explain the blood pressure lowering effects of intravenous apomorphine and pergolide in the rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett A, Fiore JW (1971) Hypotensive effects of apomorphine in anaesthetized cats. Eur J Pharmacol 14:206–208
Barrett RJ, Lokhandwala MF (1983) Central and peripheral dopaminergic mechanisms in the cardiovascular actions of pergolide in neurogenic hypertensive dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 96:211–226
Bogaert MG, Buylaert WA, Willems JL (1978) Hypotension produced by intravenous apomorphine in the anaesthetized dog is not centrally mediated. Br J Pharmacol 63:481–484
Bogaert MG, Dupont AG, Lefebvre RA (1984) Effect of apomorphine on neurogenic vasoconstriction in the isolated autoperfused hindquarters of the rat. Brit J Pharmacol 83:410P
Brody MJ, Shaffer RA, Dixon RL (1963) A method for the study of peripheral vascular responses in the rat. J Appl Physiol 18:645–647
Buylaert WA, Willems JL (1976) Effects of apomorphine on vena saphena lateralis strips of the dog. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 223:162–163
Buylaert WA, Willems JL, Bogaert MG (1977) Vasodilatation produced by apomorphine in the hindleg of the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:738–746
Cavero I (1982) Effects of pergolide, a dopamine receptor agonist, and clonidine on cardiovascular responses evoked by activation of peripheral sympathetic outflow in rats. Clin Exp Hypertens A 4:221–233
Cavero I, Lefevre-Borg F, Gomeni R (1981) Blood pressure lowering effects of N,N-di-n-propyldopamine in rats: evidence for stimulation of peripheral dopamine receptors leading to inhibition of sympathetic tone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218:515–524
Cavero I, Massingham R, Lefevre-Borg F (1982) Peripheral dopamine receptors, potential targets for a new class of antihypertensive agents. Part II: Sites and mechanisms of action of dopamine receptor agonists. Life Sci 31:1059–1069
Cavero I, Lefevre-Borg F, Lhoste F, Sabatier C, Richer C, Giudicelli JF (1984) Pharmacological, hemodynamic and autonomic nervous system mechanisms responsible for the blood pressure and heart rate lowering effects of pergolide in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:779–791
Clapham JC, Hamilton TC (1982) Presynaptic dopamine receptors mediate the inhibitory action of dopamine agonists on stimulation-evoked pressor responses in the rat. J Auton Pharmacol 3:181–188
Clark BJ (1977) Dopamine receptor stimulants in hypertension. Acta Med Scand (Suppl) 606:95–99
Davey MJ (1980) Relevant features of the pharmacology of prazosin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2:5287–5301
Dubocovich ML, Langer SZ (1980) Dopamine and alpha-adrenoceptor agonists inhibit neurotransmission in the cat spleen through different presynaptic receptors J Pharmacol Exp Ther 212:144–152
Dupont AG, Lefebvre RA, Bogaert MG (1984) Inhibition of neurogenic vasoconstriction in the isolated autoperfused hindquarters of the rat by pergolide. Proc 5th Symposium on vascular neuroeffector mechanisms, Paris, August 5–8, 1984. Blood Vessels 21:187
Finch L, Haeusler G (1973) The cardiovascular effects of apomorphine in the anaesthetized rat. Eur J Pharmacol 21:264–270
Fuder H, Muscholl E (1978) The effect of dopamine on the overflow of endogenous noradrenaline from the perfused rabbit heart evoked by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 305:109–115
Goldberg LI, Volkman PM, Kohli JD (1978) A comparison of the vascular dopamine receptor with other dopamine receptors. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 18:57–79
Grant JA, Scrutton MC (1980) Interaction of selective α-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists with human and rabbit blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol 71:121–134
Hahn RA (1981) Inhibitory effects of pergolide on peripheral adrenergic neurotransmission in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life Sci 29:2501–2509
Hahn RA, MacDonald BR, Martin MA (1983) Antihypertensive activity of LY-141865, a selective presynaptic dopamine receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:206–214
Jadhav AL, Willett RN, Sapru HN, Lokhandwala MF (1983) Involvement of central dopamine receptors in the hypotensive action of pergolide. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 324:218–286
Langer SZ (1977) Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmittor release. Br J Pharmacol 60:481–497
Langer SZ (1980) Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev 32:337–362
Laubie M, Schmitt H (1978) Inhibitory effects of piribedil on adrenergic neurotransmission Eur J Pharmacol 52:99–107
Lefevre-Borg F, Cavero I (1980) Stimulation of peripheral dopamine receptors: a mechanism of novel antihypertensive agents. Clin Sci 59:291s-294s
Lokhandwala MF, Barrett RJ (1982) Cardiovascular dopamine receptors: physiological, pharmacological and therapeutic implications. J Auton Pharmacol 3: 189–215
Lokhandwala MF, Buckley JP (1976) Effect of presynaptic α-adrenoceptor blockade on responses to cardiac nerve stimulation in anesthetized dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 40:183–186
Lokhandwala MF, Buckley JP (1977a) Analysis of presynaptic inhibitory actions of various dopamine analogs on sympathetic neurotransmission in mongrel dogs Life Sci 20:507–516
Lokhandwala MF, Buckley JP (1977b) Presynaptic dopamine receptors as mediators of dopamine-induced inhibition of neurogenic vasoconstriction. Eur J Pharmacol 45:305–309
Massingham R, Dubocovich ML, Langer SZ (1980) The role of presynaptic receptors in the cardiovascular actions of N,N-di-n-propyldopamine in the cat and dog. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 314:17–28
Mugabo P, Buylaert W, Bogaert M (1983) Cardiovascular effects of apomorphine in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 262:324–325
Patil PN, Burkman AM, Yamauchi D, Hetey S (1973) Analysis of the effect of apomorphine and bulbocapnine in relation to the proposed dopamine receptor. J Pharm Pharmacol 25:221–228
Yen TT, Stamm NB, Clemens JA (1979) Pergolide: a potent dopaminergic antihypertensive. Life Sci 25:209–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dupont, A.G., Lefebvre, R.A. & Bogaert, M.G. Inhibitory effects of apomorphine and pergolide on neurogenic vasoconstriction in the hindquarters of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 329, 146–151 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501204
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501204