Summary
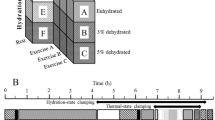
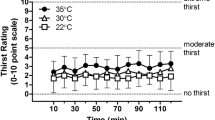
Five young unacclimatised subjects were exposed for 4 h at 34‡ C (10‡ C dew-point temperature and 0.6 m · s−1 air velocity), while exercising on a bicycle ergometer: 25 min work — 5 min rest cycles for 2 hours followed by 20 min work — 10 min rest cycles for two further hours. 5 experimental sessions were carried out: one without rehydration (NO FLUID) resulting in 3.1% mean loss of body weight (δ Mb), and four sessions with 20‡ C fluid ingestion of spring water (WATER), hypotonic (HYPO), isotonic (ISO) and hypertonic (HYPER) solutions to study the effects of fluid osmolarity on rehydration. Mean final rehydration (±SE) after fluid intake was 82.2% (±1.2). Heart rate was higher in NO FLUID while no difference among conditions was found in either δ Mb or hourly sweat rates. Sweating sensitivity was lowest in the dehydration condition, and highest in the WATER one. Modifications in plasma volume and osmolarity demonstrated that NO FLUID induced hyperosmotic hypovolemia, ISO rehydration rapidly led to plasma isoosmotic hypervolemia, while WATER led to slightly hypoosmotic normovolemia.
It is concluded that adequate rehydration through ingestion of isotonic electrolyte-sucrose solution, although in quantities much smaller than evaporative heat loss, rapidly restored and expanded plasma volume. While osmolarity influenced sweating sensitivity, the plasma volume changes (δ PV) within the range −6%⩽δ PV⩽+4% had little effect on temperature adjustments in our conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph EF (1947) Physiology of man in the desert. Interscience, New York
Candas V, Libert JP, Vogt JJ (1983) Sweating and sweat decline of resting men in hot humid environments. Eur J Appl Physiol 50:223–234
Costill DL, Fink JW (1974) Plasma volume changes following exercise and thermal dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:521–525
Costill DL, Sparks KE (1973) Rapid fluid replacement following thermal dehydration. J Appl Physiol 34:299–303
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Ekblom B, Greenleaf CJ, Greenleaf JE, Hermansen L (1970) Temperature regulation during exercise dehydration in man. Acta Physiol Scand 79:475–483
Fordtran JS, Saltin B (1967) Gastric emptying and intestinal absorption during prolonged severe exercise. J Appl Physiol 23:331–335
Fortney SM, Nadel ER, Wenger CB, Bove JR (1981) Effect of blood volume on sweating rate and body fluids in exercising humans. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51:1594–1600
Fortney SM, Wenger CB, Bove JR, Nadel ER (1984) Effect of hyperosmolarity on control of blood flow and sweating. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 57:1688–1695
Gaebelin CJ, Senay LC, Jr (1980) Influence of exercise type, hydration, and heat on plasma volume shifts in men. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 49:119–123
Gaebelin CJ, Senay LC, Jr (1982) Vascular volume changes during cycling and stepping in women at two hydration levels. Eur J Appl Physiol 48:1–10
Grande F, Taylor HL, Anderson JT, Buskirk E, Keys A (1958) Water exchange in men on a restricted water intake and a low calorie carbohydrate diet accompanied by physical work. J Appl Physiol 12:202–320
Greenleaf JE, Castle BL (1971) Exercise temperature regulation in man during hypohydration and hyperhydration. J Appl Physiol 30:847–853
Greenleaf JE, Brock PJ, Keil LC, Morse JT (1983) Drinking and water balance during exercise and heat acclimation. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 54:414–419
Harrison MH, Edwards RJ, Leitch DR (1975) Effect of exercise and thermal stress on plasma volume. J Appl Physiol 39:925–931
Harrison MH, Edwards RJ, Fennessy PA (1978) Intravascular volume and tonicity as factors in the regulation of body temperature. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 44:69–75
Harrison MH, Edwards RJ, Graveney MJ, Cochrane LA, Davies JA (1981) Blood volume and plasma protein responses to heat acclimatization in humans. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 50:597–604
Horstman DM, Horwath SM (1972) Cardiovascular and temperature regulatory changes during progressive dehydration and euhydration. J Appl Physiol 33:446–450
Hunt JN, Pathak JD (1960) The osmotic effects of some simple molecules and ions on gastric emptying. J Physiol (Lond) 154:254–269
Ladell WSS (1955) The effects of water and salt intake upon the performance of men working in hot and humid environments. J Physiol (Lond) 127:11–46
Leithead CS, Pallister MA (1960) Observations on dehydration and sweating. Lancet 2:114–117
Nadel ER, Fortney SM, Wenger CB (1980) Effect of hydration state on circulatory and thermal regulations. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 49:715–721
Nielsen B, Hansen G, Jorgensen SO, Nielsen E (1971) Thermoregulation in exercising man during dehydration and hyperhydration with water and saline. Int J Biometeor 15:195–200
Pearcy M, Robinson S, Miller DI, Thomas JT Jr, DeBrota J (1956) Effects of dehydration, salt depletion and pitressin on sweat rate and urine flow. J Appl Physiol 8:621–626
Saltin B (1964) Circulatory responses to submaximal and maximal exercise after thermal dehydration. J Appl Physiol 19:1125–1132
Sawka MN, Francesconi RP, Pimentai NA, Pandolf KB (1984) Hydration and vascular fluid shifts during exercise in the heat. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 56:91–96
Sawka MN, Toner MN, Francesconi RP, Pandolf KB (1983) Hypohydration and exercise: effects of heat acclimation, gender, and environment. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 55:1147–1153
Senay LC, Jr (1970) Movement of water, protein and crystalloids between vascular and extra-vascular compartments in heat-exposed men during dehydration and following limited relief of dehydration. J Physiol (Lond) 210:617–635
Senay LC, Jr (1975) Plasma volumes and constituents of heatexposed men before and after acclimatization. J Appl Physiol 38:570–575
Senay LC, Jr (1979) Temperature regulation and hypohydration: a singular view. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 47:1–7
Strydom NB, Holdsworth LD (1968) The effects of different levels of water deficit on physiological responses during heat stress. Int Z Angew Physiol 26:95–102
Weichselbaum TE (1946) An accurate and rapid method for the determination of protein in small amount of blood serum and plasma. Am J Clin Pathol 10: Tech Sect 40–49
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. Mc Graw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Candas, V., Libert, J.P., Brandenberger, G. et al. Hydration during exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 113–122 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714992
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714992