Abstract
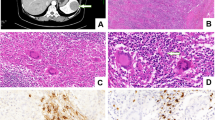
A 61-year-old woman initially presented with symptoms and findings reminiscent of infectious mononucleosis, and her illness then took a rapidly fatal course. Autopsy revealed widespread granulomatous arteritis, with multinucleated giant cells but without eosinophils and fibrinoid necrosis, affecting small arteries and arterioles and infiltration of haemophagocytic histiocytes into many organs. In situ hybridization with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specific oligonucleotide probes showed positive signals in the infiltrating immune cells and epithelial and endothelial cells of the affected organs. EBV-associated haemophagocytic syndrome (EBV-AHS) with systemic granulomatous arteritis was diagnosed. From the immunophenotypes of the infiltrating immune cells, a possible role of CD4+ T-cells in the pathogenesis of this haemophagocytic syndrome and granulomatous vasculitis was suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 April 1998/Accepted: 28 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ban, S., Goto, Y., Kamada, K. et al. Systemic granulomatous arteritis associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Virchows Archiv 434, 249–254 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280050336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280050336