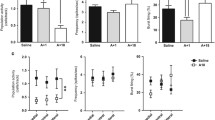
Abstract
In the present study the functional relationship between enkephalinergic and dopaminergic neurones at the level of the nucleus accumbens was investigated. The study consisted of two experiments in which dopaminergic (DA) transmission was chronically inhibited, and the behavioural locomotor response to intra-accumbens opiate injections analysed. First, specific 6-OHDA lesion of the DA-A10 neurones (either in nucleus accumbens or ventral tegmental area) was found markedly to increase the behavioural excitatory effects induced by nucleus accumbens injection of opioid peptides or morphine. Specific lesion of the central noradrenergic neurones had no such effect. Second, chronic pharmacological blockade of DA activity either with reserpine or a neuroleptic (pipothiazine palmitate) similarly induced a strong enhancement of the behavioral response to intra-accumbens opiate injection. The results are discussed in terms of novel mechanisms underlying denervation supersensitivity, and may have important implications for the relation between dopamine dysfunction in mental illness and opiate addiction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977a) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. II The brain stem. Brain Res 129: 1–12
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977b) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III The telencephalon. Brain Res 134: 393–405
Bozarth MA, Wise RA (1981) Intracranial self-administration of morphine into the ventral tegmental area in rats. Life Sci 28: 551–555
Broekkamp CLE, Phillips AG, Cools AR (1979) Stimulant effects of enkephalin microinjection into the dopaminergic A10 area. Nature 278: 560–562
Carlsson A, Rosengreen e, Bertler A, Nilsson T (1957) Effect of reserpine on the metabolism of catecholamines. In: Garattini S, Ghetti V (eds) Psychotropic drugs. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 363–370
Goeders NE, Lane JD, Smith JE (1983) Self-administration of methionine enkephalin into the nucleus accumbens. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20: 451–455
Holzbauer M, Vogt M (1956) Depression by reserpine of the noradrenaline concentration in the hypothalamus of the cat. J Neurochem 1: 8–11
Hong JS, Yang HYT, Fratta W, Costa E (1977) Determination of methionine enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res 134: 383–386
Hong JS, Yang HYT, Fratta W, Costa E (1978) Rat striatal methionine-enkephalin content after chronic treatment with cataleptogenic and non-cataleptogenic antischizophrenia drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 205: 141–147
Hong JS, Yang HYT, Gillin IC, di Guilio AM, Fratta W, Costa E (1979) Chronic treatment with haloperodol accelerates the biosynthesis of enkephalins in rat brat. Brain Res 160: 192–195
Johnson RP, Sar M, Stumpf WE (1980) A topographic localization of enkephalin on the dopamine neurons of the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area demonstrated by combined histofluorescence-immunohistochemistry. Brain Res 194: 566–571
Joyce EM, Iversen SD (1979) The effect of morphine applied locally to mesencephalic dopamine cell bodies on spontaneous activity in the rat. Neurosci Lett 14: 207–212
Kalivas PW, Widerlov E, Stanley D, Breese G, Prange AJ (1983) Enkephalin action on the mesolimbic system a dopamine-dependent and a dopamine-independent increase in locomotor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227: 227–237
Kato N, Shah KR, Friesen HG, Havlicek V (1981) Effect of chronic treatment with haloperidol on serum prolactin, striatal opiate receptors and β-endorphin content in rat brain and pituitary. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol 5: 549–552
Kelley AE, Stinus L, Iversen SD (1980) Interaction between d-ala-met-enkephalin, A10 dopaminergic neurones, and spontaneous behaviour in the rat. Behav Brain Res 1: 3–24
Kostrzewa RM, Jacobowitz DM (1974) Pharmacological actions of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Rev 26: 199–288
