Abstract
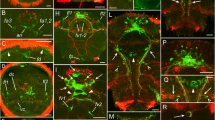
Larvae of the marine hydroid Hydractinia echinata Fleming are induced to settle and metamorphose by contact with bacteria of the genus Alteromonas espejiana (Leitz and Wagner 1992). In previous studies the biochemical mechanism for the activation of the larvae was found to include the signal transduction pathway via the phosphatidylinositol cycle and a role for a kinase C-like enzyme was established. In the present investigation laboratory-reared larvae were immunohistochemically stained with antibodies against kinase C and experiments were conducted to investigate protein phosphorylation during initial metamorphic events. A polyclonal antibody against a synthetic peptide derived from a conserved retion of kinases C binds to an antigen in neurosensory cells of the anterior part of the larvae and corresponding nerve fibres. The Western blot reveals major binding to a protein of Mr (relative molecular mass)=67 and two minor bands at Mr=66 and 48. Assays in vivo show that 3 to 25 min after induction of metamorphosis the phosphorylation of a protein with Mr=30 is enhanced. A hypothesis about the mechanism of induction at the cellular and biochemical level is presented which combines most of the ideas now available from our and other groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Amieva, M. R., Reed, C. G., Pawlik, J. R. (1987). Ultrastructure and behavior of the larva of Phragmatoma californica (Polychaeta: Sabellariidae): identification of sensory organs potentially involved in substrate selection. Mar. Biol 95:259–266
Arkett, S.A., Chia, F.-S., Goldberg, J.I., Koss, R. (1989). Identified settlement receptor cells in a nudibranch veliger respond to specific cue. Biol Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 176:155–160
Barnekow, A., Müller, W. A. (1986). An src-related tyrosine kinase activity in the hydroid, Hydractinia. Differentiation 33: 29–33
Baxter, G., Morse, D. E. (1987). G protein und diacylglycerol regulate metamorphosis of planktonic molluscan larvae. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84: 1867–1870
Berking, S. (1986). Transmethylation and control of pattern formation in hydrozoa. Differentiation 32: 10–16
Berking, S. (1988). Ammonia, tetraethylammonium, barium and amiloride induce metamorphosis in the marine hydroid Hydractinia. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 197: 1–9
Berking, S. (1991). Control of metamorphosis and pattern formation in Hydractinia (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). BioEssays 13: 323–329
Bischoff, A., Fleck, J., Hofmann, D. K. (1991). Phorbol esters induce metamorphosis in Cassiopea andromeda and Cassiopea xamachana (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Verh. dt. zool. Ges. 84: 484
Blumberg, P. M. (1988). Protein kinase C as the receptor for the phorbol ester tumor promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 48: 1–8
Burke, R. D. (1983). The induction of metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae: stimulus and response. Can. J. Zool. 61: 1701–1719
Campbell, R. D. (1983). Preparing histological sections for light microscopy. In: Lehnhoff, H. M. (ed) Hydra, research methods. Plenum Press, New York, p. 121–130
Chia, F.-S., Bickell, L. R. (1978). Mechanisms of larval attachment and the induction of metamorphosis in coelenterates: a review. In: Chia, F. S., Rice, M. E. (eds.) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier, New York, p. 1–12
Chia, F.-S., Koss, R. (1979). Fine structural studies of the nervous system and the apical organ in the planula larva of the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima. J. Morph. 160:275–297
Crisp, D. J. (1974). Factors influencing the settling of marine invertebrate larvae. In: Grant, P. T., Mackie, A. M. (eds.) Chemoreception in marine organisms. Academic Press, New York, p. 177–265
Edwards, N. C., Thomas, M. B., Long, B. A., Amyotte, S. J. (1987). Catecholamines induce metamorphosis in the hydrozoan Halocordyle disticha but not in Hydratinia echinata. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 196: 381–384
Exton, J. H., Taylor, S. J., Angert, G., Cocckino, S. B. (1991). Cell signalling through phospholipid breakdown. Molec. cell. Biochem. 104: 81–86
Freeman, G., Ridgway, E. B. (1990). Cellular and intracellular pathways mediating the metamorphic stimulus in hydrozoan planulae. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 199: 63–79
Gschwendt, M., Kittstein, W., Horn, F., Leibersperger, H., Marks, F. (1989). A phorbol-ester and phospholipid-activated, calcium-unresponsive protein kinase in mouse epidermis: characterization and separation from kinase C. J. cell. Biochem. 40: 295–307
Henning, G., Benayahu, Y., Hofmann, D. K. (1991). Natural substrates, marine bacteria and a phorbol-ester induce metamorphosis in the soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens (Anthozoa: Octocorallia). Verh. dt. zool. Ges. 84: 486–487
