Abstract
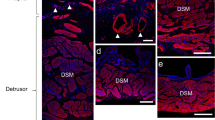
Systemic treatment with epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces growth of all wall layers in the urinary tract of pigs and rats. The present study was initiated to describe morphological and biochemical changes in the bladder smooth muscle from rats treated with EGF for 4 weeks. Eight-week-old female Wistar rats were treated with subcutaneous injections of vehicle (n=16) or EGF (n=8, 150 μg/kg per day) for 4 weeks. After EGF treatment the bladders were increased in weight [74.4±0.4 vs 122.1±0.5 mg, P<0.001 (mean ± SEM)]. Sodium dedecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analyses of six bladders from each group revealed that the total amounts of actin, myosin and desmin were statistically significantly increased by 62%, 61% and 154%, respectively. The relative amounts of actin and myosin were unchanged whereas the desmin to actin ratio was significantly increased — as previously described in rat bladder smooth muscle hypertrophy. Light and electron microscopy of two bladders from each group revealed increased wall thickness involving all wall layers. The smooth muscle fibres at a midventral bladder location seemed only slightly hypertrophic — some degree of hyperplasia was therefore suspected. In conclusion, EGF treatment for 4 weeks induced a net synthesis of contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in the urinary bladder smooth muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arner A, Malmqvist U, Uvelius B (1990) Metabolism and force in hypertrophic smooth muscle from rat urinary bladder. Am J Physiol 258:923
Beauchamp RD, Barnard JA, McCutchen CM, Cherner JA, Coffey RJJ (1989) Localization of transforming growth factor alpha and its receptor in gastric mucosal cells. Implications for a regulatory role in acid secretion and mucosal renewal. J Clin Invest 84:1017
Berk BC, Alexander RW (1989) Vasoactive effects of growth factors. Biochem Pharmacol 38:219
Berk BC, Brock TA, Webb RC, Taubman MB, Atkinson WJ, Gimbrone MAJ, Alexander RW (1985) Epidermal growth factor, a vascular smooth muscle mitogen, induces rat aortic contraction. J Clin Invest 75:1083
Carter NB, Fawcett AA, Hales JR, Moore GP, Panaretto BA (1988) Circulatory effects of a depilatory dose of mouse epidermal growth factor in sheep. J Physiol Lond 403:27
Chen Y, Bornfeldt KE, Arner A, Jennische E, Malmqvist U, Uvelius B, Arnqvist HJ (1994) Increase in insulin-like growth factor I in hypertrophying smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 266:224
Cilento BG, Freeman MR, Schneck FX, Retik AB, Atala A (1994) Phenotypic and cytogenetic characterization of human bladder urothelia expanded in vitro. J Urol 152:665
Fisher DA, Salido EC, Barajas L (1989) Epidermal growth factor and the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol 51:67
Gabella G, Uvelius B (1990) Urinary bladder of the rat: fine structure of normal and hypertrophic musculature. Cell Tissue Res 262:67
Gabella G, Uvelius B (1994) Reversal of muscle hypertrophy in the rat urinary bladder after removal of urethral obstruction. Cell Tissue Res 277:333
Hollenberg MD (1994) The acute actions of growth factors in smooth muscle systems. Life Sci 54:223
Jørgensen PE, Hilchey SD, Nexø E, Poulsen SS, Quilley CP (1993) Urinary epidermal growth factor is excreted from the rat isolated perfused kidney in the absence of plasma. J Endocrinol 139:227
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the macrophage T4. Nature 227:680
Malmquist U, Arner A, Uvelius B (1991) Contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in smooth muscle during hypertrophy and its reversal. Am J Physiol 260:1085
Malmquist U, Arner A, Uvelius B (1991) Mechanics and Ca++-sensitivity of human detrusor muscle bundles studies in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand 143:373
Neal DE, Mellon K (1992) Epidermal growth factor receptor and bladder cancer: a review. Urol Int 48:365
Olsen PS, Poulsen SS, Kirkegaard P, Nexø E (1984) Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology 87:103
Perrella MA, Maki T, Prasad S, Pimental D, Singh K, Takahashi N, Yoshizumi M, Alali A, Higashiyama S, Kelly R, Lee M-E, Smith TW (1994) Regulation of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor mRNA levels by hypertrophic stimuli in neonatal and adult rat cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 43:27045
Prigent SA, Lemoine NR (1992) The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res 4:1
Sarosiek J, Feng T, McCallum RW (1991) The interrelationship between salivary epidermal growth factor and the functional integrity of the esophageal mucosal barrier in the rat. Am J Med Sci 302:359
Shing Y, Christofori G, Hanahan D, Ono Y, Sasada R, Igarashi K, Folkman J (1993) Betacellulin: a mitogen from pancreatic beta cell tumors. Science 259:1604
Steers WD, Albo M, Tuttle JB (1994) Calcium channel antagonists prevent urinary bladder growth and neuroplasticity following mechanical stress. Am J Physiol 266:R20
Takayanagi I (1980) Effects of urogastrone on mechanical activities of the stomach and intestine of guinea-pig. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:228
Temizer DH, Yoshizumi M, Perrella MA, Susanni EE, Quertermous T, Lee ME (1992) Induction of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor mRNA by phorbol ester and angiotensin II in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 267:24892
Vinter-Jensen L, Juhl CO, Djurhuus JC, Poulsen SS, Daiani EZ, Brown KD, Ørntoft TF, Teglbjrg PS, Nexø E (1995) Chronic systemic treatment with epidermal growth factor in pigs causes pronounced urothelial growth with accumulation of glycoconjugates. Am J Pathol 147:1330
Vinter-Jensen L, Smerup M, Jørgensen PE, Juhl CO, Ørntoft T, Poulsen SS, Nexø E (1996) Chronic treatment in the rat with epidermal growth factor stimulates growth of the urinary tract. Urol Res 24:15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinter-Jensen, L., Uvelius, B., Nexø, E. et al. Contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in urinary bladder smooth muscle from rats treated with epidermal growth factor. Urol. Res. 24, 229–234 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295897
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295897