Summary
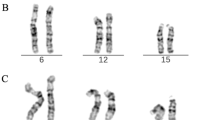
We have used two repeated DNA fragments (3.4 and 2.1 kb) released from Y chromosome DNA by digestion with the restriction endonuclease Hae III to analyze potential Y chromosome/autosome translocations. Two female patients were studied who each had an abnormal chromosome 22 with extra quinacrine fluorescent material on the short arm. The origin of the 22p+ chromosomes was uncertain after standard cytologic examinations. Analysis of one patient's DNA with the Y-specific repeated DNA probes revealed the presence of both the 3.4 and 2.1 kb Y-specific fragments. Thus, in this patient, the additional material was from the Y chromosome. Analysis of the second patient's DNA for Y-specific repeated DNA was negative, indicating that the extra chromosomal segment was not from the long arm of the Y chromosome. These two cases demonstrate that repeated DNA can distinguish between similar appearing aberrant chromosomes and may be useful in karyotypic and prenatal diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonarakis SE, Phillips JA III, Kazazian HH (1982) Genetic diseases: Diagnosis by restriction endonuclease analysis. J Pediatr 100:845–846
Borgaonkar DS (1980) Chromosomal variation in man, 35d edn. Alan R. Liss, New York
Caspersson T, Zech L, Johansson C (1970) Differential binding of alkylating fluorochromes in human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res 60:315–319
Cooke JH (1976) Repeated sequence specific to human males. Nature 262:182–186
Cooke HJ, Noel B (1979) Confirmation of Y/autosome translocation using recombinant DNA. Hum Genet 50:39–44
Davies KE (1981) The application of DNA recombinant technology to the analysis of the human genome and genetic disease. Hum Genet 58:351–357
Erdtmann B (1982) Aspects of evaluation, significance, and evolution of human C-band heteromorphism. Hum Genet 61: 281–294
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014
Kunkel LM, Smith KD, Boyer SH, Borgaonkar DS, Wachtel SS, Miller OJ, Berg WR, Jones HW, Rary JM (1977) Analysis of human Y chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:1245–1249
Kunkel LM, Smith KD, Boyer SH (1979) Organization and heterogeneity of sequences within a repeating unit of human Y chromosome deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 18:3343–3353
Otsuka A (1981) Recovery of DNA fragments inserted by the “tailing” method: regeneration of Pst 1 restriction sites. Gene 13:339–346
Rigby PWJ, Dieckmann M, Rhodes C, Berg P (1977) Labelling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251
Saunders GF, Shirakawa S, Saunders PP, Arrighi FE, Hsu TC (1972) Populations of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol 63:323–334
Schmeckpeper BJ, Willard HF, Smith KD (1981) Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 9:1853–1872
Schmid CW, Deininger PL (1975) Sequence organization of the human genome. Cell 6:345–358
Singer MF (1982) SINES and LINES: Highly repeated short and long interspersed sequences in mammalian genomes. Cell 28:433–434
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306
Szabo P, Kunkel L, Yu LC, George DL, Smith KD (1979) Chromosomal distribution of DNA sequences within a repeating unit of Y chromosome deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 18:3343–3353
Yunis JJ, Chandler ME (1978) High resolution chromosome analysis in clinical medicine. Prog Clin Pathol 7:267–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burk, R.D., Stamberg, J., Young, K.E. et al. Use of repetitive DNA for diagnosis of chromosomal rearrangements. Hum Genet 64, 339–342 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292365
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292365