Summary
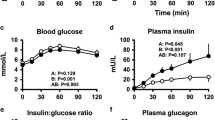
The effect of the calcium antagonist, diltiazem, on glycoregulation was investigated in 12 healthy volunteers using a standard glucose tolerance test. No significant change was observed in plasma glucose, insulin or glucagon levels after oral treatment for B days with diltiazem 180 mg/day.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen L, Kolendorf K, Thorsteinsson B (1982) Nifedipine does not decrease insulin secretion. Acta Endocrinol 100 (Suppl 247) (Copenh): 7
Andersson DEH, Rojdmark S (1981) Improvement of glucose tolerance by verapamil in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Scand 210: 27–33
Charles S, Ketelslegers JM, Buysschaert M, Lambert AE (1981) Hyperglycaemic effect of nifedipine. Br Med J 283: 19–20
Devis G, Somers G, van Obberghen E, Malaisse WJ (1975) Calcium antagonists and islet function. I. Inhibition of insulin release by verapamil. Diabetes 24: 547–551
Donnelly T, Harrower ADB (1980) Effect of nifedipine on glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Curr Med Res Opin 6: 690–693
Ferlito S, Fichera C, Carra G, Puleo F, Calafato M, Volpicelli D (1981) Effect of nifedipine on blood sugar, insulin and glucagon levels after an oral glucose load. Panminerva Med 23: 75–80
Giugliano D, Torella R, Cacciapuoti F, Gentile S, Verza M, Varricchio M (1980) Impairment of insulin secretion in man by nifedipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18: 395–398
Henquin JC, Lambert AE (1975) Cobalt inhibition of insulin secretion and calcium uptake by isolated rat islets. Amer J Physiol 228: 1669–1677
Herbert V, Lau KS, Gottlieb CW, Bleicher SJ (1965) Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 25: 1375–1384
Leclercq-Meyer V, Marchand J, Malaisse WJ (1978) The role of calcium in glucagon release. Studies with verapamil. Diabetes 27: 996–1004
Malaisse WJ, Devis G, Herchuelz A, Sener A, Somers G (1976) Calcium antagonists and islet function. VIII. The effect of magnesium. Diab Metab 2: 1–4
Morselli PL, Rovei V, Mitchard M, Durand A, Gomeni R, Larribaud J (1979) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of diltiazem in man. In: Bing RJ (ed). New drug therapy with a calcium antagonist. Diltiazem Hakone Symposium '78, Amsterdam. Elsevier North Holland: Amsterdam (19), pp 152–167
National Diabetes Data Group (1979) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 28: 1039–1057
Ostlund RE (1979) Contractile proteins and pancreatic beta cell secretion. Diabetes 26: 245–252
Rovei V, Mitchard M, Morselli PL (1977) Simple, sensitive and specific gas chromatographic method for the quantification of diltiazem in human body fluid. J Chromatogr 138: 391–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segrestaa, J.M., Caulin, C., Dahan, R. et al. Effect of diltiazem on plasma glucose, insulin and glucagon during an oral glucose tolerance test in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26, 481–483 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542145
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542145