Summary
The utilization of actinomycin D during the regeneration of young and adult Planarians shows that the two groups of animals react differently to the antibiotic.
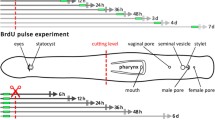
Regeneration takes place in the presence of the antibiotic in young Planarians, whereas it is entirely inhibited in adult ones, applying the same concentration (50 μg/cm3). In the young animals it begins immediately after decapitation. Their return into the water, after a treatment with the antibiotic lasting from 1 to 4 days, does not interfere with the morphological differentiation. The ultrastructural investigation exhibits that in the majority of the undifferentiated cells the nucleolus is largely dissociated.
The lesions gradually extend to the whole cell which frequently degenerates. The morphologically undifferentiated cells are weakly impaired (depletion of the granular component of the nucleolus), and they recover a normal structure after their return into water.
These results lead us to study the RNA synthesis, during these experimentations, on the whole organism as well as the cellular level.
Résumé
L'utilisation de l'actinomycine D, au cours de la régénération de Planaires à l'éclosion ou de celle d'adultes, montre que ces deux groupes d'animaux réagissent différemment à l'antibiotique.
La régénération se produit en présence de l'antibiotique chez les jeunes Planaires, alors que, pour la même concentration (50 μg/cm3), elle est totalement bloquée chez les adultes. Elle débute dès la décapitation des animaux; le retour dans l'eau, après un traitement par l'antibiotique qui va de 1 à 4 jours, ne modifie pas son déroulement morphologique.
L'examen ultrastructural montre que les cellules différenciées présentent le plus souvent des dissociations nucléolaires importantes.
Les lésions s'étendent progressivement à toute la cellule qui dégénère fréquemment. Les cellules morphologiquement indifférenciées ne sont que faiblement altérées (raréfaction du composant granulaire du nucléole), et récupèrent une structure normale après retour dans l'eau.
Ces résultats conduisent à envisager l'étude des synthèses d'ARN, au cours de ces expériences, au niveau des organismes entiers et au niveau cellulaire.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Bal, A. K., Gross, P. R.: Mitosis and differentiation in roots treated with actinomycin. Science 139, 584–586 (1963).
Bernhard, W., Granboulan, N.: Electron microscopy of the nucleolus in vertebrate cells. In: Ultrastructure in biological systems, vol. 3, p. 81–149. New York: Acad. Press 1968.
Burns, E. R.: Actinomycin D and amphibian cells in vitro: effects on monolayers, postmitotic nucleolar reconstruction, and nucleolar emptying at different temperatures. Anat. Rec. 165, 559–568 (1969).
Clark, A. M., Love, R., Studzinski, G. P., Ellem, K. A. O.: A correlated morphological and functional study of the effects of actinomycin D on HeLa cells. I. Effects on the nucleolar and cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins. Exp. Cell Res. 45, 106–119 (1966).
Eakin, R. M.: Actinomycin D inhibition of cell differentiation in the amphibian sucker. Z. Zellforsch. 63, 81–96 (1964).
Flickinger, C. J.: The fine structure of the nucleoli of normal and actinomycin D — treated Amoeba proteus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 260–271 (1968).
Gabriel, A.: Action de l'actinomycine D sur la régénération et le métabolisme de l'acide ribonucléique chez la Planaire Dugesia gonocephala (Turbellarié, Triclade). C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 266, 406–409 (1968).
Geuskens, M.: Etude autoradiographique ultrastructurale de l'action de l'actinomycine D sur les oocytes d'Astérie. Exp. Cell Res. 39, 400–412 (1965).
Goessens, G., Bassleer, R.: Réversibilité des effets de l'actinomycine D dans les fibroblastes de poulet ou de rat cultivés in vitro. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 269, 63–66 (1969).
Goldblatt, P. J., Sullivan, R. J., Farber, E.: Morphologic and metabolic alterations in hepatic cell nucleoli induced by varying doses of actinomycin D. Cancer Res. 29, 124–135 (1969).
Hamann, W., Oehlert, W., Hedderich, M.: Inkorporation und Eliminierung von Actinomycin D-3H durch verschiedene Zellarten in vitro. Virchows Arch. Abt. B Zellpath. 1, 120–130 (1968).
