Summary
Some ligand-gated ion channels are important sites of action of ethanol. The aim of the study was to find out whether the P2X-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the rat isolated vas deferens also are selectively sensitive to ethanol. Contractions were elicited by ATP (1 mmol/1), α,ß-methylene ATP (0.3 μmol/1), noradrenaline (3 μmol/1), high K+ (20 mmol/1) or electrical (neural) stimulation by pairs of pulses 3 s apart. In electrical stimulation experiments, purinergic and adrenergic response components were isolated by prazosin and suramin, respectively. Concentration-effect curves were determined for ethanol and, for comparison, nifedipine. Tritium outflow from tissues preincubated with 3H-noradrenaline was also examined.
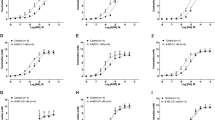
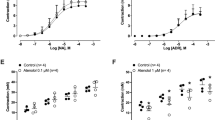
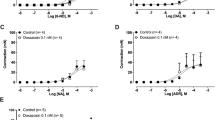
Ethanol at relatively low concentrations reduced contractions elicited by high K+ (IC30 145 mmol/1), ATP (IC30 211 mmol/1) and α,ß-methylene ATP(IC30 215 mmol/1) as well the purinergic component of neurogenic twitches (IC30 110-126 mmol/1; a significant effect at 10–32 mmol/1) and the adrenergic component of twitch 2 of the twitch pairs (IC30 63 mmol/1). These contractions also were very sensitive to nifedipine. Higher concentrations of ethanol were needed to reduce contractions elicited by noradrenaline (IC30 365 mmol/1) and the adrenergic component of twitch 1 of the twitch pairs (IC30 382 mmol/1), contractions that also were less sensitive to nifedipine. Ethanol 1 mol/l abolished all contractions. In contrast, concentration-effect curves for the inhibition by nifedipine of contractions evoked by ATP, α,ß-methylene ATP and noradrenaline (rapid phase) levelled off at 60–70% inhibition. The contractions that remained when these agonists were administered in the presence of nifedipine 10 μmol/l were depressed by ethanol (IC30 242–387 mmol/1). Ethanol 320 mmol/1 did not change the electrically evoked overflow of tritium from vasa deferentia preincubated with 3H-noradrenaline.
It is concluded that the P2X-purinoceptors of rat vas deferens smooth muscle, although ligand-gated ion channels, are not selectively sensitive to ethanol. The reduction of contractions can be explained by, first, an inhibition of L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels for which relatively low concentrations of ethanol are needed, and second, a “non-specific” depressant effect at an unknown site or at unknown sites which requires relatively high concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altura BM, Edgarian H, Altura BT (1976) Differential effects of ethanol and mannitol on contraction of arterial smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:352–361
Amobi NIB, Smith ICH (1987) Adrenergic and ‘non-adrenergic’ contributions to the two-component tetanus in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 135:173–182
Anderson K, Pollock D (1991) The effects of ethanol on responses of the rat isolated vas deferens to field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol 104:135P
Bean BP (1992) Pharmacology and electrophysiology of ATP-activated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:87–90
Benham CD (1989) ATP-activated channels gate calcium entry in single smooth muscle cells dissociated from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol (Lond) 419:689–701
Benham CD, Tsien RW (1987) A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature 328: 275–278
Blakeley AGH, Brown DA, Cunnane TC, French AM, McGrath JC, Scott NC (1981) Effects of nifedipine on electrical and mechanical responses of rat and guinea pig vas deferens. Nature 294:759–761
Bourreau JP, Zhang ZD, Low AM, Kwan CY, Daniel EE (1991) Ryanodine and the adrenergic, purinergic stimulation in the rat vas deferens smooth muscle: functional and radioligand binding studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:1063–1071
Bulloch JM, McGrath JC (1992) The effect of ethanol on responses of the isolated rabbit ileocolic artery. Eur J Pharmacol 211:1–8
Bultmann R, Starke K (1993) Chloroethylclonidine: an irreversible agonist at prejunctional α2-adrenoceptors in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 108:336–341
Bültmann R, von Kugelgen I, Starke K (1993) Effects of nifedipine and ryanodine on adrenergic neurogenic contractions of rat vas deferens: evidence for a pulse-to-pulse change in Ca2+ sources. Br J Pharmacol (in press)
Degani NC, Sellers EM, Kadzielawa K (1979) Ethanol-induced spontaneous norepinephrine release from the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 210:22–26
DeTurck KH, Pohorecky LA (1986) Development of tolerance to the inhibitory effects of ethanol in the rat isolated vas deferens: effect of acute and chronic ethanol administration in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 88:397–403
Gillespie JS, Hunter JC, McKnight AT (1982) The effect of ethanol on inhibitory and motor responses in the rat and rabbit anococcygeus and the bovine retractor penis muscles. Br J Pharmacol 75:189–198
Gonzales RA, Hoffman PL (1991) Receptor-gated ion channels may be selective CNS targets for ethanol. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:1–3
