Abstract
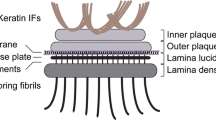
Hemidesmosomes are junctional complexes involved in the attachment of epidermal basal keratinocytes to the basement membrane. To try to understand better the sequence of events in the morphogenesis of hemidesmosomes, we undertook an ultrastructural analysis of hemidesmosome formation in fetal and neonatal digit skin. Hemidesmosomes, defined as membrane-associated densities or plaques, were counted and scored for three morphological characteristics: (1) the presence of a sub-basal dense plate, (2) association with anchoring filaments within the lamina lucida and (3) contacts with intermediate filaments. No hemidesmosomes were evident at 7 weeks' gestational age. Between 9 and 15 weeks the number of hemidesmosomes increased by about fourfold (from 20.6±3.8 (SD) to 95.5±8.4 per 40 μm of basal cell plasma membrane;P<0.01). The association of hemidesmosomes with intermediate filaments and anchoring filaments also increased after 15 weeks (P<0.05). Early attachment plaques first appeared as triangular focal densities on the basal plasma membrane with the appearance of sub-basal dense plates, which later became both larger and more electron dense. By 15 weeks, an inner plaque could be distinguished from the outer plaque, which coincided with a closer association with intermediate filaments. Hemidesmosomes appeared fully developed by 15 weeks' gestation. This study illustrates the structural relationship of hemidesmosomes to both intra- and extracellular filaments, suggesting close functional interactions. The complexity of the hemidesmo-some plaque is also revealed early during development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 213–215
Breathnach A (1971) An atlas of the ultrastructure of human skin. J and A Churchill, London
Breathnach AS, Robins J (1969) Ultrastructural features of epidermis of a 14 mm (6 weeks) human embryo. Br J Dermatol 81:504–516
Briggaman RA, Wheeler CE Jr (1975) The epidermal-dermal junction. J Invest Dermatol 65:71–84
Burgeson RE, Chiquet M, Deutzmann R, Ekblom P, Engel J, Kleinman H, Martin G, Meneguzzi G, Paulsson M, Sanes J, Timpl R, Tryggvason K, Yamada Y, Yurchenco PD (1994) A new nomenclature for the laminins. Matrix Biol 14:209–211
Chapman S, Eady RAJ (1985) Blistering in keratinocyte cultures: a regular phenomenon associated with differentiation. Eur J Cell Biol 39:352–359
Chapman SJ, Leigh IM, Tidman MJ, Eady RAJ (1990) Abnormal expression of hemidesmosome-like structures by junctional epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes in vitro. Br J Dermatol 123:137–144
Dale BA, Holbrook KA, Kimball JR, Hoff M, Sun T-T (1985) Expression of epidermal keratins and filagrin during human fetal skin development. J Cell Biol 101:1257–1269
Eady RAJ (1994) The hemidesmosome: a target in auto-immune bullous diseases. Dermatology 189:38–41
Fine JD, Horiguchi Y, Jester J, Couchman JR (1989) Detection and partial characterization of a midlamina lucida-hemidesmosome associated antigen (19-DEJ-1) present within human skin. J Invest Dermatol 92:825–830
Fine JD, Bynum K, Byrsk M (1991) LDA-1 and 19-DEJ-1 antigens: further characterization of two novel skin basement membrane components, Clin Res 39:561 A
Gipson IK, Grill SM, Spurr-Michaud SJ, Brennan SJ (1983) Hemidesmosome formation in vitro. J Cell Biol 97:849–857
Hegemann L, Kempenaar J, Ponec M (1994) The involvement of protein kinase, C in proliferentiation and differentiation of human keratinocytes—an investigation using inhibitors of protein kinase C. Arch Dermatol Res 286:278–284
Hertle MD, Adams JC, Watt FM (1991) Integrin expression during human epidermal development in vivo and in vitro. Development 112:193–206
Hirone T, Taniguchi S (1980) BAsal lamina formation by epidermal cells in culture. Curr Probl Dermatol 10:159–169
Holbrook KA, Hoff MS (1984) Structure of the developing human embryonic and fetal skin. Semin Dermatol3:185–202
Jones JCR, Green KJ (1991) Intermediate filament-plasma membrane interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3:127–132
Jonkman MF, Jonk MCJM de, Heeres K, Sonnenberg A (1992) Expression of integrins α6β4 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 99:489–496
Karnovsky MJA (1965) Formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137–138a
