Summary
-
1.
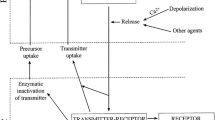
Properties of synaptic transmission during and after repetitive activation of the newly formed cortico-rubral synapses were examined in the red nucleus neurons (RN) of cats after lesions of the nucleus interpositus of the cerebellum (chronic cats) as well as in normal ones.
-
2.
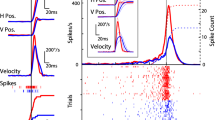
A prominent facilitation of the amplitude of cortico-rubral unitary EPSPs was observed in both normal and chronic cats when a stimulus to the cerebral peduncle (CP) was preceded by another stimulus by 2–50 msec.
-
3.
Time course of the facilitation shows that it attains maximum at the interval of about 3 msec and decays approximately exponentially lasting for 50 msec or more.
-
4.
When three successive stimuli of identical intensity were applied to CP, the degree of facilitation was more prominent than that for double shock.
-
5.
There was a positive correlation between the time to peak of the cortico-rubral EPSPs and their maximum value of facilitation.
-
6.
The posttetanic potentiation of the cortico-rubral EPSPs was observed after tetanic stimulation to CP in chronic and normal cats. It lasts for a few minutes in both cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwood, H.L., Bittner, G.D.: Matching of excitatory and inhibitory inputs to crustacean muscle fibers. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 157–170 (1971)
Bennett, M.V.L.: Analysis of parallel excitatory and inhibitory synaptic channels. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 69–75 (1971)
Brown, M.C., Ironton, R.: Motor neuron sprouting induced by prolonged tetrodotoxin block of nerve action potentials. Nature (Lond.) 265, 459–461 (1977)
Eccles, J.C.: The physiology of synapses. pp. 82–98. Berlin: Springer 1964
Frank, E.: Matching of facilitation at the neuromuscular junction of the Lobster: A possible case for influence of muscle on nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 233, 635–658 (1973)
Grinnell, A.D., Rheuben, M.B., Letinsky, M.S.: Mutual repression of synaptic efficacy by pairs of foreign nerves innervating frog skeletal muscle. Nature (Lond.) 265, 368–370 (1977)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 195, 481–492 (1968)
Kuno, M.: Quantum aspects of central and ganglionic synaptic transmission in vertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 51, 647–678 (1971)
Kuno, M., Miyata, Y., Muñoz-Martinez, E.J.: Properties of fast and slow alpha motoneurons following motor reinnervation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 242, 273–288 (1974)
Kuno, M., Weakly, J.M.: Facilitation of monosynaptic excitatory synaptic potentials in spinal motoneurons evoked in internucial impulses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 224, 271–286 (1972)
Mallart, A., Martin, A.R.: An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 193, 679–694 (1967)
Martin, A.R.: A further study of the statistical composition of the end-plate potential. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 130, 114–122 (1955)
Muir, R.B., Porter, R.: The effect of preceding stimulus on temporal facilitation at cortico-motoneuronal synapses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 228, 749–763 (1973)
Murakami, F., Fujito, Y., Tsukahara, N.: Physiological properties of the newly formed cortico-rubral synapses of red nucleus neurons due to collateral sprouting. Brain Res. 103, 147–151 (1976)
Murakami, F., Tsukahara, N., Fujito, Y.: Analysis of unitary EPSP mediated by the newly formed cortico-rubral synapses after lesion of the nucleus interpositus of the cerebellum. Exp. Brain Res. 30, 233–243 (1977)
Nelson, P.G., Frank, K.: Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1097–1113 (1967)
Phillips, C.G., Porter, R.: The pyramidal projection to motoneurones of some muscle groups of the baboon's forelimb. In: Progress in Brain Research: Physiology of spinal neurons (eds. J.C. Eccles and J.P. Schadé), Vol. 12, pp. 222–242. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964
Porter, R.: Early facilitation at the cortico-motoneuronal synapses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 207, 733–745 (1970)
Rall, W.: Theoretical significance of dendritic trees for neuronal input-output relations. In: Neural Theory and Modeling (ed. R.F. Reiss), pp. 73–97. Stanford: Stanford Univ. Press 1964
Rall, W., Rinzel, J.: Branch input resistance and steady attenuation for input to one branch of a dendritic neuron model. Biophys. J. 13, 648–688 (1973)
Spencer, W.A., Kandel, E.R.: Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. IV. Fast prepotentials. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 272–285 (1961)
Toyama, K., Tsukahara, N., Kosaka, K., Matsunami, K.: Synaptic excitation of red nucleus neurons by fibers from interpositus nucleus. Exp. Brain Res. 11, 187–198 (1970)
Tsukahara, N., Fuller, D.R.G., Brooks, V.B.: Collateral pyramidal influences on the corticorubrospinal system. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 467–484 (1968)
Tsukahara, N., Hultborn, H., Murakami, F., Fujito, Y.: Electrophysiological study of formation of new synapses and collateral sprouting in red nucleus neurons after partial dennervation. J. Neurophysiol. 38, 1359–1372 (1975a)
Tsukahara, N., Kosaka, K.: The mode of cerebral excitation of red nucleus neurons. Exp. Brain Res. 5, 102–117 (1968)
Tsukahara, N., Murakami, F., Hultborn, H.: Electrical constants of neurons of the red nucleus. Exp. Brain Res. 23, 49–64 (1975b)
Watchel, H., Kandel, E.R.: Conversion of synaptic excitation to inhibition at a dual chemical synapse. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 56–68 (1971)
Yip, J.W., Dennis, M.J.: Suppression of transmission at foregin synapses in adult newt muscle involves reduction of quantal content. Nature (Lond.) 260, 350–352 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, F., Tsukahara, N. & Fujito, Y. Properties of the synaptic transmission of the newly formed cortico-rubral synapses after lesion of the nucleus interpositus of the cerebellum. Exp Brain Res 30, 245–258 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237254
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237254