Abstract
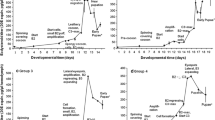
The hormone ecdysone induces a large number of changes in the puffing pattern of mid third instar larvae of Drosophila hydei. The pattern of changes occurring after experimental administration of the hormone are identical with those observed in normal development during a 6 hour period before puparium formation. After administration of the hormone a considerable number of puffs react with a change in activity within 15–20 min. During this period 3 puffs arise newly, 12 puffs show a strong increase in activity, 6 puffs show a less pronounced increase in activity and 12 puffs show a decrease in activity. At a period of 4–6 hours after administration of the hormone another 5 puffs arise newly. The effect of the hormone was identical in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. — Diameter measurements on several puffs reacting within 30 min with an increase in diameter showed that these puffs reacted simultaneously. Most of the puffs that showed a decrease in activity reacted with some delay. — A study of the effect of different hormone concentrations revealed that the kinetics of 4 puffs with respect to the relationship between concentration and puff size was identical over a range of concentrations from 33·10−5 to 33CU/μl. Three of these puffs showed a reaction with even lower concentrations. Maximum puff size is attained by all puffs at a concentration of 33·10−4CU/μl. Among the puffs studied no difference in their reaction threshold was found. — A study of the behavior of 5 puffs of the group reacting within 15–20 min and one of the group reacting after 4–6 hours in midintestine and Malpighian tubules revealed that these puffs showed the same reaction after injection of the hormone as observed in the salivary glands. — All puffs activated by administration of the hormone showed particularly strong uptake of tritiated uridine and accumulation of acidic protein. — It is concluded that the hormone ecdysone induces a pattern of changes in gene activity that is far more complex in Drosophila hydei than in Chironomus tentans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfert, M., and I. I. Geschwind: A selective staining method for the basic proteins of cell nuclei. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 39, 991–999 (1953).
Ashburner, M.: Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma (Berl.) 21, 398–427 (1967).
Becker, H. J.: Die Puffs der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Drosophila melanogaster. I. Mitt. Beobachtungen zum Verhalten des Puffmusters im Normalstamm und bei zwei Mutanten, Giant und Lethal-giant-larvae. Chromosoma (Berl.) 10, 654–678 (1959);- II. Mitt. Die Auslösung der Puffbildung, ihre Spezifität und ihre Beziehung zur Funktion der Ringdrüse. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 341–384 (1962).
Beermann, W.: Chromomerenkonstanz und spezifische Modifikationen der Chromosomenstruktur in der Entwicklung und Organdifferenzierung von Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma (Berl.) 5, 139–198 (1952).
Berendes, H. D.: Salivary gland function and chromosomal puffing patterns in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma (Berl.) 17, 35–77 (1965);- Differential replication of male and female X-chromosomes in Drosophila. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 32–43 (1966);- Amino acid incorporation into giant chromosomes of Drosophila hydei. Dros. Inf. Serv. 42, 102 (1967).
Clever, U.: Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans. I. Mitt. Genaktivierung durch Ecdyson. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 607–675 (1961);- Puffing in giant chromosomes of Diptera and the mechanism of its control. In: The nucleohistones, (J. Bonner and P. Ts'o, eds.). San Francisco: Holden Day Inc., 1964;- Induction and repression of a puff in Chironomus tentans. Develop. Biol. 14, 421–438 (1966).
Glever, U., u. P. Karlson: Induktion von Puffänderungen in den Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans durch Ecdyson. Exp. Cell Res. 20, 623–627 (1960).
Mechelke, F.: Spezielle Funktionszustände des genetischen Materials. In: Funktionelle und morphologische Organisation der Zelle. Wiss. Konf. d. Ges. Deutscher Naturforsch. u. Ärzte in Rottach-Egern 1962, 15–29 (1963).
Panitz, R.: Experimentell induzierte Inaktivierung Balbiani-Ring bildender Gen-Loci in Riesenchromosomen. In: Struktur und Funktion des genetischen Materials. Erwin-Baur-Gedächtnis-Vorlesungen III. Berlin: Akademie Verlag 1963;- Hormonkontrollierte Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Acricotopus lucigus. Biol. Zbl. 83, 197–230 (1964).
Pelling, C.: Chromosomal synthesis of ribonucleic acid as shown by incorporation of uridine labelled with tritium. Nature (Lond.) 184, 655–656 (1959).
Swift, H.: The histones of polytene chromosomes. In: The nucleohistones, (J. Bonner and P. Ts'o, eds.) San Francisco: Holden Day Inc. 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berendes, H.D. The hormone ecdysone as effector of specific changes in the pattern of gene activities of Drosophila hydei . Chromosoma 22, 274–293 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319878
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319878