Abstract
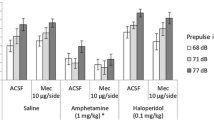
The effect of local injection of pertussis toxin (PTX) into the ventral tegmental area (VTA) on acoustic startle in rats was investigated. The PTX treatment caused only minor effects of its own on the acoustic startle response (ASR) or prepulse inhibition (PPI) of acoustic startle. However, systemic treatment with the indirect DA receptor agonist, amphetamine (2 mg/kg, SC) caused a significant increase in ASR magnitude and a significant disruption of PPI in PTX-treated rats while no such effects were observed in sham-treated rats. Treatment with the direct DA receptor agonist, apomorphine (2 mg/kg, SC), caused a significant disruption of PPI, an effect that was observed in both PTX-and sham-treated rats. Treatment with the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT (0.5 mg/kg, SC), did not affect PPI in either group but caused a marked increase in ASR magnitude in sham-treated rats. Interestingly, this effect was blocked in PTX-treated rats. The present results suggest that local injection of PTX into the VTA causes an increased sensitivity to the behavioural effects of psychostimulants on acoustic startle and may also suggest that intact midbrain 5-HT1A receptors are essential for the effect of 5-HT1A agonists on acoustic startle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Sprouse JS, Sheldon P, Rasmussen K (1990) Electrophysiology of the central serotonin system: receptor subtypes and transducer mechanisms. Ann NY Acad Sci 600:93–103
Andrade R, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA (1986) A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science 234:1261–1265
Braff DL, Grillon C, Geyer MA (1992) Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:206–215
Bunney BS, Walters JR, Roth RH, Aghajanian GK (1973) Dopaminergic neurons: effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 185:560–571
Butcher SP, Fairbrother IS, Kelly JS, Arbuthnott GW (1988) Amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the rat striatum: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 50:346–355
Caine SB, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1992) Hippocampal modulation of acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1201–1208
Davis M (1980) Neurochemical modulation of sensory-motor reactivity: acoustic and tactile startle reflexes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4:241–263
Davis M (1985) Cocaine: excitatory effects on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle. Psychopharmacology 86:31–36
Davis M, Aghajanian GK (1976) Effects of apomorphine and haloperidol in the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 47:217–233
Davis M, Cassella JV, Wrean WH, Kehne JH (1986) Serotonin receptor subtype agonists: differential effects on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:837–843
Gilman AG (1987) G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem 56:615–649
Hjorth S, Sharp T (1991) Effect of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT on the release of 5-HT in dorsal and medial raphe-innervated rat brain regions as measured by in vivo microdialysis. Life Sci 48:1779–1786
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. Some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system process sensory input. Psychol Rev 2:175–189
Innis RB, Aghajanian GK (1987a) Pertussis toxin blocks 5-HT1A and GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of serotoninergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 143:195–204
Innis RB, Aghajanian GK (1987b) Pertussis toxin blocks autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of dopaminergic neurons in the rat substantia nigra. Brain Res 411:139–143
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16:223–244
Kehne JH, Sorenson CA (1978) The effects of pimozide and phenoxybenzamine pretreatments on amphetamine and apomorphine potentiation of acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 58:137–142
Kokkinidis L (1986) Sensitization to amphetamine and tolerance to cocaine and phencyclidine stimulation in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:1175–1180
Lacey MG, Mercuri NB, North RA (1988) On the potassium conductance increase activated by GABAB and dopamine D2 receptors in rat substantia nigra neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 401:437–453
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
Nanry KP, Tilson HA (1989) The role of 5HT1A receptors in the modulation of the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 97:507–513
Peng RY, Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) A D2 dopamine receptor agonist disrupts sensorimotor gating in rats. Implications for dopaminergic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:211–218
Peroutka SJ, Schmidt AW, Sleight AJ, Harrington MA (1990) Serotonin receptor “families” in the central nervous system: an overview. Ann NY Acad Sci 600:104–113
Raiteri M, Bertollini A, Angelini F, Levi G (1975)d-Amphetamine as a releaser or reuptake inhibitor of biogenic amines in synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol 34:189–195
Rigdon GC, Weatherspoon JK (1992) 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1a receptor agonists block prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle reflex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:486–493
Steketee JD, Kalivas PW (1991) Sensitization to psychostimulants and stress after injection of pertussis toxin into the A10 dopamine region. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:916–924
Steketee JD, Striplin CD, Murray TF, Kalivas PW (1991) Possible role for G-proteins in behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Brain Res 545:287–291
Svensson L (1985) Effects of 8-OH-DPAT, lisuride and some ergot-related compounds on the acoustic startle response in the rat. Psychopharmacology 85:469–475
Svensson L, Ahlenius S (1983) Enhancement by the putative 5-HT receptor agonist 8-OH-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin of the acoustic startle response in the rat. Psychopharmacology 79:104–107
Svensson L, Harthon C, Linder B (1990) The role of the dopaminergic system in the modulation of the acoustic startle response in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 175:107–111
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9:321–353
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1993) Prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats after lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus. Behav Neurosci 107:104–117
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA, Koob GF (1986) Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:23–33
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Masten VL, Geyer MA (1990a) Schizophrenic-like sensorimotor gating abnormalities in rats following dopamine infusion into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 101:414–420
Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Pulvirenti L, Koob GF, Braff DL (1990b) Amphetamine disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle is reversed by depletion of mesolimbic dopamine. Psychopharmacology 100:413–416
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1991) Effects of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:530–536
Swerdlow NR, Caine SB, Geyer MA (1992) Regionally selective effects of intracerebral dopamine infusion on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 108:189–195
Tao R, Hjorth S (1992) Differences in the in vitro and in vivo 5-hydroxytryptamine extraction performance among three common microdialysis membranes. J Neurochem 59:1778–1785
Wang RY (1981) Dopaminergic neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. II. Evidence for autoregulation. Brain Res 3:141–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Engel, J.A., Hjorth, S. et al. Changes in the acoustic startle response and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats after local injection of pertussis toxin into the ventral tegmental area. Psychopharmacology 119, 71–78 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246056
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246056