Summary
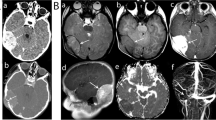
The clinical, neuroradiological, and pathologic-anatomical findings in a 26-year-old patient with chondroblastoma proceeding uncharacteristically from the inside of the right temporal bone and developing intracranially, are reported and discussed. Though this unusually located and rare tumor had caused an increase of intracranial pressure up to the limit of being tolerated, the patient was cured and complete restitution of health was obtained by the total extirpation of the tumor. —Neuroradiologic investigations showed, in addition to other informative findings, a remarkably high uptake of technetium in tumor tissue, the intensity of which exceeded by far the degree which has been found in other tumors studied until now. — It is the third case of a cranial chondroblastoma described in the literature, but the first observation of a chondroblastoma showing excessive endocranial development.
Résumé
Les auteurs rapportent et discutent les signes cliniques, neuroradiologiques et anatomo-pathologiques chez un malade de 26 ans présentant un chondroblastome provenant inhabituellement de l'intérieur de l'os temporal droit et se développant à l'intérieur du crâne. Bien que cette tumeur rare et de situation inhabituelle ait provoqué une augmentation de la tension intracrânienne jusqu'à la limite de tolérance, le malade fut guéri et se rétablit complètement après extirpation globale de la tumeur. Les examens neuroradiologiques montrèrent, en plus d'autres signes informatifs, une fixation élevée de Technetium dans le tissu tumoral, ce degré de fixation dépassant de loin ce qu'on a observé jusqu'à présent. II s'agit du troisième cas de chondroblastome crânien décrit dans la littérature, mais de la première observation d'un chondroblastome présentant un développement intra-crânien excessif.
Zusammenfassung
Es werden die klinischen, neuroradiologischen und pathologisch-anatomischen Befunde eines 26 Jahre alten Patienten beschrieben, bei dem ein Chondroblastom vorlag, das von der Innenseite der rechten Temporalschuppe ausging und sich nach intracraniell entwickelte.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, L. V., Spjut, H. J.: Tumors of bone and cartilage. In: Atlas of tumor pathology Section II, Fascicle 4. Washington: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology 1962.
Bedacht, R., Mohr, U., Spelsberg, F., Wilhelm, K., Wilhelm, M.: Zur Klinik der gutartigen Knochentumoren. Ärztliche Praxis 22, 2987–2994 (1970).
Cendelin, E.: Die chondromatösen Geschwülste des Kiefer-Gesichts-Bereichs. Dtsch. Z. Stomat. 19, 746–753 (1969).
Codman, E. A.: Epiphyseal chondromatous giant-cell tumors of the end of the humerus. Surg. Gynec. and Obstet. 52, 543–548 (1938).
Coley, B. L.: Neoplasmas of bone. Benign chondroblastoma of bone. pp 131–136. New York: Hoeber 1960.
Copeland, M. M., Geschickter, C. F.: Chondroblastic tumors of bone: Benign and malignant. Ann. Surg. 129, 724–735 (1949).
Dahlin, D. C.: Bone tumors. Benign chondroblastoma. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas 1957.
Denko, J. V., Krauel, L. H.: Benign chondroblastoma of bone. An unusual localization in temporal bone. A.M. A. Arch. Path. 59, 710–711 (1955).
Ewing, J.: Neoplastic diseases. A treatise on tumors. Philadelphia and London: W. B. Saunders Co. 1928.
Goodsell, J. O., Hubinger, H. L.: Benign chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Report of case. J. oral Surg. (Chicago) 22, 355–363 (1964).
Hadders, H. N., Donner, R., van Rijssel, T. W.: Chondroblastoma benignum. Ned. Tschr. Geneesk. 100, 2648–2652 (1956).
Jaffé, H. L., Lichtenstein, L.: Benign chondroblastoma of bone. Amer. J. Path. 18, 969–992 (1942).
Kunkel, M. G., Dahlin, D. C., Young, H. H.: Benign chondroblastoma. J. Bone and Joînt Surg. 38, 817–826 (1956).
Lichtenstein, L.: Bone tumors. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby Co. 1959.
Poppe, H.: Angiologie und Szintigraphie bei Knochenund Gelenkerkrankungen. Stuttgart: Thieme 1971.
Ühlinger, E.: Röntgendiagnostik, Ergebnisse 1952–1956. Benigne und semimaligne cystische Knochengeschwülste, 73–96. Stuttgart: Thieme 1957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piepgras, U., Hirth, R., Städtler, F. et al. Chondroblastoma of the temporal bone, an unusual cause of increasing intracranial pressure. Neuroradiology 4, 25–29 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344805
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344805