La Motte CC Snowman A, Pert CC, Snyder SH (1978) Opiate receptor binding in rhesus monkey brain: association with limbic structures. Brain Res 155: 374–379
Pert CB, Pert A, Chang JK, Fong BTW (1976) D-ala-met-enkephalinamide: a potent long-lasting synthetic pentapeptide analgesic. Science 194: 330–332
Pert CB, Sivit C (1977) Neuroanatomical focus for morphine and enkephalin induced hypermotility. Nature 265: 645–647
Phillips AG, Le Piane FG (1980) Reinforcing effects of morphine microinjection into the ventral tegmental area. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12: 965–968
Phillips AG, Le Piane FG, Fibiger HC (1983) Dopaminergic mediation of reward produced by direct injection of enkephalin into the ventral tegmental area. Life Sci 33: 2505–2511
Pollard H, Llorens-Cortes C, Bennett JJ, Constantin J, Schwartz JC (1977a) Opiate receptors on mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons. Neurosci Lett 7: 295–299
Pollard H, Llorens-Cortes C, Schwartz (1977b) Enkephalin receptors on dopaminergic neurons in rat striatum. Nature 268: 745–747
Rounsaville BJ, Weissman MM, Kleber H, Wilber C (1982a) Heterogeneity of psychiatric diagnosis in treated opiate addicts. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39: 161–166
Rounsaville BJ, Weissman MM, Crits-Christoph K, Wilber C, Kleber H (1982b) Diagnosis and symptoms of depression in opiate addicts. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39: 151–156
Scatton B, Garret C, Glowinski J, Julou L (1975) Effect of long-acting injectable neuroleptic (the palmitic ester of pipothiazine) on dopamine metabolism in the rat striatum. In: Boissier JR, Hippuis H, Pichot P (eds) Neuropsychopharmacology. Proceedings of the IX Congress of the CINP Paris 1974, Amsterdam Exc Med, pp 472–479
Scatton B, Boireau A, Garret C, Glowinski J, Julou L (1977) Action of palmitic ester of pipothiazine on dopamine metabolism in the nigro-striatal, meso-limbic and meso-cortical systems. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 296: 169–175
Schildkraut JJ (1978) Current status of the catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders. In: Lipton MA, DiMascio A, Killam KF (eds) Psychopharmacology: A generation of progress, Raven Press, New York, pp 1223–1234
Seeman P (1981) Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 32: 229–313
Stinus L, Koob GF, Ling N, Bloom FE, Le Moal M (1980) Locomotor activation induced by infusion of endorphins into the ventral tegmental area: evidence for opiate-dopamine interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 77: 2323–2327
Tang F, Schwartz JP, Costa E (1983) Increase of proenkephalin mRNA and enkephalmin content of rat striatum following daily injection of haloperidol for two to three weeks. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 80: 3841–3844
Taquet H, Javoy-Agid F, Hamon M, Le Grand JC, Agid Y, Cesselin F (1983) Parkinson's disease affects differently met-5-enkephalin and leu-5-enkephalin in the human brain. Brain Res 280: 375–382
Tarsy D, Baldessarini RJ (1973) Pharmacologically induced behavioural supersensitivity to apomorphine. Nature 245: 262–263
Thal LJ, Sharpless NS, Hirschhorn ID, Horowitz SG, Makman MH (1983) Striatal met-enkephalin concentration increases following nigrostriatal denervation Biochem Pharmacol 32: 3297–3301
Trujillo KA, Belluzi JD, Stein L (1983) Endorphin-catecholamine interactions in nucleus accumbens self-administration. Abstracts Soc Neurosci 9: 277
Ungerstedt U (1971) Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxy dopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 367: 69–73
Van Der Kooy D, Mucha RF, O'Shaughnessy M, Bucenieks P (1982) Reinforcing effects of brain microinjections of morphine revealed by conditioned place preference. Brain Res 243: 107–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stinus, L., Winnock, M. & Kelley, A.E. Chronic neuroleptic treatment and mesolimbic dopamine denervation induce behavioural supersensitivity to opiates. Psychopharmacology 85, 323–328 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428196
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428196