Jacob, J., Sirlin, J. L.: Electron microscope studies on salivary gland cells. IV. The nucleus of Smittia parthenogenetica (Chironomidae) with special reference to the nucleus and the effects of actinomycin thereon. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 11, 315–328 (1964).
Jézéquel, A. M., Bernhard, W.: Modifications ultrastructurales du pancréas exocrine de Rat sous l'effet de l'actinomycine D. J. Microscop. 3, 279–296 (1964).
Journey, L. J., Goldstein, M. N.: Electron microscope studies on HeLa cell lines sensitive and resistant to actinomycin D. Cancer Res. 21, 929–932 (1961).
Le Moigne, A.: Etude du développement et de la régénération embryonnaires de Polycelis nigra (Ehr.) et Polycelis tenuis (Iijima); Turbellariés, Triclades. Ann. Embr. Morph. 2, 51–69 (1969).
—, Gabriel, A.: Mise en évidence du caractère ≪activé≫ des cellules indifférenciées du parenchyme chez les jeunes Planaires en croissance. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 163, 1070–1073 (1969).
—: Action de l'actinomycine D sur la différenciation cellulaire au cours de la régénération de Planaires qui viennent d'éclore. II. Etudes autoradiographiques histologique et ultrastructurale de l'action de l'antibiotique sur les synthèses d'ARN. Z. Zellforsch. 115, 442–460 (1971).
Meyn, N.P., MacRae, E. K.: Inhibition of planarian head regeneration and reversal of polarity by actinomycin D. J. Cell Biol. 43, 92a-93a (1969).
Mittermayer, C., Braun, R., Rusch, H. P.: The effect of actinomycin D on the timing of mitosis in Physarum polycephalum. Exp. Cell Res. 38, 33–41 (1965).
Morita, M., Best, J. B., Noël, J.: Electron microscopic studies of planarian regeneration. I. Fine structure of neoblasts in Dugesia dorotocephala. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 7–23 (1969).
Oda, A., Chiga, M.: Effect of actinomycin D on the hepatic cells of partielly hepatectomized rats. An electron microscopic study. Lab. Invest. 14, 1419–1427 (1965).
Ro, T. S., Busch, H.: Concentration of [14C] actinomycin D in various tissues following intravenous injection. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Anat.) 108, 317–318 (1965).
—, Narayan, K. S., Busch, H.: Effects of actinomycin D on base composition and nearest neighbor frequency of nucleolar RNA of the walker tumor and liver. Cancer Res. 26, 780–785 (1966).
Rodríguez, T. G.: Ultrastructural changes in the mouse exocrine pancreas induced by prolonged treatment with actinomycin D. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 19, 116–129 (1967).
Sameshima, M., Shiokawa, K., Kawakami, I.: The effect of actinomycin D on nucleolar formation in early Xenopus laevis gastrulae. J. exp. Zool. 170, 113–120 (1970).
Sauzin, M. J.: Etude au microscope électronique du néoblaste de la Planaire Dugesia gonocephala (Turbellarié, Triclade) et de ses changements ultrastructuraux au cours des premiers stades de la régénération. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 263, 605–608 (1966).
Schoefl, G. I.: The effect of actinomycin D on the fine structure of the nucleolus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 10, 224–243 (1964).
Simard, R., Bernhard, W.: Le phénomène de la ségrégation nucléolaire: spécificité d'action de certains antimétabolites. Int. J. Cancer 1, 463–479 (1966).
Simard R., Duprat, A. M.: Action de l'actinomycine D sur les ribonucléoprotéines nucléaires de cellules d'amphibiens en différenciation. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 29, 60–75 (1969).
Smetana, K., Potměšil, M.: Ring shaped nucleoli in liver cells of rats after treatment with actinomycin D. Z. Zellforsch. 92, 62–69 (1968).
Stenram, U.: Electron-microscopic study on liver cells of rats treated with actinomycin D. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 211–219 (1965).
Stern, R., Friedman, R. M.: Double-stranded RNA synthesized in animals cells in the presence of actinomycin D. Nature (Lond.) 226, 612–616 (1970).
Stevens, B. J.: The effect of actinomycin D on nucleolar and nuclear fine structure in the salivary gland cell of Chironomus thummi. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 11, 329–353 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabriel, A., Le Moigne, A. Action de l'actinomycine D sur la différenciation cellulaire au cours de la régénération de planaires qui viennent d'éclore. Z. Zellforsch. 115, 426–441 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324944
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324944