Abstract
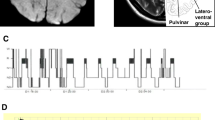
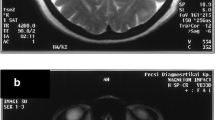
The paramedian thalamus is believed to play an important role in the regulation of sleep, and disturbances of sleep regulation are known to occur in paramedian thalamic stroke (PTS). We examined 12 consecutive patients with PTS and sleep disturbance by MRI. Two distinct groups of patients could be defined: six presenting with severe hypersomnia (group 1) and six with slight sleepiness (group 2). On MRI, all patients had ischaemic lesions involving the paramedian thalamic nuclei, the centre of the lesions being the dorsomedial and centromedial thalamic nuclei. In group 1 the lesions were bilateral, butterfly-shaped infarcts involving the paramedian nuclei (three cases), or unilateral with an extension into the subthalamic nuclei. In group 2 the lesions were unilateral and limited to the paramedian nuclei, mainly the dorsomedial nucleus. Bilateral lesions can be attributed to a common origin in some cases for both paramedian thalamic arteries and the mesencephalic arteries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 July 1996 Accepted: 14 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lövblad, K., Bassetti, C., Mathis, J. et al. MRI of paramedian thalamic stroke with sleep disturbance. Neuroradiology 39, 693–698 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050488
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050488