Summary
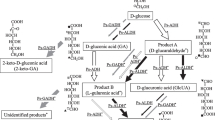
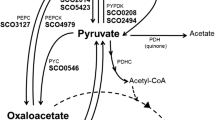
Zymomonas mobilis ATCC 29191 is able to degrade gluconate but cannot use it as a single carbon and energy source. Gluconate is phosphorylated by a gluconate kinase (EC 2.7.1.12) and the resulting 6-phosphogluconate is further catabolized to yield about 0.8 mol ethanol per mol of gluconate, considerable amounts of acetate and acetoin. This product spectrum agrees with the theoretical yield of only one reduction equivalent if gluconate is phosphorylated by a kinase and subsequently metabolized via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
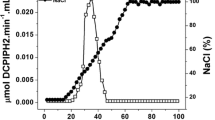
Furthermore, Z. mobilis contains a membrane-bound enzyme system which is able to oxidize glucose to gluconate. Cell-free extracts were active in an assay system with Wurster's blue as electron acceptor, and various aldoses as well as maltose, mannitol and sorbitol could be oxidized. The affinity for sorbitol was very low (K m =330 mM) but reasonable for glucose (K m =2.8 mM). The pH optimum for the glucose-oxidizing reaction was 6.5, while that for sorbitol oxidation was 5.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrow KD, Collins JG, Leigh DA, Rogers PL, Warr RG (1984) Sorbitol production by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20:225–232
Belaich JP, Senez JC (1965) Influence of aeration and pantothenate on growth yields of Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol 89:1195–1200
Bergmeyer HU, Bernt E, Schmidt F, Stork H (1974a) d-Glucose-Bestimmung mit Hexokinase und Glucose-6-P-Dehydrogenase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Bd. 2, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1241–1246
Bergmeyer HU, Gruber W, Gutman I (1974b) d-Sorbitol. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Bd. 2, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1366–1371
Bernt E, Bergmeyer HU (1974) d-Fructose. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Bd. 2, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1349–1352
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Analyt Biochem 72:248–254
Bringer S, Finn RK, Sahm H (1984) Effect of oxygen on the metabolism of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 139:376–381
Bringer S, Härtner T, Poralla K, Sahm H (1985) Influence of ethanol on the hopanoid content and the fatty acid pattern in batch and continuous cultures of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 140:312–316
Bringer-Meyer S, Scollar M, Sahm H (1985) Zymomonas mobilis mutants blocked in fructose utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:134–139
Dawes EA, Large PJ (1968) The endogenuous metabolism of anaerobic bacteria. Final technical report for European Research Office US-Army, Contract-Number DAJA 37-67-C-0567, April 1968
Duine JA, Frank J, Jongejan JA (1986) PQQ and quinoprotein enzymes in microbial oxidations. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:165–178
Everaerts FM, Beckers JL, Verheggen TPE (1976) Isotachophoresis — theorie, instrumentation and applications. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam-Oxford-New York
Finn RK, Bringer S, Sahm H (1984) Fermentation of arabinose to ethanol by Sarcina ventriculi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:161–166
Leigh D, Scopes RK, Rogers PL (1984) A proposed pathway for sorbitol production by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20:413–415
Michaelis L, Granick S (1943) The polymerization of the free radicals of the Wurster dye type: the dimeric resonance bond. J Am Chem Soc 65:1747–1755
Millis NF (1956) A study of the cider-sickness bacillus — a new variety of Zymomonas anaerobia. J Gen Microbiol 15:521–528
Möllering H, Bergmeyer HU (1974) Gluconat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, Bd. 2, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1288–1292
Rogers PL, Lee KJ, Tribe DE (1980) High productivity ethanol production with Zymomonas mobilis. Process Biochem 15:7–11
Rogers PL, Lee KJ, Skotnicki ML, Tribe DE (1982) Ethanol production by Zymomonas mobilis. Adv Biochem Eng. 23:37–84
Schie BJ van, Dijken JP van, Kuenen JG (1984) Non-coordinated synthesis of glucose dehydrogenase and its prosthetic group PQQ in Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 24:133–138
Scopes RK, Testolin V, Stoter A, Griffiths-Smith K, Algar EM (1985) Simultaneous purification and characterization of glucokinase, fructokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem J 228:622–634
Shinagawa E, Ameyama M (1982) d-Sorbitol dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter suboxydans, membran-bound. In: Wood WA (ed) Methods in enzymology, 89D. Academic Press, pp 141–145
Viikari L (1984) Foramtion of levan and sorbitol from sucrose by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:252–255
Zachariou M, Scopes RK (1985) Gluconate kinase from Zymomonas mobilis: Isolation and characteristics. Biochem International 10:367–371
Zachariou M, Scopes RK (1968) Glucose-fructose-oxidoreductase, a new enzyme isolated from Zymomonas mobilis that is responsible for sorbitol production. J Bacteriol 167:863–869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. H. Dörfel on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strohdeicher, M., Schmitz, B., Bringer-Meyer, S. et al. Formation and degradation of gluconate by Zymomonas mobilis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 378–382 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251772
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251772