Summary
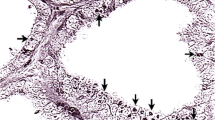
Skeletal muscles from a patient with type IV glycogenosis were studied by light and electron microscopy. The distinctive polysaccharide deposits were more abundant in the tongue and diaphragm than other skeletal muscles. The involved myofibers contained fusiform areas filled with polyhedral or rounded granules of basophilic material that was further characterized by staining with periodic acid-Schiff, Grocott methenamine silver and alcian blue. Ultrastructurally the deposits were composed of branched filaments, osmophilic granules and electron-dense amorphous material. There are sufficient ultrastructural, histochemical and chemical similarities among the deposits in type IV glycogenosis, Lafora bodies and visceral deposits in myoclonus epilepsy, corpora amylacea and basophilic degeneration of the myocardium to suggest a common composition and mechanism of synthesis possibly through reversal of the debranching enzyme system. However, sharing a biochemical pathway does not necessarily imply a common etiological factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, D. H.: Studies on glycogen disease with report of a case in which the glycogen was abnormal. In: Carbohydrate metabolism. (V. A. Najjar, ed.), pp. 28–42. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press 1952.
—: Familial cirrhosis of the liver with storage of abnormal glycogen. Lab. Invest.5, 11–2 (1956).
Brown, B. I.: personal communication (1970).
—, Brown, D. H.: Lack of an α-1, 4-glucan: α-1, 4-glucan 6-glycosyl transferase in a case of type IV glycogenosis. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)56, 725–729 (1966).
——: Glycogen-storage diseases: Types I, III, IV, V, VII and Unclassified Glycogenosis. In: Carbohydrate metabolism and its disorders. (F. Dickens, P. J. Randle, W. J. Whelan, eds.), Vol. 2, pp. 123–150. London-New York: Academic Press 1968.
Brunberg, J. A., McCormick, W. F., Schochet, S. S., Jr.: Type III glycogenosis. An adult with diffuse weakness and muscle wasting. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)25, 171–178 (1971).
Collins, G. H., Cowden, R. R., Nevis, A. H.: Myoclonus epilepsy with Lafora bodies. An ultrastructural and cytochemical study. Arch. Path.86, 239–254 (1968).
Cornog, J. L., Jr., Gonatas, N. K.: Ultrastructure of rhabdomyoma. J. Ultrastruct. Rev.20, 433–450 (1967).
Craig, J. M., Uzman, L. L.: A familial metabolic disorder with storage of an unusual polysaccharide complex. Pediatries22, 20–32 (1958).
Fernandez, J., Huijing, F.: Branching enzyme-deficiency glycogenosis: Studies in therapy. Arch. Dis. Childh.43, 347–352 (1968).
Ferrans, V. J., Hibbs, R. G., Walsh, J. J., Burch, G. E.: Cardiomyopathy, cirrhosis of the liver and deposits of a fibrillar polysaccharide: Report of a case with histochemical and electron microscopic studies. Amer. J. Cardiol.17, 457–469 (1966).
Holleman, L. W. J., van der Haar, J. A., de Vaan, G. A. M.: Type IV glycogenosis. Lab. Invest.15, 357–367 (1966).
Holmes, J. M., Houghton, C. R., Woolf, A. L.: A myopathy presenting in adult life with features suggestive of glycogen storage disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.23, 302–311 (1960).
Huijing, F., Lee, E. Y. C., Carter, J. H., Whelan, W. J.: Branching action of amylo-1,6-glucosidase/oligo-1,4→1,4-glucantransferase. FEBS Letters7, 251–253 (1970).
Illingworth, B., Cori, G. T.: Structure of glycogens and amylopectins. III. Normal and abnormal human glycogen. J. biol. Chem.199, 653–660 (1952).
Jenis, E. H., Schochet, S. S., Jr., Earle, K. M.: Myoclonus epilepsy with Lafora bodies: A case report with electron microscopic observation. Milit. Med.135, 116–119 (1970).
Karpati, G., Carpenter, S., Wolfe, L. S., Sherwin, A.: A peculiar polysaccharide accumulation in muscle in a case of cardio-skeletal myopathy. Neurology (Minneap.)19, 553–564 (1969).
Kosek, J. C., Angell, W.: Fine structure of basophilic myocardial degeneration. Arch. Path.89, 491–499 (1970).
Levin, B.: Glycogen storage disease type IV, amylopectinosis. Proc. roy. Soc. Med.61, 1264 (1968).
—, Burgess, E. A., Mortimer, P. E.: Glycogen storage disease type IV, amylopectinosis. Arch. Dis. Childh.43, 548–555 (1968).
Mercier, C., Whelan, W. J.: The fine structure of glycogen from type IV glycogen-storage disease. Europ. J. Biochem.16, 579–583 (1970).
Mortimer, P. E.: Glycogen storage disease. Proc. roy. Soc. Med.58, 700–701 (1965).
Ramsey, H. J.: Ultrastructure of corpora amylacea. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.24, 25–39 (1965).
Reed, G. B., Jr., Dixon, J. F. P., Neustein, H. B., Donnell, G. N., Landing, B. H.: Type IV glycogenosis: Patient with absence of a branching enzyme α-1,4-glucan: α-1,4-glucan 6-glycosyl transferase. Lab. Invest.19, 546–557 (1968).
Rosai, J., Lascano, F.: Basophilic (mucoid) degeneration of myocardium. A disorder of glycogen metabolism. Amer. J. Path.61, 99–115 (1970).
Sakai, M., Austin, J., Witmer, F., Trueb, L.: Studies of corpora amylacea. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization by chemical and histochemical techniques. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)21, 526–544 (1969).
———, Trueb, L.: Studies in myoclonus epilepsy. (Lafora body form.) II. Polyglucosans in the systemic deposits of myoclonus epilepsy and in corpora amylacea. Neurology20, 160–176 (1970).
Schochet, S. S., Jr., McCormick, W. F., Zellweger, H.: Type IV glycogenosis (amylopectinosis). Arch. Path.90, 354–363 (1970).
Sidbury, J. B., Jr., Mason, J., Burns, W. B., Jr., Ruebner, B. H.: Type IV glycogenosis. Report of a case proven by characterization of glycogen and studied by necropsy. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp.111, 157–181 (1962).
Steffanini, M., DeMartino, C., Zamboni, L.: Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature (Lond.)216, 173–174 (1967).
Suzuki, K., David, E., Kutschman, B.: Presenile dementia with “Lafora-like” intraneuronal inclusions. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)25, 69–80 (1971).
Vanderhaeghen, J.-J.: Correlation between ultrastructure and histochemistry of Lafora bodies. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)17, 24–26 (1971).
Wyatt, R. B., Schochet, S. S., Jr., McCormick, W. F.: Rhabdomyoma: Light and electron microscopic study of a case with intranuclear inclusions. Arch. Otolaryng.92, 32–39 (1970).
Yokoi, S., Austin, J., Witmer, F., Sakai, M.: Studies in myoclonus epilepsy. (Lafora body form.) I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Lafora bodies in two cases. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)19, 15–33 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schochet, S.S., McCormick, W.F. & Kovarsky, J. Light and electron microscopy of skeletal muscle in type IV glycogenosis. Acta Neuropathol 19, 137–144 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688492
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688492