Abstract
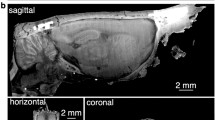
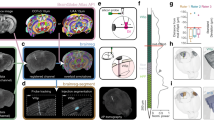
A technique is described for in vivo localization of microelectrodes during single-unit recording in the alert monkey. Four hollow glass spheres filled with copper sulfate and iohexol were affixed to the surface of the animal's skull prior to the acquisition of a series of coronal magnetic resonance (MR) images. These reference beads were visible in both X-ray and MR images. Cranial recording chambers were then implanted bilaterally over the amygdaloid complex. A microelectrode was advanced to various depths in the subject's brain. At each selected microelectrode site, five radiographs were obtained and a small electrolytic lesion was made. Based on the data from the radiographs, we computed the position of the microelectrode tip at each site relative to the reference beads. With a precision of 625 μm, this method was used to predict the neuroanatomical location of ten microlesions placed in both subcortical and cortical structures. Postmortem histological analysis revealed that the actual location of the lesions closely matched predictions arrived at using the X-ray/MRI localization technique. This technique thus provides an accurate, reliable and noninvasive method for in vivo localization of microelectrode recording sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Passingham RE (1981) Stereotaxic surgery under X-ray guidance in the rhesus monkey, with special reference to the amygdala. Exp Brain Res 44:271–276
Albright TD, Desimone R, Gross CG (1984) Columnar organization of directionally selective cells in visual area MT of the macaque. J Neurophysiol 51:16–31
Alvarez-Royo P, Clower RP, Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR (1991) Stereotaxic lesions of the hippocampus in monkeys: determination of surgical coordinates and analysis of lesions using magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci Methods 38:223–232
Dale AM, Sereno MI (1993) Improved localization of cortical activity by combining EEG and MEG with MRI cortical surface reconstruction: a linear approach. J Cogn Neurosci 5:2 162–176
Damasio H, Frank R (1992) Three-dimensional in vivo mapping of brain lesions in humans. Arch Neurol 49:137–143
Dobkins KR, Albright TD (1994) What happens if it changes color when it moves? Neurophysiological experiments on the nature of chromatic input to macaque visual area MT. J Neurosci (in press)
Hotvedt R, Platou ES, Koppang ER, Refsum H (1982) Pentobarbital plasma concentrations and cardiac electrophysiology during prolonged pentobarbital infusion anaesthesia in dogs. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 26:638–642
Lemieux L, Lester S, Fish D (1992) Multimodality imaging and intracranial EEG display for stereotactic surgery planning in epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:399–407
Press WH, Flannery BP, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT (1988) Numerical recipes in C. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Rebert CS, Hurd RE, Matteucci MJ, De LaPaz R, Enzmann DR (1992) A procedure for using proton magnetic resonance imaging to determine Stereotaxic coordinates of the monkey's brain. J Neurosci Methods 39:109–113
Van Essen DC, Maunsell JHR (1980) Two-dimensional maps of the cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 191:255–281
Wagman JH, Loeffler JR, McMillan JA (1975) Relationship between growth of brain and skull of Macaca mulatta and its importance for the stereotaxic technique. Brain Behav Evol 12:116–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nahm, F.K.D., Dale, A.M., Albright, T.D. et al. In vivo microelectrode localization in the brain of the alert monkey: a combined radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging approach. Exp Brain Res 98, 401–411 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233978
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233978