Abstract
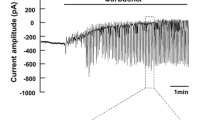
In acinar cells freshly dispersed from rat parotid glands, the effects of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) on membrane currents were studied using the whole-cell clamp method. When membrane currents were recorded with command pulses to 0 mV, applied at 2-s intervals from a holding potential of −70 mV, NH4Cl (5–20 mM) transiently decreased outward currents and then slowly increased both outward and inward currents. After reaching a peak in about 40–50 s, both outward and inward currents gradually decreased in the presence of NH4Cl and, on its wash-out, the currents returned to the control level. Butyrate (5–20 mM) had little effect on the resting membrane currents, but markedly inhibited the response to NH4Cl. Tetraethylammonium (5 mM) strongly reduced both the resting and NH4Cl-induced outward currents, whereas it slightly potentiated the NH4Cl-induced inward current without affecting the membrane current at the holding potential. Without ATP in the patch pipettes, carbachol-induced membrane currents were relatively resistant to Ca2+ removal from the external medium, but NH4Cl-induced currents were quickly abolished in the absence of Ca2+. We conclude that intracellular alkalinization with NH4Cl increases Ca2+ influx and activates Ca2+-dependent outward K+ and inward Cl− currents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkle S, Gillespie JI, Greenwell JR (1988) Interaction between intracellular pH (pHi) and calcium (Ca2+) in single isolated acini from rat parotid and mouse submandibular salivary gland. J Physiol (Lond) 400:31P
Cook DL, Ikeuchi M, Fujimoto WY (1984) Lowering of pHi inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 311:269–271
Deutsch C, Lee SC (1989) Modulation of K+ currents in human lymphocytes by pH. J Physiol (Lond) 413:399–413
Dickens CJ, Gillespie JI, Greenwell JR (1990) Measurement of intracellular calcium and pH in avian neural crest cells. J Physiol (Lond) 428:531–544
Dickens CJ, Gillespie JI, Greenwell JR, Hutchinson P (1990) Relationship between intracellular pH (pHi) and calcium (Ca2+) in avian heart fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 187:39–46
Ghigo D, Treves S, Turrini F, Pannocchia A, Pescarmona G, Bosia A (1988) Role of Na+/H+ exchange in thrombin and arachidonic acid-induced Ca2+ influx in platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta 940:141–148
Good DW, Knepper MA (1985) Ammonia transport in the mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol 248:F459-F471
Gray PTA (1989) The relation of elevation of cytosolic free calcium to activation of membrane conductance in rat parotid acinar cells. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 237:99–107
Grinstein S, Goetz JD (1985) Control of free cytoplasmic calcium by intracellular pH in rat lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 819:267–270
Iwatsuki N, Maruyama Y, Matsumoto O, Nishiyama A (1985) Activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl− and K+ conductances in rat and mouse parotid acinar cells. Jpn J Physiol 35: 933–944
Jack JJB, Noble D, Tsien RW (1985) Electric current flow in excitable cells. Clarendon, Oxford
Kume H, Takagi K, Satake T, Tokuno H, Tomita T (1990) Effects of intracellular pH on calcium-activated potassium channels in rabbit tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 424:445–457
Manganel M, Turner RJ (1989) Agonist-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells. J Membr Biol 111:191–198
Manganel M, Turner RJ (1990) Agonist-induced activation of Na+/H+ exchange in rat parotid acinar cells is dependent on calcium but not on protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 265:4284–4289
Melvin JE, Moran A, Turner RJ (1988) The role of HCO −3 and Na+/H+ exchange in the response of rat parotid acinar cells to muscarinic stimulation. J Biol Chem 263:19564–19569
Petersen OH, Gallacher DV (1988) Electrophysiology of pancreatic and salivary acinar cells. Annu Rev Physiol 50:65–80
Putnam RW, Douglas PB (1990) Effect of changes of pHi on intracellular calcium in a smooth muscle-like cell line. Mol Cell Biochem 99:89–95
Roos A, Boron WJ (1981) Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev 61:296–434
Shigetomi T, Hayashi T, Ueda M, Kaneda T, Tokuno H, Takai A, Tomita T (1991) Effects of Ca2+ removal and of tetraethylammonium on membrane currents induced by carbachol in isolated cells from the rat parotid gland. Pflügers Arch 419:332–337
Siffert W, Akkerman JWN (1989) Na+/H+ exchange and Ca2+ influx. FEBS Lett 259:1–4
Siskind MS, McCoy CE, Chobanian A, Schwartz JH (1989) Regulation of intracellular calcium by cell pH in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 256:C234-C240
Stampe P, Vestergaard-Bogind B (1985) The Ca2+-sensitive K+-conductance of the human red cell membrane is strongly dependent on cellular pH. Biochim Biophys Acta 815:313–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, T., Shigetomi, T., Ueda, M. et al. Effects of ammonium chloride on membrane currents of acinar cells dispersed from the rat parotid gland. Pflügers Arch 420, 297–301 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374462
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374462