Göthert M, Thielecke G (1976) Inhibition by ethanol of noradrenaline output from peripheral sympathetic nerves: possible interaction of ethanol with neuronal receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 37:321–328
Göthert M, Dührsen U, Rieckesmann JM (1979) Ethanol, anaesthetics and other lipophilic drugs preferentially inhibit 5-hydroxytryptamine-and acetylcholine-induced noradrenaline release from sympathetic nerves. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 242:196–209
Graefe KH, Stefano FJE, Langer SZ (1973) Preferential metabolism of (−)-3H-norepinephrine through the deaminated glycol in the rat vas deferens. Biochem Pharmacol 22:1147–1160
Harris RA, Hood WF (1980) Inhibition of synaptosomal calcium uptake by ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 213:562–568
Hay DWP, Wadsworth RM (1982) Effects of some organic calcium antagonists and other procedures affecting Ca2+ translocation on KCl-induced contractions in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 76:103–113
Hay DWP, Wadsworth RM (1984) Effects of KCl on 45Ca uptake and efflux in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 81:441–447
Hedler L, Stamm G, Weitzell R, Starke K (1981) Functional characterization of central α-adrenoceptors by yohimbine diastereomers. Eur J Pharmacol 70:43–52
Kalsner S (1970) The potentiating effects of ethanol on responses of aortic strips to stimulant drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 22:877–879
Khoyi MA, Westfall DP, Buxton ILO, Akhtar-Khavari F, Rezaei E, Salaices M, Sanchez-Garcia P (1988) Norepinephrine and potassium induced calcium translocation in rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:917–923
Langer SZ (1974) Selective metabolic pathways for noradrenaline in the peripheral and in central nervous system. Med Biol 52:372–383
Leslie SW, Barr E, Chandler J, Farrar RP (1983) Inhibition of fast- and slow-phase depolarization-dependent synaptosomal calcium uptake by ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:571–575
MacKenzie I, Manzini S, Burnstock G (1988) Regulation of voltage-dependent excitatory responses to α,ß-methylene ATP, ATP and nonadrenergic nerve stimulation by dihydropyridines in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Neuroscience 27:317–332
Mallard N, Marshall R, Sithers A, Spriggs B (1992) Suramin: a selective inhibitor of purinergic neurotransmission in the rat isolated vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 220:1–10
Messing RO, Carpenter CL, Diamond I, Greenberg DA (1986) Ethanol regulates calcium channels in clonal neural cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:6213–6215
Nakazawa K, Matsuki N (1987) Adenosine triphosphate-activated inward current in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat vas deferens. Pflügers Arch 409:644–646
Porzig H (1990) Pharmacological modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels in intact cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 114:209–262
Schneider P, Hopp HH, Isenberg G (1991) Ca2+ influx through ATP-gated channels increments [Ca2+]i and inactivates ICa in myocytes from guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol (Lond) 440:479–496
Starke K (1977) Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 77:1–124
Starke K (1991) Selectivity of ethanol on ligand-gated ion channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:182
Starke K, Hedler L, Steppeler A (1981) Metabolism of endogenous and exogenous noradrenaline in guinea-pig atria. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:193–198
Szabo B, Schultheiss A (1990) Desipramine inhibits sympathetic nerve activity in the rabbit. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:469–476
Takeda R, Momose Y (1983) An inhibitory effect of ethanol on adrenergic neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Jpn J Pharmacol 33:757–764
Takeda R, Momose Y, Nakanishi S (1984) Effects of ethanol on calcium and potassium currents in single bullfrog atrial cells. Jpn J Pharmacol 36:422–424
Triggle CR, Swamy VC, Triggle DJ (1979) Calcium antagonists and contractile responses in rat vas deferens and guinea pig ileal smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 57:804–818
Vesperinas G, Feddersen M, Lewin J, Huidobro-Toro JP (1989) The use of ryanodine and calcium channel blockers to characterize intra-and extracellular calcium pools mobilized by noradrenaline in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 165:309–313
Von Kugelgen I, Bultmann R, Starke K (1989) Effects of suramin and αß-methylene ATP indicate noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the response of the mouse vas deferens to single and low frequency pulses. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:760–763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to R. Bultmann at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bultmann, R., Szabo, B. & Starke, K. Inhibition by ethanol of contractions of rat vas deferens: no evidence for selective blockade of P2X-purinoceptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 527–533 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166746
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166746