Abstract
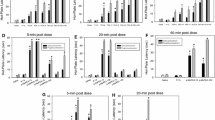
The narcotic antagonist naloxone was tested to determine its possible interaction with N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and lysergic acid diethylamide-25 (LSD) in adult male Holtzman rats trained to press a bar on a fixed-ratio four schedule (FR4), i.e., every fourth press earned a reward of 0.01 ml sugar sweetened milk. LSD (0.1 mg/kg) or increasing doses of DMT (1.0, 3.2, and 10.0 mg/kg) were administered i.p. to disrupt food-rewarded fixed ratio bar pressing in a dose related fashion. Pretreatment (5–10 min) with behaviorally ineffective doses of naloxone (1.0–5.6 mg/kg) dramatically enhanced the effects of DMT and LSD. The content of DMT in the brain and liver of rats injected with DMT alone (10 mg/kg) and with a 5 min pretreatment of naloxone (3.2 mg/kg) was determined by radiochemical analysis at 30 and 90 min after 14C-DMT injection. There was no significant difference for either brain or liver 14C-DMT levels when control DMT rats were compared with the naloxone pretreated rats. These results seem to rule out interference by naloxone with the metabolism of DMT as a mechanism of the observed behavioral potentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrist, B., Gershon, S., Sathananthan, G., Walker, R. W., Lopez-Ramos, B., Mandel, L., Van den Heuvel, W.: Dimethyltryptamine levels in blood of schizophrenic patients and control subjects. Psychopharmacology 47, 29–32 (1976)
Appel, J. B., Freedman, D. X.: The relative potencies of psychotomimetic drugs. Life Sci. 4, 2181–2186 (1965)
Belluzzi, J. D., Grant, N., Garsky, V., Sarantakis, D., Wise, C., Stein, L.: Analgesia induced in vivo by central administration of enkephalin in rat. Nature 260, 625–626 (1976)
Bloom, F., Segal, D., Ling, N., Guillemin, R.: Endorphins: Profound behavioral effects in rats suggest new etiological factors in mental illness. Science 194, 630–632 (1976)
Corbett, L., Christian, S. T., Morin, R. D., Benington, F., Smythies, J. R.: Hallucinogenic N-methylated indolealkylamines in cerebrospinal fluid of psychiatric and control populations. Br. J. Psychiatry 132, 139–144 (1978)
Davis, G. C., Bunney, W. E., DeFraites, E. G., Kleinman, J., Van Kammen, D., Post, R., Wyatt, R.: Intravenous naloxone administration in schizophrenia and affective illness. Science 197, 74–77 (1977)
Domino, E. F.: The indole hallucinogen model: Is it worth pursuing? In: Predictability in Psychopharmacology: Preclinical and clinical correlations, A. Sudilovsky, S. Gershon, and B. Beer, eds., pp. 247–268. New York: Raven Press 1975
Fertziger, A., Fischer, R.: Interaction between narcotic antagonist (naloxone) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in the rat. Psychopharmacology 54, 313–314 (1977)
Fischer, R.: A pharmacological and conceptual reevaluation of hallucinogens. Cofinia Psychiatr. 17, 143–151 (1974)
Gillin, J. C., Kaplan, J., Stillman, R., Wyatt, R. J.: The psychedelic model of schizophrenia: The case of N,N-dimethyltryptamine. Am. J. Psychiatry 133, 203–208 (1976)
Gitlin, M., Rosenblatt, M.: Possible withdrawal from endogenous opiates in schizophrenics. Am. J. Psychiatry 135, 377–379 (1978)
Gunne, L., Lindström, L., Terenius, L.: Naloxone-induced reversl of schizophrenic hallucinations. J. Neural. Transm. 40, 13–19 (1977)
Jacobsen, E.: The clinical pharmacology of the hallucinogens. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 4, 480–503 (1963)
Janowsky, D., Segal, D. S., Bloom, F., Abrams, A., Guillemin, R.: Lack of effect naloxone on schizophrenic symptoms. Am. J. Psychiatry 134, 926–928 (1977a)
Janowsky, D., Segal, D. S., Abrams, A., Bloom, F., Guillemin, R.: Negative naloxone effects in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 53, 295–297 (1977b)
Kovacic, B., Domino, E. F.: Tolerance and limited cross-tolerance to the effects of N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and lysergic acid diethylamide-25 (LSD) on food rewarded barpressing in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 197, 495–502 (1976)
Kovacic, B., Lu, L. J. Wang, Ruffing, D., Domino, E. F.: Interactions of partial LSD analogs with behavioral disrupting effects of LSD and DMT in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 47, 37–44 (1978)
Lord, J. A., Waterfield, A. A., Hughes, J., Kosterlitz, H. W.: Endogenous opioid peptides: Multiple agonists and receptors. Nature 267, 495–499 (1977)
Lu, L. J., Demetriou, S. D., Domino, E. F.: Effects of various neuroleptics, phenobarbital and SKF 525-A on dimethyltryptamine content in rat brain and liver. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 232, 117–133 (1978)
Lu, L. J., Wilson, A., Domino, E. F.: Correlation between brain N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) levels and barpressing behavior in rats. The Pharmacologist 16, 237 (1974)
Marx, J. L.: Neurobiology: Researchers high on endogenous opiates. Science 193, 1227–1229 (1976)
Mehl, E., Rüther, E., Redemann, J.: Endogenous ligands of a putative LSD-serotonin receptor in the cerebrospinal fluid: Higher level of LSD-displacing factors (LDF) in unmedicated psychotic patients. Psychopharmacology 54, 9–16 (1977)
Narasimhachari, N., Heller, B., Spaide, J., Haskovec, L., Meltzer, H., Strahilevitz, M., Himwich, H. E.: N,N-Dimethylated indoleamines in blood. Biol. Psychiatry 3, 21–23 (1971)
Oon, M. C., Murray, R. M., Rodnight, R., Murphy, M. P., Birley, J. L.: Factors affecting the urinary excretion of endogenously formed dimethyltryptamine in normal human subjects. Psychopharmacology 54, 171–175 (1977)
Snedecor, G. W.: Statistical Methods, Fifth Edition. Ames: Iowa State College Press 1956
Terenius, L., Wahlström, A., Agren, H.: Naloxone (Narcon) treatment in depression: Clinical observations and effects on CSF endorphins and monoamine metabolites. Psychopharmacology 54, 31–33 (1977)
Vogel, W. H., Evans, B. D.: Structure-activity relationships of certain hallucinogenic substances based on brain levels. Life Sci. 20, 1629–1636 (1977)
Watson, S., Berger, P., Akil, H., Mills, M., Barchas, J. D.: Effects of naloxone on schizophrenia: Reduction in hallucinations in a subpopulation of subjects. Science 201, 73–76 (1978)
Wyatt, R. J., Gillin, J. C., Kaplan, J., Stillman, R., Mandel, L., Ahn, H., Van den Heuvel, W., Walker, R.: N,N-Dimethyltryptamine — A possible relationship to schizophrenia. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 11, 299–313 (1974)
Wyatt, R. J., Saavedra, J. M., Axelrod, J.: A dimethyltryptamine (DMT) forming enzyme in human blood. Am. J. Psychiatry 130, 754–760 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruffing, D., Kovacic, B., Demetriou, S. et al. Naloxone enhancement of DMT and LSD-25 induced suppression of food-rewarded bar pressing behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology 62, 207–210 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431949
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431949