Abstract
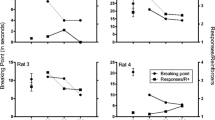
Rats were exposed to a fixed-interval 60-s schedule under which responding was maintained by electrical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus. The duration of stimulation was controlled by the duration of each lever press that initiated reinforcement. The effects of variation in current intensity and administration of several chlordiazepoxide (CDP) doses (2.5–20 mg/kg IP) were investigated. The duration of stimulation was inversely related to current intensity. Administration of CDP resulted in increases in response rate and the durations of reinforced and nonreinforced responses. CDP increased the response duration reliably more with non-reinforced responses than with responses that served to regulate the duration of stimulation. Thus CDP-induced increases in the duration of brain stimulation with the single lever self-regulation procedure may not be attributed to a specific effect of this compound on neural processes underlying reinforcement. The present results indicate the utility of intermittent schedules in establishing the specificity of drug effects on self-regulated duration of brain stimulation in the single-lever condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fowler SC, Filewich RJ, Leberer MR (1977) Drug effects upon force and duration of responses during fixed-ratio performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:421–426
Gerhardt S, Prowse J, Liebman JM (1982) Anxiolytic drugs selectively increase preferred duration of rewarding brain stimulation in a shuttlebox test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16:795–799
Greenshaw AJ, Sanger DJ, Blackman DE (1981) The effects of drugs on fixed-interval responding maintained by electrical brain stimulation in rats. In: Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E, Lowe CF (eds) Recent advances in the quantification of steady-state operant behaviour. Elsevier North Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam, pp 457–460
Kida M, Greenshaw AJ, Sanger DJ, Blackman DE (1981) The effects of d-amphetamine and chlordiazepoxide on behaviour maintained by a multiple shedule of food and electrical brain stimulation in rats. Psychol Rec 31:349–356
König JFR, Klippel RA (1967) The rat brain: A stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower parts of the brain stem. Krieger, New York
Margules DL, Stein L (1967) Neuroleptics vs. tranquillizers: Evidence from animal studies of mode and site of action. In: Brill H, Cole JO, Deniker P, Hippius H, Bradley PB (eds) Neuro-psychopharmacology. Excerpta Medica Foundation, New York, pp 108–120
Walker CH, Faustman WO, Fowler SC, Kazar DB (1981) A multivariate analysis of some operant variables used in behavioral pharmacology. Psychopharmacology 74:182–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greenshaw, A.J., Sanger, D.J. & Blackman, D.E. Effects of chlordiazepoxide on the self-regulated duration of lateral hypothalamic stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacology 81, 236–238 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427269
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427269