Summary
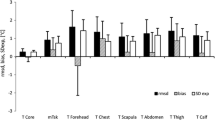
The data collected by the authors in four experimental series have been analysed together with data from the literature, to study the relationship between mean skin temperature and climatic parameters, subject metabolic rate and clothing insulation. The subjects involved in the various studies were young male subjects, unacclimatized to heat. The range of conditions examined involved mean skin temperatures between 33‡ C and 38‡ C, air temperatures (Ta) between 23‡ C and 50‡ C, ambient water vapour pressures (Pa) between 1 and 4.8 kPa, air velocities (Va) between 0.2 and 0.9 m · s−1, metabolic rates (M) between 50 and 270 W · m−2, and Clo values between 0.1 and 0.6. In 95% of the data, mean radiant temperature was within ±3‡ C of air temperature. Based on 190 data averaged over individual values, the following equation was derived by a multiple linear regression technique: ¯Tsk=30.0+0.138Ta+0.254Pa−0.57Va+1.28 · 10−3 M−0.553 Clo. This equation was used to predict mean skin temperature from 629 individual data. The difference between observed and predicted values was within ±0.6‡ C in 70% of the cases and within ±1‡ C in 90% of the cases. It is concluded that the proposed formula may be used to predict mean skin temperature with satisfactory accuracy in nude to lightly clad subjects exposed to warm ambient conditions with no significant radiant heat load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WC (1977) Influence of exercise mode and selected ambient conditions on skin temperature. Ann NY Acad Sci 301: 110–127
Alber-Wallerström A, Holmer I (1985) Efficiency of sweat evaporation in unacclimatized man working in a hot humid environment. Eur J Appl Physiol 54: 480–487
Belding HS, Hatch TF (1956) Index for evaluating heat stress in terms of resulting physiological strains. ASHRAE Trans 62: 213–228
Candas V (1980) Influence de la mouillure cutanée sur l'évolution du débit sudoral et des températures corporelles chez l'homme. Thèse Dr. Etat Sciences, Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg
Candas V, Libert JP, Vogt JJ (1979) Influence of air velocity and heat acclimation on human skin wettedness and sweating efficiency. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 47: 1194–1200
Chappuis P, Pittet P, Jéquier E (1976) Heat storage regulation in exercise during thermal transients. J Appl Physiol 40: 384–392
Christensen EH, Nielsen M (1942) Investigations of the circulation in the skin at the beginning of muscular work. Acta Physiol Scand 4: 162–170
Craig FN (1972) Evaporative cooling of men in wet clothing. J Appl Physiol 33: 331–336
Drinkwater BL, Bedi JF, Loucks AB, Roche S, Horvath SM (1982) Sweating sensitivity and capacity of women in relation to age. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 53: 671–676
Fanger PO (1970) Thermal comfort. New York, Mc GrawHill
Gagge AP, Herrington LP, Winslow CEA (1937) Thermal interchanges between the human body and its atmospheric environment. Am J Hyg 26: 84–102
Gagge AP, Stolwijk JAJ, Saltin B (1969) Comfort and thermal sensations and associated physiological responses during exercise at various ambient temperatures. Environ Res 2: 209–229
Gisolfi C, Robinson S (1969) Relations between physical training, acclimatization, and heat tolerance. J Appl Physiol 26: 530–534
Givoni B (1967) Estimation of the mean skin temperature. Report to the US Dept of Health, Education and Welfare. Irael Institute of Technology, HaÏfa
Givoni B (1969) Man, climate and architecture. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gonzalez RR, Berglund LG, Gagge AP (1978) Indices of thermoregulatory strain for moderate exercise in the heat. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 44: 889–899
Hardy JD, Stolwijk JAJ (1966) Partitional calorimetric studies of man during exposures to thermal transients. J Appl Physiol 21: 1799–1806
Houdas Y, Colin J, Timbal J, Boutelier C, Guieu JD (1972) Skin temperatures in warm environments and the control of sweat evaporation. J Appl Physiol 33: 99–104
Kobayashi K, Horvath SM, Diaz FJ, Bransford DR, Drinkwater BL (1980) Thermoregulation during rest and exercise in different postures in a hot humid environment. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 48: 999–1007
Lund DL, Gisolfi CV (1974) Estimation of mean skin temperature during exercise. J Appl Physiol 36: 625–628
Mairiaux Ph, Sagot JC, Candas V (1983) Oral temperature as an index of core temperature during heat transients. Eur J Appl Physiol 50: 331–341
Mairiaux Ph, Libert JP, Candas V, Vogt JJ (1986) Prediction of strain for intermittent heat exposures. Ergonomics 29: 913–923
Marotte H, Timbal J (1982) Circadian rhythm of thermoregulating responses in man exposed to thermal stimuli. Chronobiologia 9: 375–387
Meyer JP (1981) Prévision de la température cutanée moyenne. Thèse Dr Med, Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg
Missenard FA (1973) Température moyenne de la peau humaine en fonction de l'activité et de l'ambiance. CR Acad Sci Paris 277, D: 1557–1559
Nadel ER, Mitchell JW, Stolwijk JAJ (1973) Differential thermal sensitivity in the human skin. Pflügers Arch 340: 71–76
Nakayama T, Ohnuki Y, Niwa K (1977) Fall in skin temperature during exercise. Jpn J Physiol 27: 423–437
Olesen BW, Nielsen R (1983) Thermal insulation of clothing measured on a movable thermal manikin and on human subjects. Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark
Olesen S, Fanger PO, Bassing JJ (1972) Physiological comfort conditions at sixteen combinations of activity, clothing, air velocity and ambient temperature. ASHRAE Trans 78: 199–204
Ramanathan NL (1964) A new weighting system for mean surface temperature of the human body. J Appl Physiol 19: 531–533
Saltin B, Gagge AP, Stolwijk JAJ (1968) Muscle temperature during submaximal exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 25: 679–688
Saltin B, Gagge AP, Bergh U, Stolwijk JAJ (1972) Body temperature and sweating during exhaustive exercise. J Appl Physiol 32: 635–643
Stolwijk JAJ, Hardy JD (1966) Partitional calorimetric studies of responses of man to thermal transients. J Appl Physiol 21: 967–977
Teichner WH (1958) Assessment of mean body surface temperature. J Appl Physiol 12: 169–176
Vogt JJ, Candas V, Libert JP, Daull F (1982) Required sweat rate as an index of thermal strain in industry. In: Cena K, Clark JA (ed) Bioengineering, thermal physiology and comfort. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 99–110
Vogt JJ, Meyer JP, Candas V, Libert JP, Sagot JC (1983) Pumping effects of thermal insulation of clothing worn by human subjects. Ergonomics 26: 963–974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mairiaux, P., Malchaire, J. & Candas, V. Prediction of mean skin temperature in warm environments. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 686–692 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424811
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424811