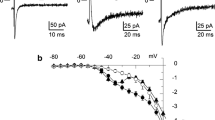
Abstract
Dispersed single smooth muscle cells of rabbit portal vein were prepared by treatment with collagenase and trypsin. The muscle cells were 100–300 μm in length, 5–10 μm in maximum width and cylindrical in shape. In insideout membrane patches, two different amplitudes of ionic currents were recorded, and these single channel conductances were 273 pS (Kl-channel) and 92 pS (Ks-channel), when both sides of the membrane were exposed to 142 mM K+ solution. The channel conductances depended on concentrations of K+ on both sides of the membrane. When K+ were replaced with Na+ or Tris+, these single-channel currents were abolished. When the concentration of Ca2+ inside the membrane was greater than 10−7 M, the channel activity was enhanced but there was enhancement when Ca2+ was applied to the extracellular membrane surface, in concentrations ranging between 10−9 and 10−3 M. During application of tetraethylammonium (TEA+; 1–10 mM) to the intracellular membrane surface, amplitudes of the single-channel current of both types of the K-channel were not modified. By contrast application of TEA+ (0.1–1 mM) to the extracellular membrane surface, reduced the amplitudes of the current and increased noise levels during the open-state of the Kl-channels, but did not have such an effect on the Ks-channel. We conclude that there are at least two different Ca-dependent K-channels distributed on the smooth muscle membrane of the rabbit portal vein. TEA+ applied to the extracellular membrane surface blocks activation of the Kl-channel, but not that of the Ks-channel. These two Ca-dependent K-channels do not seem to be important for maintenance of the resting membrane potential, but do play an important role in the repolarizing stage of the Ca spikes, in the rabbit portal vein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams DJ, Smith SJ, Thompson SH (1980) Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci 3:141–167
Barrett JM, Magleby KL, Pallotta BS (1982) Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol 331:211–230
Benham CD, Bolton TB (1983) Patch-clamp studies of slow potential-sensitive potassium channels in longitudinal smooth muscle cells of rabbit jejunum. J Physiol 340:469–486
Benham CD, Bolton TB, Kitamura K (1982) Single channel currents in collagenase dispersed smooth muscle cells of adult guineapig and rabbits. J Physiol 328:54–55
Benham CD, Bolton TB, Lang RJ, Takewaki T (1985) The mechanism of action of Ba2+ and TEA on single Ca2+-activated K+-channels in arterial and intestinal smooth muscle cell membranes. Pflügers Arch 403:120–127
Berger W, Grygorcyk R, Schwarz W (1984) Single K+-channels in membrane evaginations of smooth muscle cells. Pflügers Arch 402:18–23
Blatz AL, Magleby KL (1984) Ion conductance and selectivity of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Gen Physiol 84:1–23
Bolton TB, Tomita T, Vassor G (1981) Voltage clamp and the measurement of ionic conductances in smooth muscle. In: Bülbring E et al. (eds) Smooth muscle: an assessment of current knowledge. Arnold, London, pp 47–64
Fay FS, Singer JJ (1977) Characteristics of response of isolated smooth muscle cells to cholinergic drugs. Am J Physiol 232:C144-C154
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hayer GB, Lux HD (1976) Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pacemaker neurones of the snail,Helix pomatia. J Physiol 262:349–382
Hirata M, Itoh T, Kuriyama H (1981) Effects of external cations on calcium efflux from single cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli and porcine coronary artery. J Phsyiol 310:321–336
Hermann A, Gorman ALF (1981) Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron. J Gen Physiol 78:87–110
Itoh T, Kuriyama H, Ueno H (1983) Mechanisms of the nitroglycerine-induced vasodilation in vascular smooth muscles of the rabbit and pig. J Phsyiol 343:233–252
Kajiwara M, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1981) Neuromuscular transmission and smooth muscle membrane properties in the guinea-pig ear artery. J Physiol 315:283–302
Kitamura K, Kuriyama H, Suzuki H (1976) Prostaglandin action on the main pulmonary artery and portal vein of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 26:681–692
Kuriyama H, Ito Y, Suzuki H, Kitamura K Itoh T (1982) Factors modifying concentration-relaxation cycle in vascular smooth muscles. Am J Physiol 12:H641-H662
Magleby KL, Pallotta BS (1983) Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol 344:585–604
Marty A (1983) Blocking of large unitary calcium-dependent potassium currents by internal sodium ions. Pflügers Arch 396:179–181
Maruyama Y, Petersen OH (1982) Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature 299:161–169
Maruyama Y, Gallacher DV, Petersen OH (1983a) Voltage and Ca2+ activated K+-channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature 302:827–829
Momose K, Gomi Y (1980) Studies on isolated smooth muscle cells dispersion procedures for acetylcholine-sensitive smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig. Jpn J Smooth Muscle Res 16:29–36
Nanjo T, Kitamura K (1984) Actions of nipradilol (K-351), a new α-and β-adrenoceptor blocker, on the rabbit portal vein. Jpn J Pharmacol 35:359–369
Singer JJ, Walsh JV, Jr (1980) Passive properties of the membrane of single freshly isolated smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 239:C153-C161
Singer JJ, Walsh JV, Jr (1984) Large conductance Ca2+-activated K+-channels in smooth muscle cell membrane. Reduction in unitiary currents due to internal Na+ ions. Biophys J 45:68–70
Stefani E, Chiarandini DJ (1982) Ionic channels in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol 44:357–372
Thompson SH (1977) Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 265:465–488
Wong BS, Lecar H, Adler M (1982) Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J 39:313–317
Yellen G (1984) Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+-channels of bovine chromaffine cells. J Gen Physiol 84:157–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, R., Kitamura, K. & Kuriyama, H. Two Ca-dependent K-channels classified by the application of tetraethylammonium distribute to smooth muscle membranes of the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 405, 173–179 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582557
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582557