Abstract
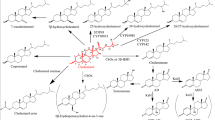
By preselection of microorganisms which preferentially attack the side chain of cholesterol we have been able to isolate a mutant of Corynebacterium spec. Chol 73 which forms 20-carboxy-pregna-1,4-dien-3-one (BNC) from cholesterol in nearly quantitative yields. The structure of this compound has been established by means of13C NMR-,1H NMR and CD spectroscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arima K, Nagasava M, Bae M, Tamura G (1969) Microbial transformation of sterols. Agric Biol Chem 33:1636–1443, 1644–1650
Arima K, Beppu T, Nakamatsu W (1977) Microbial production of 3-oxobisnorchola-1,4-dienoic acid. Japan Kokai 7776484; CA 87:182618j
Arima K, Nakamatsu W, Beppu T (1978) Microbial production of 3-oxobisnorchola-1,4-dien-22-oic acid. Agric Biol Chem 42:411–416
Atrat P, Hiller E, Hörhold C, Buchar MI, Arubasara AY, Koschtschejenko KA (1980) Steroidtransformation mit immobilisierten Mikroorganismen. II Abbau der Seitenkette von Cholesterol mit immobilisierten Zellen vonNocardia erythropolis. Z Allg Mikrobiol 20:159–166
Böhme KH, Hörhold C (1980) Mikrobieller Seitenkettenabbau von strukturmodifizierten Sterolen. Z Allg Mikrobiol 20:85–93
Brown RL, Peterson GE (1966) Cholesterol oxidation by soilActinomycetes. J Gen Microbiol 45:441–450
Breitmaier E, Voelter W (1978) “13C NMR Spectroscopy”. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 2. Auflage
Fried J, Thoma RW, Klingsberg A (1953) Oxidation of steroids by microorganisms III. Side-chain degradation, ring D-cleavage and dehydrogenation in ring A. J Am Chem Soc 75:5764–5765
Hanson JR, Siverns M (1975)13C NMR spectra of some steroid unsaturated ketones. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans I:1956–1958
Henkel KGaA (1979) Verfahren zum selektiven Seitenkettenabbau von Steroidverbindungen und zur Herstellung hierzu geeigneter Mikroorganismen-Defektmutanten sowie neue Mikroorganismen-Stämme Eur Pat Appl 4913; CA 92:106618b
Henkel KGaA (1980) Verfahren zum selektiven Seitenkettenabbau von Steroidverbindungen und zur Herstellung hierzu geeigneter Mikroorganismen-Defektmutanten sowie neue Mikroorganismen-Stämme (II). Eur Pat Appl 15308; CA 93:236940c
Jaffé HH, Orchin M (1962) Theory and application of UV spectroscopy, John Wiley, New York
Jung G, Koenig WA, Voelter W, Gupta D, Breitmaier G, Bierich JR (1973) 1,4-Androsta-diene-3,17-dione found in the urine of a boy. Steroids 22(2):293–306
Kieslich K (1980a) Industrial aspects of biotechnological production of steroids. Biotechnol Letters 2:211–217
Kieslich K (1980b) “Steroid conversions” in Economic Micobiology, Vol 5, Rose AH (ed). Academic Press, London New York Toronto Sydney San Francisco, pp 370–413
Marshek WJ, Kraychy S, Muir RD (1972) Microbial degradation of sterols. Appl Microbiol 23:72–77
Mason SF (1963) Optical rotatory power. Quart Rev 17:20–66
Martin CKA (1977) Microbial cleavage of sterol side chains. Adv Appl Microbiol 22:29–58
Martin CKA, Wagner F (1976) Microbial transformation of β-sitosterol byNocardia sp M 29. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2:243–255
Mitsubishi Chemical Industries Co. Ltd. (1979) Steroidal alcohols by cultivatingMycobacterium. Eur Pat Appl 1622; CA 92:4699g
Mogil'nitskii GM, Andreev LV, Koshcheenko KA (1974) Enzymatic destruction of steroids in the process of 11α-and 11β-hydroxylation of the 21-acetate of the Reichstein substance “S” by the fungus Tieghemella orchidis. Mikrobiologiya 44:351–356
Nagasava M, Watanabe N, Hashiba H, Tamura G, Arima K (1970) Microbial transformation of sterols. Agric Biol Chem 34:798–800, 801–804, 838–844
Neff G, Eder U, Seeger A, Wiechert R (1980) Aufbau von Pregnan-Seitenketten. Chem Ber 113:1184–1188
Nominé G (1980) La place des bioconversions dans l'accès industriel aux steroides. Bull Soc Chim France II:18–23
Schatz A, Savard K, Pintner IF (1949) The ability of soil microorganisms to decompose steroids. J Bacteriol 58:117–125
Schering AG (1979) Verfahren zur Herstellung von 21-Hydroxy-20-methyl-pregnan-Derivaten. Eur Pat Appl 2535; CA 91:173386n
Schoemer U, Martin CKA (1980) Microbial transformation of sterols. Biotechnol Bioeng 80: (Suppl I Ferment Sci Technol Future): 11–25
Schoemer U, Wagner F (1980) Production of steroid-ring-b-seco acid from β-sitosterol and influence of surfactants on sterol uptake inNocardia sp. M29-40. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 10:99–106
Schubert K, Böhme KH, Hörhold C (1978) Verfahren zur Herstellung von 20-Carboxy-pregna-1,4-dien-3-one. East-G. patent 132271; CA 91:106618b
Sih CJ, Wang KC, Tai HH (1967a) Mechanism of steroid oxidation by microorganisms XIII. C22 acid intermediates in the degradation of the cholesterol side chain. Biochem 7:796–807
Sih CJ, Tai HH, Tsong YY (1967b) The mechanism of microbial conversion of cholesterol into 17-keto steroids. J Am Chem Soc 89:1957–1958
Stadtman TC, Cherkes A, Anfinsen CB (1954) Studies on the microbial degradation of cholesterol. J Biol Chem 206:511–235
Turfitt GE (1944) Microbial agencies in the degradation of sterols. J Bacteriol 47:487–494, 54:557–562
VanRheenen V, Shephard KP (1979) New synthesis of corticosteroids from 17-keto steroids: application and sterochemical study of the unsaturated sulfoxide-sulfonate rearrangement. J Org Chem 44:1582–1584
Whitmarsh JM (1964) Intermediates of microbiological metabolism of cholesterol. Biochem J 90:23p-24p
Wovcha MG, Antosz FJ, Knight JC, Kominek LA, Pyke, TR (1978) Bioconversion of sitosterol to useful steroidal intermediates by mutants ofMycobacterium fortuitum. Biochim Biophys Acta 531:308–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Dr. Bruno Werdelmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, F.F., Schindler, J., Schmid, R. et al. Microbial conversion of sterols. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15, 25–32 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01875396
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01875396