Abstract
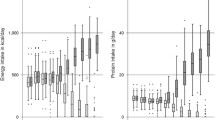
An adapted cow's milk infant formula without or with extra taurine (350 μmol/l) was fed to four and five infants, respectively. The infants, born after 28–32 weeks gestation, and initially fed with a starting formula for preterms, were switched to one of the two above-mentioned formulae at approximately the 16th day of life. Each infant was studied during 4 consecutive weeks.
The faecal excretion of fat, energy and total bile acids was determined from 3-day stool collections each week.
The addition of taurine to the infant formula neither improved the uptake of fat and energy nor changed the faecal bile acid excretion. Growth velocity was similar in both groups of infants.
Based on these results there is no rationale for adding taurine to adapted cow's milk infant formula to obtain a better fat absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba N, Bracco EF, Hashim SA (1982) Enhanced thermogenesis and diminished deposition of fat in response to overfeeding with diet containing medium chain triglyceride. Am J Clin Nutr 35:678–682
Beher WT, Stradnicks S, Lin GJ, Sanfield J (1981) Rapid analysis of human fecal bile acids. Steroids 38:281
Darling PB, Lepage G, Leroy C, Masson P, Roy CC (1985) Effect of taurine supplements on fat absorption in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res 19:578–582
Fernandes J, van de Kamer JH, Weijers HA (1962) Differences in absorption of the various fatty acids studied in children with steatorrhea. J Clin Invest 41:488–494
Fomon SJ, Ziegler EE, Thomas LN, Jensen RL, Filer LF (1970) Excretion of fat by normal full-term infants fed various milks and formulas. Am J Clin Nutr 23:1299–1313
Geggel HS, Ament ME, Heckenlively JR, Martin DA, Kopple JD (1985) Nutritional requirement for taurine in patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition. N Engl J Med 312:142–146
Hardison WGM, Grundy SM (1983) Effect of bile acid conjugation pattern on bile acid metabolism in normal humans. Gastroenterology 84:617–620
Hayes KC (1985) Taurine requirement in primates. Nutr Rev 43:65–70
Järvenpää AL, Rassin DK, Kuitonen P, Gaull GE, Räihä NCR (1983) Feeding the low-birth-weight infant: III. Diet influences bile acid metabolism. Pediatrics 72:677–683
Järvenpää AL (1983) Feeding the low-birth-weight infant: IV. Fat absorption as a function of diet and duodenal bile acids. Pediatrics 72:684–689
Katz L, Hamilton JR (1974) Fat absorption in infants of birth weight less than 1300 grams. J Pediatr 85:608–614
Kamer JH van de, Bokkel Huinink H ten, Weijers HA (1949) Rapid method for the determination of fat in feces. J Biol Chem 177:347–355
Little M, Smallwood RA, Lester R, Piasechi GJ, Jackson BT (1975) Bile salt metabolism in the primate fetus. Gastroenterology 69:1315–1320
Miller DS, Payne PR (1959) A ballistic bomb calorimeter. Br J Nutr 13:501–508
Okamoto E, Rassin DK, Zucker CL, Salen GS, Heird WC (1984) Role of taurine in feeding the low-birth-weight infant. J Pediatr 104:936–940
Rassin DK, Gull GE, Järvenpää AL, Räihä NCR (1983) Feeding the low-birth-weight infant: II. Effects of taurine and cholesterol supplementation on amino acids and cholesterol. Pediatrics 71:179–186
Roy CC, Ste-Marie M, Chartrand L, Weber A, Bard H, Doray B (1975) Correction of the melabsorption of the preterm infant with a medium-chain triglyceride formula. J Pediatr 86:446–450
Watkins JB, Ingall D, Szczepanik P, Klein PD, Lester R (1973) Bile-salt metabolism in the newborn. Measurement of pool size and synthesis by stable isotope technic. N Engl J Med 288:431–434
Zoppi GL, Andreotti G, Pajno-Ferrara F, Njai DM, Gaburro D (1972) Exocrine pancreas function in premature and full term neonates. Pediatr Res 6:880–886
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bijleveld, C.M.A., Vonk, R.J., Okken, A. et al. Fat absorption in preterm infants fed a taurine-enriched formula. Eur J Pediatr 146, 128–130 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343216
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02343216