Summary
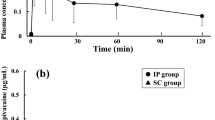
The basic pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of ketobemidone have been studied in 6 patients after surgery. Plasma concentrations were first determined following intravenous administration of Ketogin® 2 ml, containing ketobemidone chloride 10 mg and the spasmolytic N,N-dimethyl-3,3-diphenyl-1-methylallylamine chloride 50 mg, and then, on the second postoperative day, following oral administration of 2 tablets of Ketogin®, each containing ketobemidone chloride 5 mg and the spasmolytic agent 25 mg. The average oral bioavailability of ketobemidone was 34%±16% (SD, n=6). The mean plasma half-life of elimination (t1/2β) was about the same following oral (2.45±0.73 h; SD, n=5) as after intravenous administration (2.25±0.35 h; SD, n=6). The low oral bioavailability and rapid elimination of ketobemidone demonstrated in this study suggest that the usual dosage recommendation for oral Ketogin® (ketobemidone 5–10 mg every 6–7 h) in patients with severe pain is too low.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein, A.: Klinische Erfahrungen mit Cliradon, einem neuen synthetischen Analgeticum. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr.79, 1159–1162 (1949)
Liessem, H.: Chirurgische Erfahrungen mit dem neuen synthetischen Analgetikum Cliradon. Münch. Med. Wochenschr.93, 604–606 (1951)
Peregalli, P. F.: Ricerche cliniche su un nuovo preparato analgesico di sintesi. Minerva Chir.7, 248–250 (1952)
Peltola, P.: Clinical experience with “Cliradon”. Duodecim68, 296–305 (1952)
Eddy, N. B., Halbach, H., Braenden, O. J.: Synthetic substances with morphine-like effect. Clinical experience: potency, side-effect, addiction liability. Bull. WHO17, 569–863 (1957)
Isbell, H.: The addiction liability of some derivatives of meperidine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.97, 182–189 (1949)
Blanke, K.: Ergebnisse der klinischen Erprobung des neuen Analgeticums Cliradon. Med. Klin.45, 1171–1174 (1950)
Petersen, P. V.: Studies on a new spasmolytical compound 1,1-diphenyl-3-dimethylaminobutene-1 (A 29), related to methadone, and on the combined use of this compound and a potent analgesic, ketobemidone (A 21). Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.7, 51–64 (1951)
Peltola, P., Soisalo, P.: The analgesic properties and addiction liability of ketobemidone and morphine. Arch. Int. Med.101, 741–746 (1958)
Bernsmeier, A., Heine, G.: Klinische Erfahrungen und experimentelle Untersuchungen mit dem neuen synthetischen Analgeticum Cliradon. Med. Welt1, 1491–1493 (1950)
Bondesson, U., Hartvig, P.: Mass fragmentographic method for the determination of ketobemidone in plasma. J. Chromatography179, 207–212 (1979)
Mather, L. E., Meffin, P. J.: Clinical pharmacokinetics pethidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet.3, 352–368 (1978)
Burns, J. J., Berger, B. L., Lief, P. A., Wollack, A., Papper, E. M., Brodie, B. B.: The physiological disposition and fate of meperidine (Demerol) in man and a method for its estimation in plasma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.114, 289–298 (1955)
Klotz, U., McHorse, T. S., Wilkinson, G. R., Schenker, S.: The effect of cirrhosis on the disposition and elimination of meperidine in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.16, 667–675 (1974)
McHorse, T. S., Wilkinson, G. R., Johnson, R. F., Schenker, S.: Effect of acute viral hepatitis in man on the disposition and elimination of meperidine. Gastroenterology68, 775–780 (1975)
Mather, L. E., Tucker, G. T., Pflug, A. E., Lindop, M. J., Wilkerson, C.: Meperidine kinetics in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.17, 21–30 (1975)
Mather, L. E., Tucker, G. T.: Systemic availability of orally administered meperidine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.20, 535–540 (1976)
Stambough, J. E., Wainer, I. W.: Metabolic studies of hydroxyzine and meperidine in human subjects. In: Advances in pain research and therapy. Bonica and Albe-Fessard (eds.), Vol. 1, p. 559–565. New York: Raven Press 1976
Dunkerley, R., Johnson, R., Schenker, S., Wilkinson, G. R.: Gastric and biliary excretion of meperidine in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.20, 546–551 (1976)
Brunk, S. F., Delle, M.: Morphine metabolism in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.16, 51–57 (1974)
Berkowitz, B. A., Ngai, S. H., Yang, J. C., Hempstead, J., Spector, S.: The disposition of morphine in surgical patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.17, 629–635 (1975)
Ehrnebo, M., Boréus, L. O., Lönroth, U.: Bioavailability and first-pass metabolism of oral pentazocine in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.22, 888–892 (1977)
Säwe, J., Dahlström, B., Paalzow, L., Rane, A.: Pharmacokinetics of orally administered morphine in cancer patients. (To be published)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bondesson, U., Arnér, S., Anderson, P. et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of ketobemidone. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17, 45–50 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561676
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561676