Summary
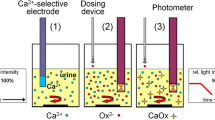
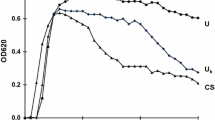
In this study, an efficient microtechnique (gel crystallization method) was used to investigate the in-vivo effect of sodium-potassium citrate on the crystal growth rate of calcium oxalate (Vcr) in human urine samples of 6 healthy volunteers. With a daily dose of 3x11 mmol of alkali citrate, Vcr decreased by 70%. This could have been due to the decrease of calcium excretion, which caused 50–60% of the total change, and to the increase of citrate and pH, each contributing about 20–25% to the decline of Vcr. The findings explain the clinical advantages of alkali citrates in the prevention of recurrent calcium oxalate stone formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilles W (1985) Methodische Neuerungen des kinetischen Gelkristallisationsverfahrens (GKV); Automatisierte Messung des Kalziumoxalat-Kristallwachstums durch Scanning-Mikroskopphotometrie. Fortschr Urol Nephrol 23:252
Achilles W (1987) Crystallization in gel matrices: a new experimental model of calcium stone formation. Contrib Nephrol 58:59
Achilles W, Schalk Ch, Bewernick J, Frömmel H, Rodeck G (1988) Microdetermination of urinary constituents by vertical light-path photometry in microplates. Urol Res 16:174
Achilles W, Schalk Ch, Schulze D, Ulshöfer B, Rodeck G (1988) Calcium, citrate and pH as effectors and inhibitors of calcium oxalate formation in urine. In: Martelli A, Buli P, Marchesini B (eds) Crystallization in renal lithiasis and their clinical application. Acta Medica Edizioni e Congressi, Rome, p 63
Achilles W, Schalk Ch, Ulshöfer B, Rodeck G (1987) Die Wertigkeit kristallisationskinetischer Meßgrößen und anderer Harnparameter für Diagnostik und Therapie der Harnsteinbildung. Fortschr Urol Nephrol 26:111
Achilles W, Schalk Ch, Krzyzanek E, Coors D (1988) The effect of urinary constituents of low molecular weight on the crystal growth of calcium oxalate in gel. Urol Res 16:218
Achilles W, Ulshöfer B (1985) Calculation of complex chemical equilibria in urine: estimation of the risk of stone formation and derivation of prophylactic measures. In: Schwille PO, Smith LH, Robertson WG, Vahlensieck W (eds) Urolithiasis and related clinical research. Plenum Press, New York, p 777
Achilles W, Ulshöfer B (1985) Der Einfluß von Harnparametern auf das “kinetische und thermodynamische Kristallbildungsrisiko” von Kalziumoxalat. Fortschr Urol Nephrol 23:341
Butz M, Knispel HH, Dulce HJ (1988) Seven years experience with citrate therapy in recurrent oxalate stone formers. In: Martelli A, Buli P, Marchesini B (eds) Crystallization in renal lithiasis and their clinical application. Acta Medica Edizioni e Congressi, Rome, p 159
Hesse A, Böhmer I, Classen A, Vahlensieck W (1985) Einfluß von Oxalyt-C auf Urinausscheidungsparameter und die relative Übersättigung von Kalziumoxalat unter standardisierten Ernährungsbedingungen. Fortschr Urol Nephrol 23:56
Pak CYC, Fuller C, Sakhaee K, Preminger GM, Britton F (1981) Long-term treatment of calcium nephrolithiasis with potassium citrate. J Urol 134:11
Preminger GM, Harvey JA, Pak CYC (1985) Comparative efficacy of “specific” potassium citrate therapy versus conservative management in nephrolithiasis of mild to moderate severity. J Urol 134:658
Preminger GM, Sakhaee K, Skurla C, Pak CYC (1985) Prevention of recurrent calcium stone formation with potassium citrate therapy in patients with distal renal tubular acidosis. J Urol 134:20
Scurr DS, Robertson WG (1986) Modifiers of calcium oxalate crystallization found in urine. III. Studies on the role of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein and of ionic strength. J Urol 136:505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achilles, W., Schulze, D., Schalk, C. et al. The in-vivo effect of sodium-potassium citrate on the crystal growth rate of calcium oxalate and other parameters in human urine. Urol Res 18, 1–6 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294572
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294572