Abstract
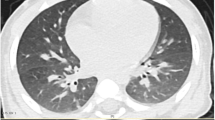
We report a case of acute pulmonary adema following exposure to organophosphate insecticide. Hypoxia, respiratory failure, and parasympathetic discharge are implicated in the pathogenesis and are related to the anticholinesterase activity of the toxicant. Rapid onset of acute pulmonary edema without cardiomegaly followed by prompt clearing are the radiographic features.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bledsoe, F., Seymour, E. Q.: Acute pulmonary edema associated with parathion poisoning. Radiology103, 53 (1972)
DeReuck, J., Willems, J.: Acute parathion poisoning: myopathic changes in the diaphragm. J. Neurol.209, 309 (1975)
Grob, D., Garlick, W. L., Harvey, A. M.: The toxic effects in man of the anticholinesterase insecticide parathion (p-nitrophenyl diethyl thionophosphate). Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp.87, 106 (1950)
Namba, T., Nolte, C., et al.: Poisoning due to organophosphate insecticides. Am. J. Med.50, 475 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kass, J.B., Khamapirad, T. & Wagner, M.L. Pulmonary edema following skin absorption of organophosphate insecticide. Pediatr Radiol 7, 113–114 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00975681
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00975681