Jensen, R. A., Morse, D. E., Hooker, N., Petty, R. (1980). Artificial induction of larval metamorphosis by free fatty acids. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 67: 55–71
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, Lond 227: 680–685
Leitz, T., Klingmann, G. (1990). Metamorphosis in Hydractinia: studies with activators and inhibitors aiming at protein kinase C and potassium channels. Wilhelm Roux Arch dev. Biol. 199: 107–113
Leitz, T., Müller, U. (1991). Stimulation of metamorphosis in Hydractinia echinata involves generation of lysophosphatidylcholine. Wilhelm Roux Arch dev. Biol. 200: 249–255
Leitz, T., Müller, W. A. (1987). Evidence for the involvement of PI-signaling and diacylglycerol second messengers in the initiation of metamorphosis in the hydroid Hydractinia echinata Fleming. Dev. Biol. 121: 82–89
Leitz, T., Wagner, T. (1993). The marine bacterium Alteromonas espejiana induces metamorphosis in the hydroid Hydractinia echinata. Mar. Biol. 115(2): 173–178
Leitz, T., Wirth, A. (1991). Vanadate, known to interfere with signal transduction, induces metamorphosis in Hydractinia (Coelenterata; Hydrozoa) and causes profound alterations of the larval and postmetamorphic body pattern. Differentiation 47: 119–127
May, G., Müller, W. A. (1975). Aktivitäten von Enzymen des Kohlenhydrat-Stoffwechsels und der Na+, K+-ATPase im Zuge der Embryonalentwicklung und Metamorphose von Hydractinia echinata. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 177: 235–254
Müller, W. A. (1969). Auslösurg der Metamorphose durch Bakterien bei den Larven von Hydractinia echinata. Zool. Jb. (Abt. Anat. Ontog. Tiere). 86: 84–95
Müller, W. A. (1973a). Induction of metamorphosis by bacteria and ions in the planulae of Hydractinia echinata; an approach to the mode of action. Pulbs Seto mar. biol. Lab. (Proc. 2nd Intn. Symp. Cnidaria). 20: 195–208
Müller, W. A. (1983b). Metamorphoseinduktion bei Planulalarven. I. Der bakterielle Induktor. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 173: 107–121
Müller, W. A. (1985). Tumor promoting phorbol esters induce metamorphosis and multiple head formation in the hydroid Hydractinia. Differentiation 29: 216–222
Müller, W. A., Buchal, G. (1973). Metamorphose-Induktion bei Planulalarven; II. Induktion durch monovalente Kationen. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 173: 122–135
Pawlik, J. R., Faulkner, D. J. (1986). Specific free fatty acids induce larval settlement and metamorphosis in the reef-building tube worm Phragmatopoma californica (Fewkes). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 102: 301–310
Pechenik, J. A., Heyman, W. D. (1987). Using KCl to determine size at competence for larvae of the marine gastropod, Crepidula fornica (L.). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 112: 27–38
Plickert, G. (1989). Proportion-altering factor (PAF) stimulates nerve cell formation in Hydractinia echinata. Cell Diff. Devel. 26: 19–28
Plickert, G. (1990). Experimental analysis of developmental processes in marine hydroids. In: Marthy, H. J. (ed.) Experimental analysis of developmental processes. Plenum Press, New York, p. 59–81
Rana, R. S., Hokin, L. E. (1990). Role of phosphoinositides in transmembrane signaling. Physiol. Rev. 70: 115–164
Rando, R. R. (1988). Regulation of protein kinase C activity by lipids. FASEB J 2: 2348–2355
Romano, M., Hawiger, J. (1990). Interaction of endotoxic lipid A and lipid X with purified human platelet protein kinase C. J. biol. Chem. 265: 1765–1770
Scheltema, R. S. (1974). Biological interactions determining larval settlement of marine invertebrates. Thalassia jugosl. 10: 263–296
Schwoerer-Böhning, B., Kroiher, M., Müller, W. A. (1990). Signal transmission and covert prepattern in the metamorphosis of Hydractinia echinata. Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol 198: 245–251
Spindler, K. D., Müller, W. A. (1972). Indiction of metamorphosis by bacteria and by a lithium pulse in the larvae of Hydractinia echniata (Hydrozoa). Wilhelm Roux Arch. dev. Biol. 169: 271–280
Thomas, M. B., Freeman, G. Martin, V. J. (1987). The embryonic origin of neurosensory cells in metamorphosis in Phialidium gregarium (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa). Int. J. Invert. Reprod. Dev. (Amsterdam) 11: 265–287
Trapido-Rosenthal, H. G., Morse, D. E. (1986). Availability of chemosensory receptors is down-regulated by habituation of larvae to a morphogenetic signal. Proc. natn. Acad Sci. U.S.A. 83: 7658–7662
Vandermeulen, J. H., (1974). Studies on reef corals II. Fine structure of planktonic planula larva of Pocillopora damicornis, with emphasis on the aboral epidermis. Mar. Biol. 27 239–249
Yool, A. J., Grau, S. M., Hadfield, M. G., Jensen, R. A., Markell, D. A., Morse, D. E. (1986). Excess potassium induces larval metamorphosis in four marine invertebrate species. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 170: 255–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leitz, T. Biochemical and cytological bases of metamorphosis in Hydractinia echinata . Marine Biology 116, 559–564 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355474