Abstract
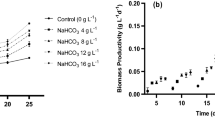
Addition of a cereal protein hydrolysate increased the growth rate and biomass producivity of Spirulina. Net oxygen production rate measurements from outdoor culture samples indicated that the photosynthetic capacity of the alga changed throughout the light period. Daily reduction in the OPR correlated with the growth of the cultures. These studies indicated that measurement of the reduction in net OPR can serve as an indicator of the performance of the culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA): Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 16th Edtion, APHA AWWA WPCI, Washington, DC (1985)
Becker, E.W.: Microalgae: biotechnology and microbiology, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (1994)
Ben Yaakov, S.; Guterman, H.; Vonshak, A.; Richmond, A.: An automatic method for on-line estimation of photosynthetic rate in open algal ponds. Biotechnol. Bioengg. 27 (1985) 1136–1147
Bonnin, C.: Spirulina Production Engineering Handbook, Fevrier, Nantes, France (1992)
Chaumont, D.: Biotechnology of algal mass production: a review of systems for outdoor mass culture. J. Appl. Phycol. 5 (1993) 593–604
De la Naue, J.; Laliberti, G.; Proulx, D.: Algae and wastewater. J. Appl. Phycol. 4 (1992) 247–254
Guterman, H.; Ben Yaakov, S.; Vonshak, A.: Automatic online growth estimation method for outdoor algal biomass production. Biotechnol. Bioengg. 34 (1989) 143–152
Post, A.E.; Loogman, J.G.; Mur, L.R.: Photosynthesis, carbon flows and growth of Oscillatoria agrdhii Gomant in environments with a periodic supply of light. J. Gen Microbiol. 13 (1986) 2129–2136
Singh, G.; Kothari, R.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Ramamurthy, V.: Enhancement of Spirulina biomass prductivity by a protein hydrolysate. Appl.Biochem. Biotechnol. 50 (1995) 285–290
Sharma, R.K.; Kothari, R.M.: Recycled cereal protein as a foliar spray enhances quality and production of food crops. Resrouce Conservation Recycling 9 (1993) 213–221
Tadros, M.G.; Smith, W.; Joseph, B.; Phillips,.: Yield and quality of cyanobacteria: Spirulina maxima in continuous culture in response to light intensity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 39/40 (1993) 337–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, V.S., Ramamurthy, V. Enhanced spirulina growth in outdoor ponds correlates with daily reduction in oxygen production rate. Bioprocess Engineering 15, 9–12 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435521
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435521