Abstract
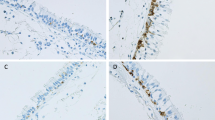
Collagen IV and laminin are important constituents of the basement membrane (BM). By use of immunocytochemistry we examined the occurrence and distribution of these two components in the BM beneath normal, mucoid and metaplastic epithelium of large bronchi in 22 adults suffering from chronic nonspecific lung diseases. Both collagen IV and laminin were expressed as a thin and continuous layer beneath the epithelium in most tissue specimens with normal epithelium. In a few specimens the layer showed interruptions with a patchy distribution of the immunoreactivity. Three patterns of distribution of BM components were found under the metaplastic epithelium. Total absence of immunoreactive collagen IV and laminin was the most common variant. Weak and scarce staining for both proteins in the BM characterized the second pattern. The third variant showed strong collagen IV immunoreactivity but lack of laminin. The BM beneath the mucoid epithelium was characterized by irregular distribution of collagen IV and laminin. We suggest that the occurrence and distributional pattern of the BM components are related to the type of overlying epithelium and connected with an altered synthesis of these components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonelli AR, Nicolai P, Cappiello J, Peretti G, Molinary Tosatti MP, Rosa D, Grigolato PG, Favret M, Maroccolo D (1991) BM components in normal, dysplastic, neoplastic laryngeal tissue and metaplastic lymph nodes. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 111:437–443
Caselitz J, Schmitt P, Seifert G, Wustrow J, Schuppan D (1983) Basal membrane associated substances in human salivary glands and salivary gland tumours. Pathol Res Pract 183:3866394
Collier JE, Wilhelm SM, Eisen AZ, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Seltzer IL, Kronenberg A, He C, Bauer EA, Goldberg GI (1988) H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE)-1 secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem 268:6579–6587
Daneker IGW, Mercurio AM, Guerra L (1987) Laminin expression in colorectal carcinomas varying in degree of differentiation. Arch Surg 122:1470–1474
Ehrmann RL, Dwyer JM, Yavner D, Hancock WW (1988) An immunoperoxidase study of laminin and type IV collagen distribution in carcinoma of the cervix and vulva. Obstet Gynecol 72:257–262
Keenan KP, Saffiotti U, Stinson SF, Riggs CW, Mc Dowell EM (1989) Multifactorial hamster respiratory carcinogenesis with interdependent effects of cannula-induced mucosal wounding, saline, ferric oxide, benzo(a)puring and N-methyl-N-nitrosurea. Cancer Res 49:1528–1540
Kirkpatrick CJ, Kampe M, Rixen H, Fischer EG, Mittermayer C (1989) In vitro simulation of endothelial regeneration: the migration of endothelial cells on basement membrane components. J Pathol 158:3461
Leblond CP, Inoue S (1989) Structure, composition and assembly of basement membrane. Am J Anat 185:367–390
Madri JA, Pratt BM, Yurcheno PD, Furthmayr H (1984) The ultrastructural organisation and architecture of basement membranes. In: Basement membrane and cell movement. Ciba Foundation Symposium, London 108:6–24
nMc Dowell EM, Mc Laughlin IS, Merenyl DK, Kieffer RF, Harris CC, Trump BF (1978) The respiratory epithelium. V. Histogenesis of lung carcinomas in the human. J Natl Cancer Inst 61:537–575
Pfeifer AMA, Lechner JF, Masui T, Reddelt RR, Mark GE, Harris CC (1989) Control of growth and squamous differentiation in normal human bronchial epithelial cells by chemical and biological modifiers and transferred genes. Environ Health Persp 80:209–220
Roche WR (1991) Fibroblasts and asthma. Clin Allergy 21:545–548
Roche WR, Beasley R, Williams JH, Holgate ST (1989) Subepithelial fibrosis in the bronchi of asthmatics. Lancet 1:520–524
Sakr WA, Larbo RJ, Jacobs IR, Crissman JD (1987) Distribution of basement membrane in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Hum Pathol 18:1043–1050
Terranova VP, Rohrbach DH, Martin GR (1980) Role of laminin in the attachment of PAM 212 (epithelial) cells to basement membrane collagen. Cell 22:719–726
Trump BF, Mc Dowell EM, Glavin F, Barrett LA, Becci PJ, Schürch W, Kaiser HE, Harris CC (1978) The respiratory epithelium. III. Histogeneses of epidermoid metaplasia and carcinoma in situ in the human. J Natl Cancer Inst 61:563–575
Tsuchiya E, Kitagawa T, Oh S, Nakagawa K, Matsubara T, Kinceshitu J, Sugano H (1981) Incidence of squamous metaplasia in large bronchi of Japanese lungs: relation to pulmonary carcinomas of various subtypes. Jpn J Cancer Res (Gann) 78:559–564
Visser R, Van Der Beek JMK, Havenith MG, Cleutjens IPM, Bosman FT (1986) Immunocytochemical detection of basement membrane antigens in the histopathological evaluation of laryngeal dysplasia and neoplasia. Histopathology 10:171–180
Woodworth CD, Mossman BT, Craighead JE (1983) Squamous metaplasia of the respiratory tract. Possible pathogenic role in asbestos-associated bronchogenic carcinoma. Lab Invest 48:573–584
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilmane, M., Magone, M., Luts, A. et al. Basement membrane components of bronchial epithelium in humans suffering from chronic nonspecific lung diseases. Cell Tissue Res 277, 505–510 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300223
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300223