Krawczyk WS, Wilgram GF (1973) Hemidesmosome and desmosome morphogenesis during epidermal wound healing. J Ultrastruct Res 45:93–101
Lane AT (1986) Human fetal skin development. Pediatr Dermatol 3:487–491
Lane AT, Helm KF, Goldsmith LA (1985) Identification of bullous pemphigoid antigen, pemphigus, laminin and anchoring fibril antigens in human fetal skin. J Invest Dermatol 84:27–30
Legan PK, Collins JE, Garrod DR (1992) The molecular biology of desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: “What's in a name?” Bioessays 14:385–392
Moll I, Moll R (1992) Changes of expression of intermediate filament proteins during ontogenesis of eccrine sweat glands. J Invest Dermatol 98:771–785
Mutasim DF, Takahashi Y, Labib RS, Anhalt GJ, Patel HP and Diaz LA (1985) A pool of bullous pemphigoid antigen is intracellular and associated with the basal cell cytoskeleton-hemidesmosome complex. J Invest Dermatol 84:47–53
Niessen CM, Hogervorst F, Jaspars LH, De Melker AA, Delwel GO, Hulsman EH, Kuikman I, Sonnenberg A (1994) The α6β4 integrin is a receptor for both laminin and kalinin. Exp Cell Res 211:360–367
Owaribe K, Kartenbeck J, Stumpp S, Magin T, Kreig T, Diaz LA, Franke WW (1990) The hemidesmosomal plaque 1. Characterization of a major constituent protein as a differentiation marker for certain forms of epithelia. Differentiation 45:207–220
Rempen A (1991) Vaginal ultrasonography in the first trimester. II Quantitative parameters. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 195:163–171
Richardson KC, Jarret L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323
Rodeck CH, Eady RAJ, Gosden CM (1980) Prenatal diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa lethalis. Lancet I:949–952
Sakai LY, Keene DR, Morris NP, Burgeson RE (1986) Type VII collagen is a major structural component of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol 103:1577
Sawamura D, Li K, Chu ML, Uitto J (1991) Human bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG 1) Amino acid sequence deduced from cloned cDNAs predict biologically important peptide segments and protein domains. J Biol Chem 266:17784–17790
Schofield OMV, Fine JD, Pisani A, Heagerty AHM, Ortonne JP, Eady RAJ (1990) GB3 monoclonal antibody for the diagnosis of junctional epidermolysis bullosa: results of a multicenter study. J Am Acad Dermatol 23:1078
Smith LT, Sakia LY, Burgeson RE, Holbrook KA (1988) Ontogeny of structural components at the dermal epidermal junction in human embryonic and fetal skin: the appearance of anchoring fibrils and type VII collagen. J Invest Dermatol 90:480–485
Sonnenberg A, Calafat J, Janssen H, Daams H, Raaij-Helmer LM van der, Falcioni R, Kennel SJ, Aplin JD, Baker J, Lorizidou M, Garrod D (1991) Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol 113:907–917
Stepp MA, Spurr-Michaud SJ, TisdaleA, Elwell J (1990) α6β4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8970–8974
Tanaka T, Korman NJ, Shimizu H, Eady RAJ, Klaus-Kovtun V, Cehrs K, Stanley JR (1990) Production of rabbit antibodies against carboxy-terminal epitopes encoded by bullous pemphigoid cDNA. J Invest Dermatol 94:617–623
Thatcher SM, Malone KL, Dave K, Zhao S (1991) Localization of the 230 kD bullous pemphigoid antigen in cultured keratino-cytes: formation of a prehemidesmosome. Exp Cell Res 194:238–247
Tidman MJ, Eady RAJ (1984) Ultrastructural morphometry of the normal human dermal epidermal junction: the influence of age, sex and body region on laminar and non-laminar components. J Invest Dermatol 83:448
Tidman MJ, Eady RAJ (1986) Hemidesmosome heterogeneity in junctional epidermolysis bullosa revealed by morphometric analysis. J Invest Dermatol 86:51–56
Trolle D (1948) Age of foetus determined from its measures. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 27:327–337
Zeng L, Daniels A, Ridelle K, Fine JD (1994) Uncein, an anchoring filament component is biochemically similar to kalinin but differs markedly in its in vitro expression by normal human keratinocyte monolyaers (abstract) J Invest Dermatol 102:535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMillan, J.R., Eady, R.A.J. Hemidesmosome ontogeny in digit skin of the human fetus. Arch Dermatol Res 288, 91–97 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02505050
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02505050