Abstract.
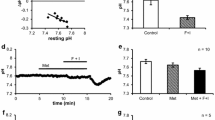
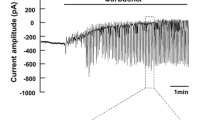
Previously we have shown that stimulation of in vitro perfused rectal gland tubules (RGT) of the dogfish Squalus acanthias by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP), (as a cocktail comprising 0.1 mmol/l dibutyryl-cAMP, 10 µmol/l forskolin and 0.1 mmol/l adenosine, hereafter termed STIM) leads to an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) and that this assists Cl– secretion by enhancing basolateral K+ conductance. In the present study we examined the mechanism of the cAMP-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. [Ca2+]i was measured using the fura-2 technique in isolated in vitro perfused RGT. As before, STIM enhanced [Ca2+]i. This elevation of [Ca2+]i was prevented completely when STIM was added in the presence of the Na+2Cl–K+ cotransport inhibitor furosemide (0.5 mmol/l). This suggests that the increase in [Ca2+]i induced by STIM is caused by a concomitant increase in cytosolic Na+ ([Na+]i) and not by the activation of second messenger cascades. Furosemide prevents this increase in [Na+]i and hence the elevation of [Ca2+]i. Moreover, the plateau phase of the [Ca2+]i transient produced by carbachol (CCH, 0.1 mmol/l) was augmented strongly when bath Na+ was reduced to 5 mmol/l. These data suggest that the level of [Ca2+]i is determined by Na+-dependent Ca2+ export, most likely via a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. The increase in [Na+]i accompanying stimulation of Cl– secretion reduces the rate of Ca2+ export leading to an elevation of [Ca2+]i, as does a reduction in bath Na+ which augments the [Ca2+]i plateau produced by CCH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision and accepted: 3 September 1999
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bleich, M., Hug, M., Heitzmann, D. et al. Evidence for Na+/Ca2+ exchange in the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias . Pflügers Arch – Eur J Physiol 439, 49–51 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900163
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900163